Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloy
FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloyLi, C.*; Fang, W.*; Yu, H. Y.*; Peng, T.*; Yao, Z. T.*; Liu, W. G.*; Zhang, X.*; Xu, P. G.; Yin, F.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 892, p.146096_1 - 146096_11, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.04(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology) Sn
Sn
Huang, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Ye, H.*; Bao, S.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Liao, J.*; Cao, S.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Deng, G.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 109(1), p.014434_1 - 014434_9, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0Bao, S.*; Gu, Z.-L.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, B.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Wang, W.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.6093_1 - 6093_9, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:61.99(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Jiang, X.*; Hattori, Takanori; Xu, X.*; Li, M.*; Yu, C.*; Yu, D.*; Mole, R.*; Yano, Shinichiro*; Chen, J.*; He, L.*; et al.
Materials Horizons, 10(3), p.977 - 982, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:87.86(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)As a promising environment-friendly alternative to current vapor-compression refrigeration, solid-state refrigeration based on the barocaloric effect has been attracting world wide attention. Generally, both phases in which a barocaloric effect occurs are present at ambient pressure. Here, instead, we demonstrate that KPF exhibits a colossal barocaloric effect due to the creation of a high-pressure rhombohedral phase. The phase diagram is constructed based on pressure-dependent calorimetric, Raman scattering, and neutron diffraction measurements. The present study is expected to provide an alternative routine to colossal barocaloric effects through the creation of a high-pressure phase.
exhibits a colossal barocaloric effect due to the creation of a high-pressure rhombohedral phase. The phase diagram is constructed based on pressure-dependent calorimetric, Raman scattering, and neutron diffraction measurements. The present study is expected to provide an alternative routine to colossal barocaloric effects through the creation of a high-pressure phase.
Chen, J.*; Yamamoto, Kei; Zhang, J.*; Ma, J.*; Wang, H.*; Sun, Y.*; Chen, M.*; Ma, J.*; Liu, S.*; Gao, P.*; et al.
Physical Review Applied (Internet), 19(2), p.024046_1 - 024046_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:90.23(Physics, Applied)Haoran, W.*; Yu, H.*; Liu, J.*; Kondo, Sosuke*; Okubo, Nariaki; Kasada, Ryuta*
Corrosion Science, 209, p.110818_1 - 110818_12, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:45.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The corrosion behavior of newly developed Al O
O forming high Mn oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) austenitic steels was examined in oxygen-saturated lead-bismuth eutectic at 450
forming high Mn oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) austenitic steels was examined in oxygen-saturated lead-bismuth eutectic at 450 C for 430 h. Compared with non-ODS steels, the ODS steels possessed superior resistance to corrosion and spallation. The high density grain boundaries in the ODS steels acted as channels for the rapid outward diffusion of metallic elements, forming an internal continuous Cr
C for 430 h. Compared with non-ODS steels, the ODS steels possessed superior resistance to corrosion and spallation. The high density grain boundaries in the ODS steels acted as channels for the rapid outward diffusion of metallic elements, forming an internal continuous Cr O
O scale at the original surface. Accelerated Al diffusion, along with oxidation prevention by the external (Fe, Mn) oxide scale and the internal Cr
scale at the original surface. Accelerated Al diffusion, along with oxidation prevention by the external (Fe, Mn) oxide scale and the internal Cr O
O scale, jointly resulted in the formation of a continuous Al-rich oxide scale in ODS-7Al steel, contributing to its superior corrosion resistance.
scale, jointly resulted in the formation of a continuous Al-rich oxide scale in ODS-7Al steel, contributing to its superior corrosion resistance.
 BaCo(PO
BaCo(PO )
)
Sheng, J.*; Wang, L.*; Candini, A.*; Jiang, W.*; Huang, L.*; Xi, B.*; Zhao, J.*; Ge, H.*; Zhao, N.*; Fu, Y.*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 119(51), p.e2211193119_1 - e2211193119_9, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Boznar, M. Z.*; Charnock, T. W.*; Chouhan, S. L.*; Grsic, Z.*; Halsall, C.*; Heinrich, G.*; Helebrant, J.*; Hettrich, S.*; Ku a, P.*; Mancini, F.*; et al.
a, P.*; Mancini, F.*; et al.
IAEA-TECDOC-2001, 226 Pages, 2022/06
The IAEA organized a programme from 2012 to 2015 entitled Modelling and Data for Radiological Impact Assessments (MODARIA), which aimed to improve capabilities in the field of environmental radiation dose assessment by acquiring improved data, model testing and comparison of model inputs, assumptions and outputs, reaching a consensus on modelling philosophies, aligning approaches and parameter values, developing improved methods and exchanging information. This publication describes the activities of Working Group 2, Exposures in Contaminated Urban Environments and Effect of Remedial Measures.
Thiessen, K. M.*; Boznar, M. Z.*; Charnock, T. W.*; Chouhan, S. L.*; Federspiel, L.; Gra i
i , B.*; Grsic, Z.*; Helebrant, J.*; Hettrich, S.*; Hulka, J.*; et al.
, B.*; Grsic, Z.*; Helebrant, J.*; Hettrich, S.*; Hulka, J.*; et al.
Journal of Radiological Protection, 42(2), p.020502_1 - 020502_8, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:78.52(Environmental Sciences)Takahara, Shogo; Charnock, T. W.*; Silva, K.*; Hwang, W. T.*; Lee, J.*; Yu, C.*; Kamboj, S.*; Yankovich, T.*; Thiessen, K. M.*
Journal of Radiological Protection, 42(2), p.020517_1 - 020517_13, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)State-of-the-art dose assessment models were applied to estimate doses to the population in urban areas contaminated by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Assessment results were compared among five models, and comparisons of model predictions with actual measurements were also made. Assessments were performed using both probabilistic and deterministic approaches. Predicted dose distributions in indoor and outdoor workers from a probabilistic approach were in good agreement with the actual measurements. In addition, when the models were applied to assess the doses to a representative person, based on a concept suggested by the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP), it was evident that doses to the representative person obtained with a deterministic approach were always higher than those obtained with a probabilistic approach.
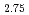 GeTe
GeTe
Bao, S.*; Wang, W.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Cai, Z.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Si, W.*; Ma, Z.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Physical Review X, 12(1), p.011022_1 - 011022_15, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:78.27(Physics, Multidisciplinary) /La
/La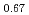 Sr
Sr MnO
MnO heterostructures
heterostructuresZhang, J.*; Chen, M.*; Chen, J.*; Yamamoto, Kei; Wang, H.*; Hamdi, M.*; Sun, Y.*; Wagner, K.*; He, W.*; Zhang, Y.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 12, p.7258_1 - 7258_8, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:77.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences) Cu
Cu TeO
TeO
Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Cai, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Huang, Z.*; Ma, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; et al.
Physical Review B, 104(22), p.224430_1 - 224430_8, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yamamoto, Kei; Yu, W.*; Yu, T.*; Puebla, J.*; Xu, M.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; Bauer, G.*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 89(11), p.113702_1 - 113702_5, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:62.22(Physics, Multidisciplinary) TeO
TeO
Bao, S.*; Cai, Z.*; Si, W.*; Wang, W.*; Wang, X.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Ma, Z.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Physical Review B, 101(21), p.214419_1 - 214419_8, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:74.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Mn
Mn Sb
Sb
Cai, Z.*; Bao, S.*; Wang, W.*; Ma, Z.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Wang, J.*; Ran, K.*; Li, S.*; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; et al.
Physical Review B, 101(13), p.134408_1 - 134408_10, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:38.95(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dirac matters provide a platform for exploring the interplay of their carriers with other quantum phenomena. Sr Mn
Mn Sb
Sb has been proposed to be a magnetic Weyl semimetal and provides an excellent platform to study the coupling between Weyl fermions and magnons. We performed inelastic neutron scattering measurements on single crystals of Sr
has been proposed to be a magnetic Weyl semimetal and provides an excellent platform to study the coupling between Weyl fermions and magnons. We performed inelastic neutron scattering measurements on single crystals of Sr Mn
Mn Sb
Sb , and found The dispersion in the magnetic Mn layer extends up to about 76 meV, while that between the layers has a narrow band width of 6 meV. Despite the coexistence of Weyl fermions and magnons, we find no clear evidence that the magnetic dynamics are influenced by the Weyl fermions in Sr
, and found The dispersion in the magnetic Mn layer extends up to about 76 meV, while that between the layers has a narrow band width of 6 meV. Despite the coexistence of Weyl fermions and magnons, we find no clear evidence that the magnetic dynamics are influenced by the Weyl fermions in Sr Mn
Mn Sb
Sb , possibly because that the Weyl fermions and magnons reside in the Sb and Mn layers separately, and the interlayer coupling is weak due to the quasi-two-dimensional nature of the material.
, possibly because that the Weyl fermions and magnons reside in the Sb and Mn layers separately, and the interlayer coupling is weak due to the quasi-two-dimensional nature of the material.
 He
He
 excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron-
excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron- He absorption reaction
He absorption reactionSonnenschein, V.*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; Kokuryu, Shoma*; Kubo, Wataru*; Suzuki, So*; Tomita, Hideki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Matsushita, Taku*; Wada, Nobuo*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 91(3), p.033318_1 - 033318_12, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Instruments & Instrumentation) decay of
decay of 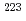 U
USun, M. D.*; Liu, Z.*; Huang, T. H.*; Zhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Ding, B.*; Wang, J. G.*; Liu, X. Y.*; Lu, H. Y.*; Hou, D. S.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 800, p.135096_1 - 135096_5, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:79.42(Astronomy & Astrophysics) He
He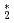 clusters via neutron-
clusters via neutron- He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulence
He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulenceMatsushita, Taku*; Sonnenschein, V.*; Guo, W.*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hirota, Katsuya*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Ito, Daisuke*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 196(1-2), p.275 - 282, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.76(Physics, Applied)Li, B.*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Kawamura, Seiko; Sugahara, Takeshi*; Wang, H.*; Wang, J.*; Chen, Y.*; Kawaguchi, Saori*; Kawaguchi, Shogo*; Ohara, Koji*; et al.
Nature, 567(7749), p.506 - 510, 2019/03
Times Cited Count:182 Percentile:99.31(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Refrigeration is of vital importance for modern society for example, for food storage and air conditioning- and 25 to 30% of the world's electricity is consumed for refrigeration. Current refrigeration technology mostly involves the conventional vapour compression cycle, but the materials used in this technology are of growing environmental concern because of their large global warming potential. As a promising alternative, refrigeration technologies based on solid-state caloric effects have been attracting attention in recent decades. However, their application is restricted by the limited performance of current caloric materials, owing to small isothermal entropy changes and large driving magnetic fields. Here we report colossal barocaloric effects (CBCEs) (barocaloric effects are cooling effects of pressure-induced phase transitions) in a class of disordered solids called plastic crystals. The obtained entropy changes in a representative plastic crystal, neopentylglycol, are about 389 joules per kilogram per kelvin near room temperature. Pressure-dependent neutron scattering measurements reveal that CBCEs in plastic crystals can be attributed to the combination of extensive molecular orientational disorder, giant compressibility and highly anharmonic lattice dynamics of these materials. Our study establishes the microscopic mechanism of CBCEs in plastic crystals and paves the way to next-generation solid-state refrigeration technologies.