Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -ray spectrometer and its performance under intense
-ray spectrometer and its performance under intense  Cs and
Cs and  Co radiation fields
Co radiation fieldsKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1010, p.165544_1 - 165544_9, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)The number of nuclear facilities being decommissioned has been increasing worldwide, in particular following the accident of the Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in 2011. In these nuclear facilities, proper management of radioactive materials is required. Then, A  -ray spectrometer with four segmentations using small volume CeBr
-ray spectrometer with four segmentations using small volume CeBr scintillators with a dimension of
scintillators with a dimension of 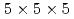
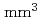 was developed. The four scintillators were coupled to a multi-anode photomultiplier tube specific to intense radiation fields. We performed the
was developed. The four scintillators were coupled to a multi-anode photomultiplier tube specific to intense radiation fields. We performed the  -ray exposure study under
-ray exposure study under  Cs and
Cs and  Co radiation fields. Under the
Co radiation fields. Under the  Cs radiation field, the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was 9.2
Cs radiation field, the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was 9.2 0.05%, 8.0
0.05%, 8.0 0.08%, 8.0
0.08%, 8.0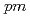 0.03%, and 9.0
0.03%, and 9.0 0.04% for the four channels, respectively.
0.04% for the four channels, respectively.
 scintillator under intense
scintillator under intense  -ray fields for nuclear decommissioning
-ray fields for nuclear decommissioningKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 988, p.164900_1 - 164900_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:89.29(Instruments & Instrumentation)An increasing number of nuclear facilities have been decommissioned worldwide following the 2011 accident of the TEPCO' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. During the decommissioning, radioactive materials have to be retrieved under proper management. In this study, a small cubic CeBr spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm
spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm  5 mm
5 mm  5 mm was manufactured to perform
5 mm was manufactured to perform  -ray spectroscopy under intense
-ray spectroscopy under intense  -ray fields. Furthermore, thanks to a fast digital process unit and a customized photomultiplier, the device could perform
-ray fields. Furthermore, thanks to a fast digital process unit and a customized photomultiplier, the device could perform  -ray spectroscopy at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 662 keV ranged from 4.4% at 22 mSv/h to 5.2% at 1407 mSv/h for a
-ray spectroscopy at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 662 keV ranged from 4.4% at 22 mSv/h to 5.2% at 1407 mSv/h for a  Cs radiation field. Correspondingly, at 1333 keV, it ranged from 3.1% at 26 mSv/h to 4.2% at 2221 mSv/h for a
Cs radiation field. Correspondingly, at 1333 keV, it ranged from 3.1% at 26 mSv/h to 4.2% at 2221 mSv/h for a  Co radiation field, which suggested to realize
Co radiation field, which suggested to realize  -ray assessment of
-ray assessment of  Cs,
Cs,  Cs,
Cs,  Co, and
Co, and  Eu at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h.
Eu at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h.
 measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPS
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPSToyoda, Satoshi*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Yoshimura, Masashi*; Sumida, Hirosuke*; Mineoi, Susumu*; Machida, Masatake*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Suzuki, Satoru*; Yokoyama, Kazushi*; Ohashi, Yuji*; et al.
Vacuum and Surface Science, 64(2), p.86 - 91, 2021/02
We have developed  measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
 gamma-ray spectrometer suitable for the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
gamma-ray spectrometer suitable for the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power StationKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Otaka, Yutaka*; Uenomachi, Mizuki*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 971, p.164118_1 - 164118_8, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:66.68(Instruments & Instrumentation) (Al,Ga)
(Al,Ga) O
O scintillator Compton camera mounted on an unmanned helicopter
scintillator Compton camera mounted on an unmanned helicopterShikaze, Yoshiaki; Nishizawa, Yukiyasu; Sanada, Yukihisa; Torii, Tatsuo; Jiang, J.*; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; Yoshino, Masao*; Ito, Shigeki*; Endo, Takanori*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(12), p.1907 - 1918, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:96.48(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Compton camera was improved for use with the unmanned helicopter. Increase of the scintillator array from 4 4 to 8
4 to 8 8 and expanse of the distance between the two layers contributed to the improvements of detection efficiency and angular resolution, respectively. Measurements were performed over the riverbed of the Ukedo river of Namie town in Fukushima Prefecture. By programming of flight path and speed, the areas of 65 m
8 and expanse of the distance between the two layers contributed to the improvements of detection efficiency and angular resolution, respectively. Measurements were performed over the riverbed of the Ukedo river of Namie town in Fukushima Prefecture. By programming of flight path and speed, the areas of 65 m  60 m and 65 m
60 m and 65 m  180 m were measured during about 20 and 30 minutes, respectively. By the analysis the air dose rate maps at 1 m height were obtained precisely with the angular resolution corresponding to the position resolution of about 10 m from 10 m height. Hovering flights were executed over the hot spot areas for 10-20 minutes at 5-20 m height. By using the reconstruction software the
180 m were measured during about 20 and 30 minutes, respectively. By the analysis the air dose rate maps at 1 m height were obtained precisely with the angular resolution corresponding to the position resolution of about 10 m from 10 m height. Hovering flights were executed over the hot spot areas for 10-20 minutes at 5-20 m height. By using the reconstruction software the  -ray images including the hot spots were obtained with the angular resolution same as that evaluated in the laboratory (about 10
-ray images including the hot spots were obtained with the angular resolution same as that evaluated in the laboratory (about 10 ).
).
; Horiike, Hiroshi; Neyatani, Yuzuru; Matsukawa, Makoto; Ando, Toshiro; Yoshino, Ryuji; Arai, Takashi; Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Yamamoto, Masahiro; ; et al.
Proc. of the 14th Symp. on Fusion Engineering,Vol. 1, p.177 - 180, 1992/00
no abstracts in English
Imai, Tsuyoshi; Ushigusa, Kenkichi; Sakamoto, Keishi; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Saigusa, Mikio; Yoshino, Ryuji; Uehara, Kazuya; Nagashima, Takashi; Kimura, Haruyuki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 28(8), p.1341 - 1350, 1988/00
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:64.83(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Shikaze, Yoshiaki; Torii, Tatsuo; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Jiang, J.*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; Kurosawa, Shunsuke*; Kamada, Kei*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Yoshino, Masao*; Ito, Shigeki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shikaze, Yoshiaki; Torii, Tatsuo; Nishizawa, Yukiyasu; Yoshida, Mami*; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Jiang, J.*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; Kurosawa, Shunsuke*; Kamada, Kei*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kodama, Shohei*; Kurosawa, Shunsuke*; Morishita, Yuki; Usami, Hiroshi; Hayashi, Masateru*; Tanaka, Hiroki*; Yoshino, Masao*; Kamada, Kei*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Torii, Tatsuo
no journal, ,
After Fukushima 1st Nuclear Plant accident, a large number of radioactive pollutants or nuclear debris with very high dose of more than a few Sv/h still have existed. To estimate the dose of such pollutants, a Japan Atomic Energy Agency research group has suggested a new technique to use a long optical fiber and a red-emitting scintillator, and the scintillation photons are read outside of high dose area. We tested the gamma-ray detection performance of a ruby (Cr:Al O
O ) and a newly developed Cs
) and a newly developed Cs HfI
HfI scintillators as a scintillating probe coupled with an optical fiber in this study.
scintillators as a scintillating probe coupled with an optical fiber in this study.
Kaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Otaka, Yutaka*; Foong, W. S.*; Uenomachi, Mizuki*; Kamada, Kei*; Kin, J. Y.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 gamma-ray spectrometer toward the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
gamma-ray spectrometer toward the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power StationKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Otaka, Yutaka*; Foong, W. S.*; Uenomachi, Mizuki*; Kamada, Kei*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Otaka, Yutaka*; Uenomachi, Mizuki*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
 -ray spectrometric system for the decommissioning of the Tokyo Electric Power Company Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
-ray spectrometric system for the decommissioning of the Tokyo Electric Power Company Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power StationKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Otaka, Yutaka*; Uenomachi, Mizuki*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
The retrieval of the nuclear fuel debris, which is the substance including melted nuclear fuel and structural materials, will be started from fiscal 2021. Then, as a non-destructive analysis technology of the nuclear fuel debris, a  -ray spectroscopy system is being developed to measure high energy
-ray spectroscopy system is being developed to measure high energy  rays due to
rays due to  Eu and nuclear reactions under high dose rate, which was composed of a CeBr
Eu and nuclear reactions under high dose rate, which was composed of a CeBr cubic, photomultiplier tube, and fast signal processing unit. This presentation reports that the exposure study of the detector system was performed for a
cubic, photomultiplier tube, and fast signal processing unit. This presentation reports that the exposure study of the detector system was performed for a  Co field at the dose rates of up to 750 mSv/h, and the detector response was investigated at each dose rate.
Co field at the dose rates of up to 750 mSv/h, and the detector response was investigated at each dose rate.
 -ray spectrometry system specific to high dose-rate radiation fields for the retrieval of nuclear fuel debris in Tokyo Electrical Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
-ray spectrometry system specific to high dose-rate radiation fields for the retrieval of nuclear fuel debris in Tokyo Electrical Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power StationKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
The retrieval of nuclear fuel debris will be started at Tokyo Electrical Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. Because of high dose-rate fields on the surface of nuclear fuel debris and these inhomogeneous elements, non-destructive analysis is required during the retrieval. Here, it is presented that a  -ray spectrometry system specific to high dose-rate fields was developed and its performance under intense
-ray spectrometry system specific to high dose-rate fields was developed and its performance under intense  -ray fields was evaluated for the retrieval of nuclear fuel debris.
-ray fields was evaluated for the retrieval of nuclear fuel debris.