Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Xu, L.*; Yue, Z.*; Wang, M.*; Zhai, M.*; Yoshii, Fumio; Seko, Noriaki; Peng, J.*; Wei, G.*; Li, J.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 265(1), p.394 - 398, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:40.96(Instruments & Instrumentation)A water insoluble cellulose derivative, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose phthalate (HPMCP) hydrogels, was converted to Na type to form hydrogel in paste-like status by radiation crosslinking. Mechanism for radiation crosslinking of cellulose-derivatives in paste-like status was discussed. Crosslinkers, i.e., methyl 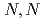 -bis-acrylamide (MBA) or ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) has been used to decrease gelation dose (Dg) of synthesis HPMCP hydrogels and improve its mechanical properties. MBA was found to be more effective for accelerating the crosslinking of HPMCP than EGDMA. Swelling degree of HPMCP hydrogel in many kinds ofsalt solutions followed Hofmeister series, which is ubiquitous in polyelectrolyte hydrogel. Specific reswelling was observed in concentrated KF solution, implying a very strong F
-bis-acrylamide (MBA) or ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) has been used to decrease gelation dose (Dg) of synthesis HPMCP hydrogels and improve its mechanical properties. MBA was found to be more effective for accelerating the crosslinking of HPMCP than EGDMA. Swelling degree of HPMCP hydrogel in many kinds ofsalt solutions followed Hofmeister series, which is ubiquitous in polyelectrolyte hydrogel. Specific reswelling was observed in concentrated KF solution, implying a very strong F binding ability of benzyl group. The comprehensive results obtained in this study will be utilized on the design of HPMCP-based controlled release system.
binding ability of benzyl group. The comprehensive results obtained in this study will be utilized on the design of HPMCP-based controlled release system.