Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tian, Q.*; Feng, L.*; Wu, C.*; Wen, J.*; Qiu, X.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Onuki, Toshihiko*; Yu, Q.*
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 669, p.1006 - 1014, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:31.33(Chemistry, Physical)Zhang, A.*; Deng, K.*; Sheng, J.*; Liu, P.*; Kumar, S.*; Shimada, Kenya*; Jiang, Z.*; Liu, Z.*; Shen, D.*; Li, J.*; et al.
Chinese Physics Letters, 40(12), p.126101_1 - 126101_8, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:83.08(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Xi, N.*; Gao, Y.-P.*; Ma, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Qi, Z.*; Zhang, S.*; Huang, Z.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(12), p.1883 - 1889, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:94.19(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -MnO
-MnO for peroxymonosulfate activation reaction; Via direct electron transfer or via free radical reactions
for peroxymonosulfate activation reaction; Via direct electron transfer or via free radical reactionsOuyang, H.*; Wu, C.*; Qiu, X.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Onuki, Toshihiko*; Yu, Q.*
Environmental Research, 217, p.114874_1 - 114874_10, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:82.02(Environmental Sciences) BaCo(PO
BaCo(PO )
)
Sheng, J.*; Wang, L.*; Candini, A.*; Jiang, W.*; Huang, L.*; Xi, B.*; Zhao, J.*; Ge, H.*; Zhao, N.*; Fu, Y.*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 119(51), p.e2211193119_1 - e2211193119_9, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:93.24(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Wu, C.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Tani, Yukinori*; Bi, X.*; Liu, J.*; Yu, Q.*
Science of the Total Environment, 821, p.153265_1 - 153265_9, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:96.66(Environmental Sciences)Microplastics (MPs) with different particle sizes were co-cultured with a model freshwater fungus, 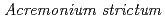 strain KR21-2, to form biofilms on their surface. We also determined the changes in surface physicochemical properties of the biofilm-covered MPs (BMPs) and the heavy metal adsorption capacity of the original MPs and BMPs. The results revealed that the biofilms improve the adsorption of heavy metals on MPs, and the particle size of MPs plays a crucial role in biofilm colonization and adsorption of heavy metals by BMPs.
strain KR21-2, to form biofilms on their surface. We also determined the changes in surface physicochemical properties of the biofilm-covered MPs (BMPs) and the heavy metal adsorption capacity of the original MPs and BMPs. The results revealed that the biofilms improve the adsorption of heavy metals on MPs, and the particle size of MPs plays a crucial role in biofilm colonization and adsorption of heavy metals by BMPs.
Deng, G.*; Ma, T.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Onuki, Toshihiko*; Qiu, X.*; Yu, Q.*
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 286, p.143 - 158, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:36.40(Geochemistry & Geophysics)In this study, Ce(III) adsorption on Mn(IV) oxide was investigated in the presence of dextran, one of polysaccharides. As a result, Ce(IV) on Mn(IV) oxide was solubilized by the complexation with dextran.
 decay of
decay of 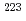 U
USun, M. D.*; Liu, Z.*; Huang, T. H.*; Zhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Ding, B.*; Wang, J. G.*; Liu, X. Y.*; Lu, H. Y.*; Hou, D. S.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 800, p.135096_1 - 135096_5, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:74.01(Astronomy & Astrophysics) , Zn
, Zn +, and Co
+, and Co
Kato, Tomoaki*; Yu, Q.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Saito, Takumi*; Onuki, Toshihiko
Journal of Environmental Sciences, 86, p.78 - 86, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:10.02(Environmental Sciences)This paper investigated the fate of the dissolved permanganate in aqueous solution after contact with bacterial cells and metal accumulation during precipitation of Mn oxides. When Mn(VII) was contacted with bacterial cells, cells were damaged and Mn(VII) was reduced by cells to lower valence and precipitated as Mn oxides (biomass Mn oxides). When Co ions were present, Co was incorporated into Mn oxides as Co
ions were present, Co was incorporated into Mn oxides as Co . These results suggest that Mn(VII) can be used to remove metal ions when introduced to wastewater as disinfectant.
. These results suggest that Mn(VII) can be used to remove metal ions when introduced to wastewater as disinfectant.
Yu, Q.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Tani, Yukinori*; Onuki, Toshihiko
ACS Earth and Space Chemistry (Internet), 2(8), p.797 - 810, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:54.42(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Most of Mn oxides are biogenic and known to adsorb cesium (Cs) on the surface. This study investigated structural transformation of biogenic birnessite by accommodating commonly occurring natural heavy metals (Zn, Ni) during the formation of Mn oxides and the influence of those metals on the adsorption behavior of Cs on Mn oxides. It was found that the presence of heavy metals during bio-oxidation of Mn(II), followed by exposure to a low pH aqueous solution, increased the number of available layer vacancies, which consequently increased the adsorption capacity of Cs in the final product birnessite.
Li, B.; Wang, H.*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Zhang, Q.*; Feygenson, M.*; Yu, H. L.*; Wu, D.*; Ohara, Koji*; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Shibata, Kaoru; et al.
Nature Materials, 17(3), p.226 - 230, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:155 Percentile:97.17(Chemistry, Physical)Yu, Q.*; Onuki, Toshihiko*; Kozai, Naofumi; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Tanaka, Kazuya; Sasaki, Keiko*
Chemical Geology, 470, p.141 - 151, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:52.35(Geochemistry & Geophysics)In this work, the Cs retention onto two types of Mn oxide was investigated. We found that Todorokite has sorption sites with a higher selectivity for Cs than birnessite. When the initial Cs concentration was 10 mol/L for the sorption experiments, approximately 34% of the sorbed Cs was residual in the todorokite after the extraction using 1 M NaCl and NH
mol/L for the sorption experiments, approximately 34% of the sorbed Cs was residual in the todorokite after the extraction using 1 M NaCl and NH Cl; this value was much higher than the results for the Cs-sorbed birnessite. These results strongly suggest that todorokite contributes to the fixation of radioactive Cs in soils.
Cl; this value was much higher than the results for the Cs-sorbed birnessite. These results strongly suggest that todorokite contributes to the fixation of radioactive Cs in soils.
Yu, Q.; Onuki, Toshihiko; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Tani, Yukinori*
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 174, p.1 - 12, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:56.05(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Although microorganisms possess high sorption capability for lanthanides (Lns), their biological response affecting Lns migration is unclear. We investigated the effects of microbial activity on transformation of Lns by contact of Lns with Aeremonium strictum under metabolically active condition with Mn(II). A biomolecule that specifically complex to Ce(IV) was found to be released from the fungal cell, facilitating the desorption of Ce(IV) from Mn oxide. This biomolecule was not associated with any other trivalent Lns or Fe, which differed from those non-nuclide-specific organic substances released from resting cells, as reported previously.
Onuki, Toshihiko; Jiang, M.*; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Kozai, Naofumi; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Yu, Q.; Tanaka, Kazuya; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*; Xia, X.*; Yange, K.*; et al.
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 163, p.1 - 13, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:59.75(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The association of Ce(III) with the microbial cell surface and the formation of Ce phosphate nano-particles are responsible for suppressing the oxidation of Ce(III) to Ce(IV) in the mixtures.
Yu, Q.*; Qi, L.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Traylor, R.*; Rugg, D.*; Morris, J. W. Jr.*; Asta, M.*; Chrzan, D. C.*; Minor, A. M.*
Science, 347(6222), p.635 - 639, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:288 Percentile:98.58(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Given that solute atoms interact weakly with the long-range elastic fields of screw dislocations, it has long been accepted that solution hardening is only marginally effective in materials with mobile screw dislocations. This accepted wisdom has recently been questioned by first-principles calculations suggesting that solutes may interact much more strongly with the screw dislocation core. We report here the results of a combined experimental and computational study undertaken to elucidate the profound hardening effect of oxygen in pure hexagonally-close-packed structured  -Ti. High resolution and in situ transmission electron microscopy nanomechanical characterization establish that the strengthening is due to the strong interaction between oxygen and the core of screw dislocations that mainly glide on prismatic planes. First-principles calculations of the screw dislocation core reveal a simple crystallographic source for the oxygen-dislocation interaction that is consistent with experimental observations. The distortion of the interstitial sites at the dislocation core creates a very strong but short-range repulsion for oxygen atoms. These mechanisms effectively pin the dislocation near the oxygen interstitial. These results establish a highly effective mechanism for strengthening by interstitial solutes that, contrary to prior understanding, may be significant in many structural alloys.
-Ti. High resolution and in situ transmission electron microscopy nanomechanical characterization establish that the strengthening is due to the strong interaction between oxygen and the core of screw dislocations that mainly glide on prismatic planes. First-principles calculations of the screw dislocation core reveal a simple crystallographic source for the oxygen-dislocation interaction that is consistent with experimental observations. The distortion of the interstitial sites at the dislocation core creates a very strong but short-range repulsion for oxygen atoms. These mechanisms effectively pin the dislocation near the oxygen interstitial. These results establish a highly effective mechanism for strengthening by interstitial solutes that, contrary to prior understanding, may be significant in many structural alloys.
Yu, Q.; Sasaki, Keiko*
Hydrometallurgy, 150, p.253 - 258, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:39.44(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering) on biogenic birnessite
on biogenic birnessiteSasaki, Keiko*; Yu, Q.; Momoki, Taichi*; Kaseyama, Takuya*
Applied Clay Science, 101, p.23 - 29, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:40.47(Chemistry, Physical)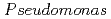 sp. strain NGY-1
sp. strain NGY-1Tanaka, Kazuya*; Yu, Q.; Sasaki, Keiko*; Onuki, Toshihiko
Geomicrobiology Journal, 30(10), p.874 - 885, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:47.86(Environmental Sciences)no abstracts in English
Deng, Z.*; Zhao, K.*; Gu, B.; Han, W.*; Zhu, J. L.*; Wang, X. C.*; Li, X.*; Liu, Q. Q.*; Yu, R. C.*; Goko, Tatsuo*; et al.
Physical Review B, 88(8), p.081203_1 - 081203_5, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:76 Percentile:91.63(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yu, Q.; Sasaki, Keiko*; Tanaka, Kazuya*; Onuki, Toshihiko; Hirajima, Tsuyoshi*
Geomicrobiology Journal, 30(9), p.829 - 839, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:71.20(Environmental Sciences)no abstracts in English