Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shinotsuka, Hiroshi*; Nagata, Kenji*; Yoshikawa, Hideki*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Applied Surface Science, 685, p.162001_1 - 162001_11, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:35.22(Chemistry, Physical)Silicon (Si) 2p photoelectron spectra of thermally oxidized Si(001) surfaces were analyzed using Bayesian estimation, a type of mathematical statistical processing, considering spin-orbit interactions. The accuracy of the estimation of fitting parameters and the model selection of the number of peaks were discussed. The spectral analysis was performed without any prior information on the positions of other Si peaks, except for the prominent bulk Si peak, and without using chemical-state assumptions. Our method completely verified previous findings on the surface species and the changes in peaks due to oxidation-induced strain as oxidation progressed.
Igarashi, Junya*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Zheng, J.*; Zhang, Z. J.*; Fukuda, Miho*; Aono, Tatsuo*; Minowa, Haruka*; Yoshikawa, Hideki*; Sueki, Keisuke*; Satou, Yukihiko; et al.
Environmental Science & Technology, 58(33), p.14823 - 14830, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Environmental)Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Igarashi, Junya*; Zhang, Z. J.*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Shinohara, Atsushi*; Satou, Yukihiko; Minowa, Haruka*; Yoshikawa, Hideki
KEK Proceedings 2019-2, p.54 - 59, 2019/11
no abstracts in English
 Cl in soil near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant
Cl in soil near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power PlantOta, Yuki*; Sueki, Keisuke*; Sasa, Kimikazu*; Takahashi, Tsutomu*; Matsunaka, Tetsuya*; Matsumura, Masumi*; Tosaki, Yuki*; Honda, Maki*; Hosoya, Seiji*; Takano, Kenta*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2018-002, p.99 - 102, 2019/02
no abstracts in English
Satou, Yukihiko; Sueki, Keisuke*; Sasa, Kimikazu*; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Nakama, Shigeo; Minowa, Haruka*; Abe, Yoshinari*; Nakai, Izumi*; Ono, Takahiro*; Adachi, Koji*; et al.
Geochemical Journal, 52(2), p.137 - 143, 2018/00
Times Cited Count:73 Percentile:95.99(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Yoshikawa, Hideki
Enerugi Rebyu, 37(10), p.13 - 14, 2017/10
We introduce the R&D activities of Japan Atomic Energy Agency immediately after the accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and some facilities established in Fukushima Prefecture.
Ise, Kotaro; Sasaki, Yoshito; Amano, Yuki; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Nanjo, Isao*; Asano, Takahiro*; Yoshikawa, Hideki
Geomicrobiology Journal, 34(6), p.489 - 499, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:18.45(Environmental Sciences)We investigated the change in bacterial community structure after drilling boreholes, 09-V250-M02 and 09-V250-M03 in the 250 m depth research gallery of Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL). In 09-V250-M02,  -Proteobacteria was predominantly detected in the clone library analyses of the groundwater samples conducted immediately after drilling the borehole. All these
-Proteobacteria was predominantly detected in the clone library analyses of the groundwater samples conducted immediately after drilling the borehole. All these  -Proteobacteria clones are closely related to
-Proteobacteria clones are closely related to 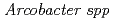 . which is known as sulfide oxidizing chemoautotrophic bacteria. After four years, the microbial structure was drastically changed and most detected OTUs were uncultured species such as candidate division OP9 and Chloroflexi relatives which are frequently detected in deep-sea sediments.
. which is known as sulfide oxidizing chemoautotrophic bacteria. After four years, the microbial structure was drastically changed and most detected OTUs were uncultured species such as candidate division OP9 and Chloroflexi relatives which are frequently detected in deep-sea sediments.
Saegusa, Jun; Tagawa, Akihiro; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Iijima, Kazuki; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Tokizawa, Takayuki; Nakayama, Shinichi; Ishida, Junichiro
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 3(3), p.15-00609_1 - 15-00609_7, 2016/06
After the Fukushima nuclear accident, JAEA lead off demonstration tests to find out effective decontamination methods for various school facilities in Fukushima. It included (1) dose reduction measures at schoolyards, (2) purification of swimming pool water and (3) removal of surface contamination of playground equipments. Through these tests, they established practical methods suitable for each situation; (1) At school yards, dose rates were drastically reduced by removing topsoil which was then placed in trenches of 1 m deep; (2) For the purification of pool water, the flocculation-coagulation treatment was found to be effective for collecting radiocesium dissolved in the water; (3) Demonstration tests for playground equipments, such as horizontal bars and a sandbox wood frame, suggested that effectiveness of decontamination considerably varied depending on the material, paint or coating condition. This paper reviews these demonstrations.
Saegusa, Jun; Tagawa, Akihiro; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Iijima, Kazuki; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Tokizawa, Takayuki; Nakayama, Shinichi; Ishida, Junichiro
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2015/05
After the Fukushima nuclear accident, JAEA lead off demonstration tests to find out effective decontamination methods for various school facilities in Fukushima. It included (1) dose reduction measures at schoolyards, (2) purification of swimming pool water and (3) removal of surface contamination of playground equipments. Through these tests, they established practical methods suitable for each situation; (1) At school yards, dose rates were drastically reduced by removing topsoil which was then placed in trenches of 1 m deep; (2) For the purification of pool water, the flocculation-coagulation treatment was found to be effective for collecting radiocesium dissolved in the water; (3) Demonstration tests for playground equipments, such as horizontal bars and a sandbox wood frame, suggested that effectiveness of decontamination considerably varied depending on the material, paint or coating condition. This paper reviews these demonstrations.
Shibata, Masahiro; Sawada, Atsushi; Tachi, Yukio; Makino, Hitoshi; Wakasugi, Keiichiro; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Kitamura, Akira; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Oda, Chie; Ishidera, Takamitsu; et al.
JAEA-Research 2014-030, 457 Pages, 2015/03
JAEA and NUMO have conducted a collaborative research work which is designed to enhance the methodology of repository design and post-closure performance assessment in preliminary investigation stage. With regard to (1) study on rock suitability in terms of hydrology, based on some examples of developing method of hydro-geological structure model, acquired knowledge are arranged using the tree diagram, and model uncertainty and its influence on the evaluation items were discussed. With regard to (2) study on scenario development, the developed approach for "defining conditions" has been reevaluated and improved from practical viewpoints. In addition, the uncertainty evaluation for the effect of use of cementitious material, as well as glass dissolution model, was conducted with analytical evaluation. With regard to (3) study on setting radionuclide migration parameters, based on survey of precedent procedures, multiple-approach for distribution coefficient of rocks was established, and the adequacy of the approach was confirmed though its application to sedimentary rock and granitic rock. Besides, an approach for solubility setting was developed including the procedure of selection of solubility limiting solid phase. The adequacy of the approach was confirmed though its application to key radionuclides.
 promoter on Pt electro-catalyst
promoter on Pt electro-catalystFugane, Keisuke*; Mori, Toshiyuki*; Yan, P.*; Masuda, Takuya*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Ye, F.*; Yoshikawa, Hideki*; Auchterlonie, G.*; Drennan, J.*
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 7(4), p.2698 - 2707, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:64.85(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Yasushi*; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Yoshikawa, Hideki
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(1), p.147 - 152, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.34(Chemistry, Analytical)A heterogeneous partition coefficient for Ra in BaCO (witherite) was determined from a coprecipitation experiment using the free drift method. The initial solution was bubbled with 100% CO
(witherite) was determined from a coprecipitation experiment using the free drift method. The initial solution was bubbled with 100% CO (g) and equilibrated with witherite. After a small amount of Ra was added into the solution, a coprecipioitation reaction was induced by increase of pH caused by degassing of CO
(g) and equilibrated with witherite. After a small amount of Ra was added into the solution, a coprecipioitation reaction was induced by increase of pH caused by degassing of CO (g). A kinetic reaction of precipitation was restricted to be slow due to slow degassing of CO
(g). A kinetic reaction of precipitation was restricted to be slow due to slow degassing of CO (g). Precipitation rate was observed to be enough low comparing with values of low precipitation rates to derive equilibirium partitioning of elements in coprecipitation experiments with CaCO
(g). Precipitation rate was observed to be enough low comparing with values of low precipitation rates to derive equilibirium partitioning of elements in coprecipitation experiments with CaCO (calcite). The
(calcite). The  -value derived for Ra was
-value derived for Ra was  = (1.3
= (1.3 0.7)
0.7) 10
10 . This value was similar to that of Ra in CaCO
. This value was similar to that of Ra in CaCO (calcite). It indicated that partitioning behavior of Ra in carbonate minerals did not depend on affinity in radius of a cation in host carbonate.
(calcite). It indicated that partitioning behavior of Ra in carbonate minerals did not depend on affinity in radius of a cation in host carbonate.
 , SO
, SO ) precipitates
) precipitatesRai, D.*; Felmy, A. R.*; Moore, D. A.*; Kitamura, Akira; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Doi, Reisuke; Yoshida, Yasushi*
Radiochimica Acta, 102(8), p.711 - 721, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:15.09(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)The solubility of Ba(SeO , SO
, SO ) precipitates was determined as a function of the BaSeO
) precipitates was determined as a function of the BaSeO mole fractions, ranging from 0.0015 to 0.3830, and time with an equilibration period extending to as long as 302 days. Equilibrium/steady state conditions in this system are reached in
mole fractions, ranging from 0.0015 to 0.3830, and time with an equilibration period extending to as long as 302 days. Equilibrium/steady state conditions in this system are reached in  65 days. Pitzer's ion interaction model was used to calculate solid and aqueous phase activity coefficients. Thermodynamic analyses showed that the data do not satisfy Gibbs-Duhem equation, thereby demonstrating that a single-solid solution phase does not control both the selenate and sulfate concentrations. Our extensive data with [Ba], [SeO
65 days. Pitzer's ion interaction model was used to calculate solid and aqueous phase activity coefficients. Thermodynamic analyses showed that the data do not satisfy Gibbs-Duhem equation, thereby demonstrating that a single-solid solution phase does not control both the selenate and sulfate concentrations. Our extensive data with [Ba], [SeO ], and [SO
], and [SO ] can be explained with the formation of an ideal BaSeO
] can be explained with the formation of an ideal BaSeO solid solution phase that controls the selenium concentrations and a slightly disordered/less-crystalline BaSO
solid solution phase that controls the selenium concentrations and a slightly disordered/less-crystalline BaSO (s) that controls the sulfate concentrations. In these experiments the BaSO
(s) that controls the sulfate concentrations. In these experiments the BaSO component of the solid solution phase never reaches thermodynamic equilibrium with the aqueous phase. Thermodynamic interpretations of the data show that both the ideal BaSeO
component of the solid solution phase never reaches thermodynamic equilibrium with the aqueous phase. Thermodynamic interpretations of the data show that both the ideal BaSeO solid solution phase and less-crystalline BaSO
solid solution phase and less-crystalline BaSO (s) phase are in equilibrium with each other in the entire range of BaSeO
(s) phase are in equilibrium with each other in the entire range of BaSeO mole fractions investigated in this study.
mole fractions investigated in this study.
 (cr) in the aqueous Ba
(cr) in the aqueous Ba -SeO
-SeO
 -Na
-Na -H
-H -OH
-OH -H
-H O system; Extending to high selenate concentrations
O system; Extending to high selenate concentrationsRai, D.*; Felmy, A. R.*; Moore, D. A.*; Kitamura, Akira; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Doi, Reisuke; Yoshida, Yasushi*
Radiochimica Acta, 102(9), p.817 - 830, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:15.09(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)The aqueous solubility of BaSeO (cr) was studied in Na
(cr) was studied in Na SeO
SeO solutions ranging in concentration from 0.0001 to 4.1 mol.kg
solutions ranging in concentration from 0.0001 to 4.1 mol.kg and maintained in a N
and maintained in a N atmosphere at room temperature (296
atmosphere at room temperature (296  2 K). The studies were conducted from both the undersaturation and oversaturation directions, with equilibration periods ranging from 3 to 596 days. The equilibrium in this system was reached rather rapidly (
2 K). The studies were conducted from both the undersaturation and oversaturation directions, with equilibration periods ranging from 3 to 596 days. The equilibrium in this system was reached rather rapidly ( 3 days). The SIT and Pitzer's ion-interaction models were used to interpret these data and the predictions based on both of these models agreed closely with the experimental data.
3 days). The SIT and Pitzer's ion-interaction models were used to interpret these data and the predictions based on both of these models agreed closely with the experimental data.
Katsuyama, Chie*; Nashimoto, Hiroaki*; Nagaosa, Kazuyo*; Ishibashi, Tomotaka*; Furuta, Kazuki*; Kinoshita, Takeshi*; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Aoki, Kazuhiro; Asano, Takahiro*; Sasaki, Yoshito; et al.
FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 86(3), p.532 - 543, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:36.67(Microbiology)Anaerobic microbial activity has a major influence on the subsurface environment, and should be considered in subsurface activities including the construction of radioactive waste repositories. We investigated denitrification and methanogenesis in anoxic groundwater from 140 m depth in two boreholes, where the redox potential fluctuated. The average maximum potential denitrification rates, measured under anaerobic conditions in the two boreholes using an  N tracer. Methanogenesis candidates were detected by 16S rRNA gene analysis. Although the stable isotope signatures suggested that some of the dissolved methane was of biogenic origin, no potential for methane production was evident during the incubations. The groundwater at 140 m depth did not contain oxygen, had an Eh ranging from -144 to 6.8 mV, and was found to be a potential field for denitrification.
N tracer. Methanogenesis candidates were detected by 16S rRNA gene analysis. Although the stable isotope signatures suggested that some of the dissolved methane was of biogenic origin, no potential for methane production was evident during the incubations. The groundwater at 140 m depth did not contain oxygen, had an Eh ranging from -144 to 6.8 mV, and was found to be a potential field for denitrification.
Yoshikawa, Hideki; Iijima, Kazuki; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Fujiwara, Kenso; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Kitamura, Akira; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Tokizawa, Takayuki; Yui, Mikazu; Nakayama, Shinichi
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1518, p.269 - 275, 2013/10
Following the release of radionuclides into the environment as a result of the accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) had to develop an immediate and effective method of reducing the dose rate received by students in school facilities. A demonstration of a reducing method was carried out by JAEA at a junior high school ground and kindergarten yard in the center of Fukushima-city. Dose rates of the released radionuclides are largely controlled by the ground level contamination and accumulation of mainly cesium-137 ( Cs) and cesium-134 (
Cs) and cesium-134 ( Cs) in populated areas. An effective means of reducing dose rate was to remove the surface soil and to bury it on-site under fresh uncontaminated soil or soil collected under deep depth at the site for shielding. The dose rate at1 m above ground level was reduced from 2.5
Cs) in populated areas. An effective means of reducing dose rate was to remove the surface soil and to bury it on-site under fresh uncontaminated soil or soil collected under deep depth at the site for shielding. The dose rate at1 m above ground level was reduced from 2.5  Sv/h to 0.15
Sv/h to 0.15  Sv/h.
Sv/h.
Nagao, Seiya*; Niibori, Yuichi*; Tanaka, Tadao; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Saito, Takumi*; Kirishima, Akira*; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Iijima, Kazuki; Hama, Katsuhiro; Iwatsuki, Teruki; et al.
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 20(1), p.3 - 14, 2013/06
This paper shows a current status of groundwater colloids studies on the performance assessment of geological disposal of radioactive wastes in Japan, and summaries realistic approach of the colloids studies at a substantial research network for Japanese universities and institutes.
Kitamura, Akira; Fujiwara, Kenso; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Gomi, Katsuhiko*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 20(1), p.15 - 19, 2013/06
We developed an integrated system on setting many monitoring spots in playgrounds and fields and simultaneously recording of monitored results with spot, date and time for a decontamination project. This system enables to set grid squares containing many spots to be monitored and to integrate all the monitored spots using a geographic information system (GIS). Furthermore, we could easily access to the monitoring spots in pre-set grid squares using a personal digital assistant with a highly accurate global positioning system (GPS) and a camera. All the monitored results are linked up with location, date and time, and photos taken around the spot, and could be efficiently managed in an integrated fashion in a personal computer. As a result, we saved many times and manpowers for monitoring and data summarizing, and succeeded to conduct the monitoring quickly and accurately.
Kurikami, Hiroshi; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Iijima, Kazuki; Zaima, Naoki; Munakata, Masahiro; Tokizawa, Takayuki; Nakayama, Shinichi
JAEA-Review 2012-045, 129 Pages, 2013/01
This report shows the records of JAEA's investigation on dose rate reduction at the Fukushima University Junior High School and Kindergarten. The main outcomes are as follows. (1)  experiments were performed to investigate intrusion depth of radiocesium in the soil. Based on the experiment, we proposed a countermeasure to reduce air dose rates. (2) The action we proposed allowed dose rate reduction to about one tenth to one twentieth at playgrounds. (3) Follow-up monitoring was performed after one year, and shows no obvious evidence of recontamination at the playgrounds. (4) Decontamination of a tree was tested. Radiocesium was accumulated around the root. By removing the soil, the air dose rate at about one-meter distance from the tree was decreased.
experiments were performed to investigate intrusion depth of radiocesium in the soil. Based on the experiment, we proposed a countermeasure to reduce air dose rates. (2) The action we proposed allowed dose rate reduction to about one tenth to one twentieth at playgrounds. (3) Follow-up monitoring was performed after one year, and shows no obvious evidence of recontamination at the playgrounds. (4) Decontamination of a tree was tested. Radiocesium was accumulated around the root. By removing the soil, the air dose rate at about one-meter distance from the tree was decreased.