Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloy
FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloyLi, C.*; Fang, W.*; Yu, H. Y.*; Peng, T.*; Yao, Z. T.*; Liu, W. G.*; Zhang, X.*; Xu, P. G.; Yin, F.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 892, p.146096_1 - 146096_11, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:79.11(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology) Be ground-state molecular structure using
Be ground-state molecular structure using  Be(
Be(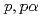 )
) He triple differential reaction cross-section measurements
He triple differential reaction cross-section measurementsLi, P. J.*; Beaumel, D.*; Lee, J.*; Assi , M.*; Chen, S.*; Franchoo, S.*; Gibelin, J.*; Hammache, F.*; Harada, T.*; Kanada-En'yo, Yoshiko*; et al.
, M.*; Chen, S.*; Franchoo, S.*; Gibelin, J.*; Hammache, F.*; Harada, T.*; Kanada-En'yo, Yoshiko*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 131(21), p.212501_1 - 212501_7, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:94.59(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The cluster structure of the neutron-rich isotope  Be has been probed via the (
Be has been probed via the (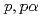 ) reaction. The triple differential cross-section was extracted and compared to distorted-wave impulse approximation reaction calculations performed in a microscopic framework using the Tohsaki-Horiuchi-Schuck-R
) reaction. The triple differential cross-section was extracted and compared to distorted-wave impulse approximation reaction calculations performed in a microscopic framework using the Tohsaki-Horiuchi-Schuck-R pke wave function and the wave function deduced from Antisymmetrized Molecular Dynamics calculations. The remarkable agreement between calculated and measured cross-sections in both shape and magnitude validates the description of the
pke wave function and the wave function deduced from Antisymmetrized Molecular Dynamics calculations. The remarkable agreement between calculated and measured cross-sections in both shape and magnitude validates the description of the  Be ground-state as a rather compact nuclear molecule.
Be ground-state as a rather compact nuclear molecule.
Bao, S.*; Gu, Z.-L.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, B.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Wang, W.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.6093_1 - 6093_9, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:92.84(Multidisciplinary Sciences) CoCrFeNi eutectic high entropy alloy
CoCrFeNi eutectic high entropy alloyYun, D.*; Chae, H.*; Lee, T.*; Lee, D.-H.*; Ryu, H. J.*; Banerjee, R.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Lee, S. Y.*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 918, p.165673_1 - 165673_7, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:65.57(Chemistry, Physical)Boznar, M. Z.*; Charnock, T. W.*; Chouhan, S. L.*; Grsic, Z.*; Halsall, C.*; Heinrich, G.*; Helebrant, J.*; Hettrich, S.*; Ku a, P.*; Mancini, F.*; et al.
a, P.*; Mancini, F.*; et al.
IAEA-TECDOC-2001, 226 Pages, 2022/06
The IAEA organized a programme from 2012 to 2015 entitled Modelling and Data for Radiological Impact Assessments (MODARIA), which aimed to improve capabilities in the field of environmental radiation dose assessment by acquiring improved data, model testing and comparison of model inputs, assumptions and outputs, reaching a consensus on modelling philosophies, aligning approaches and parameter values, developing improved methods and exchanging information. This publication describes the activities of Working Group 2, Exposures in Contaminated Urban Environments and Effect of Remedial Measures.
Takahara, Shogo; Charnock, T. W.*; Silva, K.*; Hwang, W. T.*; Lee, J.*; Yu, C.*; Kamboj, S.*; Yankovich, T.*; Thiessen, K. M.*
Journal of Radiological Protection, 42(2), p.020517_1 - 020517_13, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)State-of-the-art dose assessment models were applied to estimate doses to the population in urban areas contaminated by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Assessment results were compared among five models, and comparisons of model predictions with actual measurements were also made. Assessments were performed using both probabilistic and deterministic approaches. Predicted dose distributions in indoor and outdoor workers from a probabilistic approach were in good agreement with the actual measurements. In addition, when the models were applied to assess the doses to a representative person, based on a concept suggested by the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP), it was evident that doses to the representative person obtained with a deterministic approach were always higher than those obtained with a probabilistic approach.
Thiessen, K. M.*; Boznar, M. Z.*; Charnock, T. W.*; Chouhan, S. L.*; Federspiel, L.; Gra i
i , B.*; Grsic, Z.*; Helebrant, J.*; Hettrich, S.*; Hulka, J.*; et al.
, B.*; Grsic, Z.*; Helebrant, J.*; Hettrich, S.*; Hulka, J.*; et al.
Journal of Radiological Protection, 42(2), p.020502_1 - 020502_8, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:60.29(Environmental Sciences)Yamamoto, Kei; Yu, W.*; Yu, T.*; Puebla, J.*; Xu, M.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; Bauer, G.*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 89(11), p.113702_1 - 113702_5, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:76.54(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Deng, G.*; Ma, T.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Onuki, Toshihiko*; Qiu, X.*; Yu, Q.*
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 286, p.143 - 158, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:35.77(Geochemistry & Geophysics)In this study, Ce(III) adsorption on Mn(IV) oxide was investigated in the presence of dextran, one of polysaccharides. As a result, Ce(IV) on Mn(IV) oxide was solubilized by the complexation with dextran.
 decay of
decay of 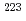 U
USun, M. D.*; Liu, Z.*; Huang, T. H.*; Zhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Ding, B.*; Wang, J. G.*; Liu, X. Y.*; Lu, H. Y.*; Hou, D. S.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 800, p.135096_1 - 135096_5, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:75.82(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Takechi, Manabu; Matsunaga, Go; Sakurai, Shinji; Sasajima, Tadayuki; Yagyu, Junichi; Hoshi, Ryo*; Kawamata, Yoichi; Kurihara, Kenichi; JT-60SA Team; Nishikawa, T.*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 96-97, p.985 - 988, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:69.44(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kim, S. H.*; Hwang, S.; Ahn, J. K.*; Ekawa, Hiroyuki; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Hong, B.*; Hosomi, Kenji; Imai, Kenichi; Kim, M. H.*; Lee, J. Y.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 795, p.39 - 44, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.26(Instruments & Instrumentation)Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Choi, I. W.*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Nakamura, Tatsufumi*; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Yogo, Akifumi*; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Orimo, Satoshi; Daito, Izuru*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 57(2), p.025001_1 - 025001_9, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:12.55(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Projection images of a metal mesh produced by directional MeV electron beam together with directional proton beam, emitted simultaneously from a thin foil target irradiated by an ultrashort intense laser. The mesh patterns are projected to each detector by the electron beam and the proton beam originated from tiny virtual sources of  20 micron meter and
20 micron meter and  10 micron meter diameters, respectively. Based on the observed quality and magnification of the projection images, we estimate sizes and locations of the virtual sources for both beams and characterize their directionalities. To carry out physical interpretation of the directional electron beam qualitatively, we perform 2D particle-in-cell simulation which reproduces a directional escaping electron component, together with a non-directional dragged-back electron component, the latter mainly contributes to building a sheath electric field for proton acceleration.
10 micron meter diameters, respectively. Based on the observed quality and magnification of the projection images, we estimate sizes and locations of the virtual sources for both beams and characterize their directionalities. To carry out physical interpretation of the directional electron beam qualitatively, we perform 2D particle-in-cell simulation which reproduces a directional escaping electron component, together with a non-directional dragged-back electron component, the latter mainly contributes to building a sheath electric field for proton acceleration.
Sako, Hiroyuki; Ahn, J. K.*; Baek, K. H.*; Bassalleck, B.*; Fujioka, H.*; Guo, L.*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hicks, K.*; Honda, R.*; Hwang, S. H.*; et al.
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 9(4), p.C04009_1 - C04009_10, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:14.89(Instruments & Instrumentation)A TPC has been developed for J-PARC E42 experiment to search for H-dibaryon in (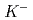 ,
, 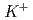 ) reaction. An event with 2
) reaction. An event with 2 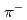 and 2 protons decaying from H-dibaryon is searched for inside the TPC. The TPC has octagonal prism shape drift volume with about 50 cm diameter with 55 cm drift length filled with Ar-CH
and 2 protons decaying from H-dibaryon is searched for inside the TPC. The TPC has octagonal prism shape drift volume with about 50 cm diameter with 55 cm drift length filled with Ar-CH (90:10) gas. At the end of the drift volume, 3-layer GEMs are equipped. In order to analyze momenta of produced particles, the TPC is applied with 1 T dipole magnetic field parallel to the drift electric field with a superconducting Helmholz magnet. In order to maximize the acceptance of H-dibaryon events, a diamond target is installed inside the TPC drift volume, in a cylindrical hole opened from the top to the middle of the drift volume. Since extremely high-rate
(90:10) gas. At the end of the drift volume, 3-layer GEMs are equipped. In order to analyze momenta of produced particles, the TPC is applied with 1 T dipole magnetic field parallel to the drift electric field with a superconducting Helmholz magnet. In order to maximize the acceptance of H-dibaryon events, a diamond target is installed inside the TPC drift volume, in a cylindrical hole opened from the top to the middle of the drift volume. Since extremely high-rate 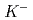 beam is directly injected into the TPC drift volume to the target, a gating grid and GEMs are adopted to suppress positive-ion feedback.
beam is directly injected into the TPC drift volume to the target, a gating grid and GEMs are adopted to suppress positive-ion feedback.
Vostner, A.*; Pong, I.*; Bessette, D.*; Devred, A.*; Sgobba, S.*; Jung, A.*; Weiss, K.-P.*; Jewell, M. C.*; Liu, S.*; Yu, W.*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 23(3), p.9500705_1 - 9500705_5, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:53.56(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The ITER Cable-In-Conduit Conductor (CICC) used in the superconducting magnet system consists of a cable made of 300 to 1440 strands housed in a stainless steel tube (a.k.a. jacket or conduit). There are circular, square, as well as circle-in-square jackets, made of either a very low carbon AISI 316LN grade stainless steel or a high Mn austenitic stainless steel developed for ITER called JK2LB. Selected mechanical properties of the base material and weld joint were tested at room temperature and/or cryogenic temperatures ( 7 K). The Domestic Agencies (DAs) reference laboratories and the ITER-IO appointed reference laboratories, CERN and Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) performed mechanical tests. This paper will compare the test results (e.g. elongation to failure) from different laboratories.
7 K). The Domestic Agencies (DAs) reference laboratories and the ITER-IO appointed reference laboratories, CERN and Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) performed mechanical tests. This paper will compare the test results (e.g. elongation to failure) from different laboratories.
Bruzzone, P.*; Stepanov, B.*; Wesche, R.*; Mitchell, N.*; Devred, A.*; Nunoya, Yoshihiko; Tronza, V.*; Kim, K.*; Boutboul, T.*; Martovetsky, N.*; et al.
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/03
Starting March 2007, over 60 ITER cable-in-conduit conductors (CICC) have been tested in the SULTAN test facility, Switzerland. For the NbTi CICC, the results confirm the prediction from the strand data, which are made taking the peak field over the conductor cross section as operating field. All the NbTi samples passed the supplier qualification phase. For the Nb Sn CICC, the performance prediction is not straightforward because of the irreversible degradation caused by filament damage occurring during cyclic loading. At the first run of the test campaign, the performance of all the Nb
Sn CICC, the performance prediction is not straightforward because of the irreversible degradation caused by filament damage occurring during cyclic loading. At the first run of the test campaign, the performance of all the Nb Sn samples largely meets the target for all the tested samples. Contrary to the NbTi CICC case, the n-index of the transition is substantially lower than in the strands, providing evidence of irreversible degradation. The performance loss upon load cycles and thermal cycles has a broad range among the various conductor samples.
Sn samples largely meets the target for all the tested samples. Contrary to the NbTi CICC case, the n-index of the transition is substantially lower than in the strands, providing evidence of irreversible degradation. The performance loss upon load cycles and thermal cycles has a broad range among the various conductor samples.
Choi, I. W.*; Kim, I. J.*; Pae, K. H.*; Nam, K. H.*; Lee, C.-L.*; Yun, H.*; Kim, H. T.*; Lee, S. K.*; Yu, T. J.*; Sung, J. H.*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 99(18), p.181501_1 - 181501_3, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:56.02(Physics, Applied)We report the manufacturing of a thin foil target made of conjugated polymer, and the simultaneous observation of laser accelerated ions and second harmonic radiation, when irradiated with ultrahigh-contrast laser pulse at a maximum intensity of 4 10
10 W/cm
W/cm . Maximum proton energy of 8 MeV is achieved along the target normal direction. Strong second harmonic with over 6% energy ratio compared to fundamental is emitted along the specular direction. Two-dimensional particle-in-cell simulations confirm the simultaneous generation of protons and high-order harmonics, which demonstrates the feasibility of applications requiring particle and radiation sources at once, effectively using the same laser and target.
. Maximum proton energy of 8 MeV is achieved along the target normal direction. Strong second harmonic with over 6% energy ratio compared to fundamental is emitted along the specular direction. Two-dimensional particle-in-cell simulations confirm the simultaneous generation of protons and high-order harmonics, which demonstrates the feasibility of applications requiring particle and radiation sources at once, effectively using the same laser and target.
Deng, Z.*; Jin, C. Q.*; Liu, Q. Q.*; Wang, X. C.*; Zhu, J. L.*; Feng, S. M.*; Chen, L. C.*; Yu, R. C.*; Arguello, C.*; Goko, Tatsuo*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 2, p.1425_1 - 1425_5, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:172 Percentile:93.60(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In a prototypical ferromagnet (Ga,Mn)As based on a III-V semiconductor, substitution of divalent Mn atoms into trivalent Ga sites leads to severely limited chemical solubility and metastable specimens available only as thin films. The doping of hole carriers via (Ga,Mn) substitution also prohibits electron doping. To overcome these difficulties, Masek et al. theoretically proposed systems based on a I-II-V semiconductor LiZnAs, where isovalent (Zn,Mn) substitution is decoupled from carrier doping with excess/deficient Li concentrations. Here we show successful synthesis of Li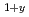 (Zn
(Zn Mn
Mn )As in bulk materials. We reported that ferromagnetism with a critical temperature of up to 50 K is observed in nominally Li-excess compounds, which have p-type carriers.
)As in bulk materials. We reported that ferromagnetism with a critical temperature of up to 50 K is observed in nominally Li-excess compounds, which have p-type carriers.
Park, J. M.*; Murakami, Masanori*; Petty, C. C.*; Heidbrink, W. W.*; Osborne, T. H.*; Holcomb, C. T.*; Van Zeeland, M. A.*; Prater, R.*; Luce, T. C.*; Wade, M. R.*; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 16(9), p.092508_1 - 092508_10, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:66.67(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Neutral beam current drive (NBCD) experiments in DIII-D using vertically shifted plasmas to move the current drive away from the axis have clearly demonstrated robust off-axis NBCD. Time-dependent measurements of magnetic pitch angles by the motional Stark effect diagnostic are used to obtain the evolution of the poloidal magnetic flux, which indicates a broad off-axis NBCD profile with a peak at about half the plasma radius. In most cases, the measured off-axis NBCD profile is consistent with calculations using an orbit-following Monte-Carlo code for the beam ion slowing down including finite-orbit effects, provided there is no large-scale MHD activity such as Alfv n eigenmodes modes or sawteeth. Good agreement is found between the measured pitch angles and those from simulations using transport-equilibrium codes. Two-dimensional image of Doppler-shifted fast ion D
n eigenmodes modes or sawteeth. Good agreement is found between the measured pitch angles and those from simulations using transport-equilibrium codes. Two-dimensional image of Doppler-shifted fast ion D light emitted by neutralized energetic ions shows clear evidence for a hollow profile of beam ion density, consistent with classical beam ion slowing down. The magnitude of off-axis NBCD is sensitive to the alignment of the beam injection relative to the helical pitch of the magnetic field lines. If the signs of B and I yield the proper helicity, both measurement and calculation indicate that the efficiency is as good as on-axis NBCD because the increased fraction of trapped electrons reduces the electron shielding of the injected ion current, in contrast with electron current drive schemes where the trapping of electrons degrades the efficiency. The measured off-axis NBCD increases approximately linearly with the injection power, although a modest amount of fast ion diffusion is needed to explain an observed difference in the NBCD profile between the measurement and the calculation at high injection power.
light emitted by neutralized energetic ions shows clear evidence for a hollow profile of beam ion density, consistent with classical beam ion slowing down. The magnitude of off-axis NBCD is sensitive to the alignment of the beam injection relative to the helical pitch of the magnetic field lines. If the signs of B and I yield the proper helicity, both measurement and calculation indicate that the efficiency is as good as on-axis NBCD because the increased fraction of trapped electrons reduces the electron shielding of the injected ion current, in contrast with electron current drive schemes where the trapping of electrons degrades the efficiency. The measured off-axis NBCD increases approximately linearly with the injection power, although a modest amount of fast ion diffusion is needed to explain an observed difference in the NBCD profile between the measurement and the calculation at high injection power.
Murakami, Masanori*; Park, J. M.*; Petty, C. C.*; Luce, T. C.*; Heidbrink, W. W.*; Osborne, T. H.*; Prater, R.*; Wade, M. R.*; Anderson, P. M.*; Austin, M. E.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(6), p.065031_1 - 065031_8, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:82.24(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Modification of the two existing DIII-D neutral beam lines is planned to allow vertical steering to provide off-axis neutral beam current drive (NBCD) peaked as far off-axis as half the plasma minor radius. New calculations for a downward-steered beam indicate strong current drive with good localization off-axis so long as the toroidal magnetic field, BT, and the plasma current, Ip, point in the same direction. This is due to good alignment of neutral beam injection (NBI) with the local pitch of the magnetic field lines. This model has been tested experimentally on DIII-D by an injecting equatorially-mounted NBs into reduced size plasmas that are vertically displaced with respect to the vessel midplane. The existence of off-axis NBCD is evident in the changes seen in sawtooth behavior in the internal inductance. By shifting the plasma upward or downward, or by changing the sign of the toroidal field, measured off-axis NBCD profiles measured with motional Stark effect data and internal loop voltage show a difference in amplitude (40%-45%) consistent with predicted differences predicted by the changed NBI alignment with respect to the helicity of the magnetic field lines. The effects of NB injection direction relative to field line helicity can be large even in ITER: off-axis NBCD can be increased by more than 20% if the BT direction is reversed. Modification of the DIII-D NB system will strongly support scenario development for ITER and future tokamaks as well as providing flexible scientific tools for understanding transport, energetic particles and heating and current drive.