Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kubo, Shinji; Yoshino, Koji*; Takemoto, Jumpei*; Kasahara, Seiji; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Onuki, Kaoru
JAEA-Technology 2012-037, 20 Pages, 2013/01
Densities of Bunsen reaction solutions in the iodine-sulfur process were measured with an oscillating U-tube density meter. Two types of the solutions were prepared to simulate sulfuric acid solutions and hydriodic acid solutions of the Bunsen reaction step. The former solution ranged in concentration from 0 to 45 wt% of sulfuric acid containing HI and I of 0-2 mole%; the latter solution contained 0-17 mole% I
of 0-2 mole%; the latter solution contained 0-17 mole% I , 1-15 mole% HI and 0-2 mole% H
, 1-15 mole% HI and 0-2 mole% H SO
SO . The temperature of the measured solution were 10-60
. The temperature of the measured solution were 10-60  C. It was found that, in both solutions, the effect of HI and I
C. It was found that, in both solutions, the effect of HI and I concentration on the density could well be represented by using a kind of mole fraction of iodine atom. Based on the finding, a set of correlation equations between the densities and the compositions were derived. Additionally, viscosities of ploy-hydriodic acid were measured using an oscillating viscosity meter in temperature range of 5-40
concentration on the density could well be represented by using a kind of mole fraction of iodine atom. Based on the finding, a set of correlation equations between the densities and the compositions were derived. Additionally, viscosities of ploy-hydriodic acid were measured using an oscillating viscosity meter in temperature range of 5-40  C, and in the composition range of 0-17 mole% I
C, and in the composition range of 0-17 mole% I and 1-15 mole% HI; a empirical equation to calculate viscosity from the composition and the temperature are obtained.
and 1-15 mole% HI; a empirical equation to calculate viscosity from the composition and the temperature are obtained.
Miyamoto, Seiji; Sugihara, Masayoshi*; Shinya, Kichiro*; Nakamura, Yukiharu*; Toshimitsu, Shinichi*; Lukash, V. E.*; Khayrutdinov, R. R.*; Sugie, Tatsuo; Kusama, Yoshinori; Yoshino, Ryuji*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 87(11), p.1816 - 1827, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:73.09(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nakamura, Yukiharu*; Pautasso, G.*; Sugihara, Masayoshi*; Miyamoto, Seiji; Toshimitsu, Shinichi; Yoshino, Ryuji; ASDEX Upgrade Team*
Proceedings of 37th European Physical Society Conference on Plasma Physics (EPS 2010) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2010/06
Of particular importance for the assessment of electromagnetic loads on vacuum vessel and in-vessel components of ITER is the halo current which achieves a maximum during VDEs (VDE: vertical displacement event). However, halo current models have a limited development so far with a few exceptions such as a validation study of the JT-60U halo current modelling using the DINA code. Recently, several experimental groups have prepared systematic halo current data, and further model development and validation with these data need to be performed using an axisymmetric, two-dimensional, free boundary code, TSC. To enhance an understanding of the maximum halo current and large vertical shifts, a reference discharge was selected from those included in the ASDEX upgrade disruption database. Systematic TSC simulations were performed to mimic the observation of a slow VDE of hot plasma and an ensuing fast downward-going VDE during a subsequent plasma current quench. Careful parameter adjustment of the temperature and width of the halo region was examined to mimic measurements of the halo current. A spontaneous, downward-going VDE was reproduced accurately in a manner that closely resembled experimental observations.
Miyamoto, Seiji; Nakamura, Yukiharu*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Sugie, Tatsuo; Kusama, Yoshinori; Yoshino, Ryuji
Proceedings of 36th European Physical Society Conference on Plasma Physics (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2009/07
The neutral dynamics including fueling, divertor pumping, charge exchange penetration, wall retention and so on would complicate the analysis of ITER plasma behavior such as H-L back transition during plasma current ramp-down. Recently, a relatively simple model of neutral dynamics was developed by us with TSC code to describe the plasma behavior during L-H and H-L transition phase. This model is compared with a JT-60U shot, in which it is possible to extract the effect of particle confinement change on neutral because H-mode discharge is switched on/off according to EC injection and thereby particle source density is kept constant during transition. It is shown that TSC simulation can account the behavior of neutral inferred from the experimental D signal. It is concluded that this model is applicable to scenario development of the ITER.
signal. It is concluded that this model is applicable to scenario development of the ITER.
Nakamura, Yukiharu*; Miyamoto, Seiji; Toshimitsu, Shinichi; Sugie, Tatsuo; Kusama, Yoshinori; Yoshino, Ryuji
Proceedings of 36th European Physical Society Conference on Plasma Physics (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2009/07
The ITER termination scenario from 15 MA to 1.5 MA (500 s  t
t  700 s) was reviewed by self-consistent simulations with the TSC code, comprised of newly developed D-T fuelling and pumping-out system. At 600 s, when the plasma current decreased to 10 MA, auxiliary NB heating was switched off to cease fusion
700 s) was reviewed by self-consistent simulations with the TSC code, comprised of newly developed D-T fuelling and pumping-out system. At 600 s, when the plasma current decreased to 10 MA, auxiliary NB heating was switched off to cease fusion  -heating. Simultaneously, the energy confinement switches H to L mode by intentionally removing the H mode pedestal of edge transport barrier. The H to L mode transition dynamics,
-heating. Simultaneously, the energy confinement switches H to L mode by intentionally removing the H mode pedestal of edge transport barrier. The H to L mode transition dynamics, 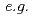 reduction in the plasma density while building-up of in-vessel neutral gas, disappearance of the edge BS current and consequent jump in the internal inductance
reduction in the plasma density while building-up of in-vessel neutral gas, disappearance of the edge BS current and consequent jump in the internal inductance 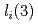 , were investigated to assess performance of the ITER pump-out system. It was newly shown that the forced H to L mode transition may trigger a radiation collapse, consequently terminating the discharge. It was also demonstrated that EC heating with 170 GHz O-mode wave after the H to L mode transition provides an effective control means to hedge risk of the radiation collapse.
, were investigated to assess performance of the ITER pump-out system. It was newly shown that the forced H to L mode transition may trigger a radiation collapse, consequently terminating the discharge. It was also demonstrated that EC heating with 170 GHz O-mode wave after the H to L mode transition provides an effective control means to hedge risk of the radiation collapse.
Miyamoto, Seiji; Nakamura, Yukiharu*; Toshimitsu, Shinichi; Sugie, Tatsuo; Kusama, Yoshinori; Yoshino, Ryuji; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oikawa, Toshihiro*
no journal, ,
Development of ITER operation scenario using TSC code in JAEA is reviewed. TSC is a numerical code to simulate plasma evolution solving the MHD equation in an axisymmetric cylindrical coordinates. We have incorporated numerical models of electron cyclotron heating (ECH) / current drive (ECCD) and neutral beam injection (NBI) heating / current drive into the TSC code. Using the incorporated ECH/ECCD model, flux saving during plasma current ramp-up by EC is discussed. It is shown that resistive flux is effectively reduced due to heating of electron by EC. Recently, we are incorporating a neutral particle fueling and pumping model for studying effect of H-L transition on the poloidal field coil system of ITER size machine. A plan of neutral model development in TSC is also presented.
Miyamoto, Seiji; Sugihara, Masayoshi*; Shinya, Kichiro*; Nakamura, Yukiharu*; Toshimitsu, Shinichi; Sugie, Tatsuo; Kusama, Yoshinori; Yoshino, Ryuji
no journal, ,
When Plasma Control System (PCS) generates wrong signal to the PF coils and in-vessel vertical stabilization (VS) coils, it could be happen that the vertical force somewhat larger than presently specified could be generated. Example is that though plasma moves downward, but PCS erroneously recognizes it is moving upward. Then PF coils start to generate the field pattern that tends to push plasma further downward and resultantly the force could be larger than the present specification, in which it is evaluated with the assumption that control system (PF coils) does nothing (i.e., short-circuited.) In fact, in the existing machines, this is the worst case. The DINA code is used to analyze the vertical force, which has been updated to incorporate the recent design change of the vacuum vessel and in-vessel VS coils. In the presentation, analysis of VS effect on the vertical force is discussed using the updated DINA code.
Takemoto, Jumpei; Yoshino, Koji; Kubo, Shinji; Kasahara, Seiji; Takahashi, Toshio*; Hino, Ryutaro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ozu, Akira; Takase, Misao; Kurata, Noritaka; Kobayashi, Nozomi; Yoshino, Seiji; Kureta, Masatoshi; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Nakamura, Hironobu; Seya, Michio; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takemoto, Jumpei; Yoshino, Koji*; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Kubo, Shinji; Kasahara, Seiji; Takahashi, Toshio*; Hino, Ryutaro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Miyamoto, Seiji; Nakamura, Yukiharu*; Fujieda, Hirobumi; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Sugie, Tatsuo; Kusama, Yoshinori; Yoshino, Ryuji
no journal, ,
Recently, we developed a simulation model in which an ECRF ray tracing and current drive calculations are combined with TSC. This model is applied to the evaluation of magnetic flux consumption in the ITER current ramp-up scenario. In this model, real geometry of PF/CS coils and EC launcher is taken into account, and EC deposition/current drive profile are calculated in self-consistent with the plasma profile evolution. Central current drive (present ITER design) and off-axis current drive (test case) is compared. Resistive flux is lowered in both cases. Internal flux is also reduced by the off-axis EC due to reduction of internal inductance. It is although shown that, even in the case of central EC, comparable reduction of internal flux is expected due to the skin effect of inductive current.
Nakamura, Yukiharu*; Miyamoto, Seiji; Fujieda, Hirobumi; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Sugie, Tatsuo; Kusama, Yoshinori; Yoshino, Ryuji
no journal, ,
In tokamak fusion reactors with superconducting PF coil system, ramping-up of the plasma current for startup of discharges is essentially restrained at a rate much slower than the current tokamak with normal PF conductors. Therefore, the induced plasma current can penetrate deeply into the core region with higher electron temperature, i.e. low Ohmic resistivity, leading to a centrally peaked current profile. Consequently, such the high li, highly elongated configuration imperative to divertor formation has the dangerous property of causing vertical instability. Additional heating at early phase of the ramp-up has been addressed as one of startup procedures that retard the penetration of plasma current. A potential drawback, however, is the substantial increase of direct heat load to limiter. Hence, it follows that discharge optimization, e.g. timing of the heating, has been critical to plasma formation during the startup phase. The feasible ramp-up scenario to obtain a stable current profile while increasing bootstrap current fraction is discussed, as well as the interests: how quickly the plasma current needs to be ramped up and how slowly it can be.
Nakamura, Yukiharu*; Miyamoto, Seiji; Sugie, Tatsuo; Kusama, Yoshinori; Yoshino, Ryuji
no journal, ,
The ITER termination scenario from 15 MA to 1.5 MA (500 s  t
t  700 s) [A.A. Kavin
700 s) [A.A. Kavin 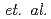 , Progress report of plasma startup and termination, ITER_D_2F55U5 (2008)] was reviewed by self-consistent simulations with the TSC code, comprised of newly developed D-T fuelling and pumping-out system. The dynamics of a forced H- to L-mode transition,
, Progress report of plasma startup and termination, ITER_D_2F55U5 (2008)] was reviewed by self-consistent simulations with the TSC code, comprised of newly developed D-T fuelling and pumping-out system. The dynamics of a forced H- to L-mode transition, 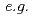 reduction in the plasma density while building-up of the in-vessel neutral gas, disappearance of the edge BS current and consequent jump in the internal inductance, were investigated to assess the performance of the ITER pump-out system. It was newly demonstrated that the forced H-L mode transition may trigger a radiation collapse, consequently terminating the discharge even in magnetic divertor configuration, if the effective pumping speed is insufficient or if the wall retention of the neutral particle remains saturated. In order to avoid the radiation collapse during plasma termination, off-axis heating and current drive with 170 GHz O-mode EC wave was utilized and shown to be effective.
reduction in the plasma density while building-up of the in-vessel neutral gas, disappearance of the edge BS current and consequent jump in the internal inductance, were investigated to assess the performance of the ITER pump-out system. It was newly demonstrated that the forced H-L mode transition may trigger a radiation collapse, consequently terminating the discharge even in magnetic divertor configuration, if the effective pumping speed is insufficient or if the wall retention of the neutral particle remains saturated. In order to avoid the radiation collapse during plasma termination, off-axis heating and current drive with 170 GHz O-mode EC wave was utilized and shown to be effective.
Sakasai, Kaoru; Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Suzuki, Hiroyuki; Ozu, Akira; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Takase, Misao; Kurata, Noritaka; Yoshino, Seiji; et al.
no journal, ,
We have developed the neutron-sensitive scintillator neutron counter for nuclear safeguards. The detector is made based on the scintillator detector technology developed long in the J-PARC/MLF. The detector is comprised of the ZnS/B O
O ceramic scintillator, rectangular shaped light guide and photomultiplier tubes. The detector performances including detector efficiency and its incident position dependence and
ceramic scintillator, rectangular shaped light guide and photomultiplier tubes. The detector performances including detector efficiency and its incident position dependence and  -ray sensitivity are presented in detail.
-ray sensitivity are presented in detail.
Miyamoto, Seiji; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Toshimitsu, Shinichi; Sugie, Tatsuo; Kusama, Yoshinori; Yoshino, Ryuji
no journal, ,
In the operation of ITER, transition from the high confinement (H) mode to the low confinement (L) mode (H-L transition) is serious disturbance to control system, and therefore it is an important issue in operation scenario development to model the plasma behavior during the transition. Especially, the analysis must include neutral particles in plasma behavior. In the ITER current ramp-down scenario, the plasma is kept in H-mode, and thereby in low internal inductance, to leave a control margin. Then the plasma goes to L-mode at the final stage of the discharge. When the plasma particles emitted at the H-L transition flow back to the plasma as neutrals, the discharge may lead to a radiation collapse if the pumping capacity is too low. It is therefore required to perform a simulation including a model of fueling and pumping system. We did not take into account the scrape-off-layer (SOL) and divertor models previously. However, these models influence the plasma particle behavior through neutralization of ions in front of the divertor target and re-ionization of neutrals in the SOL. In the presentation, we describe the implementation of the SOL and divertor models in the tokamak simulation code (TSC) and the effect on the plasma and neutral behavior.