Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Petoussi-Henss, N.*; Satoh, Daiki; Schlattl, H.*; Zankl, M.*; Spielman, V.*
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 60(1), p.93 - 113, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.37(Biology)In this study, the nuclide-specific organ dose coefficients of pregnant female and its fetus for environmental external exposures have been evaluated. The radiation sources were uniformly put in the soil at the depth of 0.5 g cm or in the atmosphere. The environmental radiation fields for the soil contamination were analyzed by using the radiation transport code PHITS, and the fields for the air submersion were taken from the existing data analyzed by the YURI code. The numerical models of the pregnant female and its fetus were put in the environmental radiation fields, and the radiation transport simulations were performed using the EGS code to obtain the organ absorbed doses. From the simulation results, it was found that the radionuclide-specific uterus doses of the pregnant female agreed with the total body doses of the fetus within 6%, except for some radionuclides which emit the low-energy photons below 50 keV. Using the organ dose coefficients evaluated in the present study, the doses of the pregnant female and its fetus can be estimated easily from the data of activity concentration of the radionuclides distributed in the environment.
or in the atmosphere. The environmental radiation fields for the soil contamination were analyzed by using the radiation transport code PHITS, and the fields for the air submersion were taken from the existing data analyzed by the YURI code. The numerical models of the pregnant female and its fetus were put in the environmental radiation fields, and the radiation transport simulations were performed using the EGS code to obtain the organ absorbed doses. From the simulation results, it was found that the radionuclide-specific uterus doses of the pregnant female agreed with the total body doses of the fetus within 6%, except for some radionuclides which emit the low-energy photons below 50 keV. Using the organ dose coefficients evaluated in the present study, the doses of the pregnant female and its fetus can be estimated easily from the data of activity concentration of the radionuclides distributed in the environment.
Endo, Akira; Petoussi-Henss, N.*; Zankl, M.*; Bolch, W. E.*; Eckerman, K. F.*; Hertel, N. E.*; Hunt, J. G.*; Pelliccioni, M.*; Schlattl, H.*; Menzel, H.-G.*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 161(1-4), p.11 - 16, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:28.36(Environmental Sciences)In 2007, the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) revised its fundamental recommendations on radiation protection in ICRP Publication 103 (ICRP103). The recommendations updated the radiation and tissue weighting factors in the radiological protection quantities, equivalent and effective doses, and adopted reference computational phantoms for the calculation of organ doses. These revisions required calculations of conversion coefficients for the protection quantities. The sets of conversion coefficients for external exposures were compiled by the Task Group DOCAL of ICRP, and published in ICRP116. The presentation reviews the conversion coefficients for external radiations calculated using the reference computational phantoms. The conversion coefficients are compared with the existing values given in ICRP74. Contributing factors for any differences between these sets of conversion coefficients as well as the impact for radiation monitoring practice are discussed.
Petoussi-Henss, N.*; Bolch, W. E.*; Eckerman, K. F.*; Endo, Akira; Hertel, N.*; Hunt, J.*; Menzel, H. G.*; Pelliccioni, M.*; Schlattl, H.*; Zankl, M.*
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 59(18), p.5209 - 5224, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:58.08(Engineering, Biomedical)ICRP Publication 116 (ICRP116) on "Conversion Coefficients for Radiological Protection Quantities for External Radiation Exposures", provides fluence-to-dose conversion coefficients for organ absorbed doses and effective dose for external exposures. ICRP116 supersedes the ICRP74, expanding also the particle types and energy ranges considered. The coefficients were calculated using the ICRP/ICRU computational phantoms representing the Reference Adult Male and Reference Adult Female, together with Monte Carlo codes simulating the radiation transport in the body. Idealised whole-body irradiation from unidirectional and rotational parallel beams as well as isotropic irradiation was considered. Comparison of the effective doses with operational quantities revealed that the latter quantities continue to provide a good approximation of effective dose for photons, neutrons and electrons for the conventional energy ranges considered previously, but not at the higher energies of ICRP116.
Kinase, Sakae; Mohammadi, A.; Takahashi, Masa; Saito, Kimiaki; Zankl, M.*; Kramer, R.*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 146(1-3), p.191 - 194, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.12(Environmental Sciences)Sato, Tatsuhiko; Endo, Akira; Zankl, M.*; Petoussi-Henss, N.*; Yasuda, Hiroshi*; Niita, Koji*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 1, p.134 - 137, 2011/02
We calculated the dose conversion coefficients for the 2 irradiation geometries; one is for the semi-isotropic irradiation from the upper hemisphere, and the other is for exactly representing the geometrical condition of aircrew exposure, whose angular distribution was estimated from the atmospheric propagation simulation of cosmic-rays performed by PHITS.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Endo, Akira; Zankl, M.*; Petoussi-Henss, N.*; Niita, Koji*
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 54(7), p.1997 - 2014, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:72 Percentile:87.03(Engineering, Biomedical)The fluence to organ-dose and effective-dose conversion coefficients for neutrons and protons with energies up to 100 GeV were calculated using the PHITS code coupled to the male and female adult reference computational phantoms, which are to be released as a common ICRP/ICRU publication. For the calculation, the radiation and tissue weighting factors, wR and wT, as revised in ICRP Publication 103 were employed. The calculated data of these dose conversion coefficients are indispensable for constructing the radiation protection systems based on the new recommendations given in ICRP103 for aircrews and astronauts, as well as for workers in accelerators and nuclear facilities.
G mez-Ros, J.-M.*; de Carlan, L.*; Franck, D.*; Gualdrini, G.*; Lis, M.*; L
mez-Ros, J.-M.*; de Carlan, L.*; Franck, D.*; Gualdrini, G.*; Lis, M.*; L pez, M. A.*; Moraleda, M.*; Zankl, M.*; Badal, A.*; Capello, K.*; et al.
pez, M. A.*; Moraleda, M.*; Zankl, M.*; Badal, A.*; Capello, K.*; et al.
Radiation Measurements, 43(2-6), p.510 - 515, 2008/02
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:81.22(Nuclear Science & Technology)This communication summarizes the results concerning the Monte Carlo modeling of Germanium detectors for the measurement of low energy photons arising from the "International comparison on MC modeling for in vivo measurement of Americium in a knee phantom" organized within the EU Coordination Action CONRAD (Coordinated Network for Radiation Dosimetry) as a joint initiative of EURADOS working groups 6 (computational dosimetry) and 7 (internal dosimetry).
Kinase, Sakae; Zankl, M.*; Funabiki, Jun*; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Saito, Kimiaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.136 - 139, 2004/03
The present study was performed to evaluate S values to the urinary bladder wall for several beta-ray emitters such as  C,
C,  Na,
Na,  P,
P,  Co,
Co, 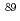 Sr,
Sr,  Sr,
Sr,  Y,
Y, 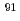 Y,
Y,  Cs,
Cs, 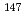 Pm and
Pm and  Tl for a MIRD 5 type phantom using Monte Carlo simulation. S values were also evaluated on the adult voxel phantoms developed at JAERI and were compared with those for the MIRD 5 type phantom. Furthermore, each of the S values was compared with those derived from the simple assumption (ICRP 30). Consequently, it was found that the absorbed dose to the urinary bladder wall for those radionuclides are not one-half of the absorbed dose in bladder content and largely depend on the mass of the urinary bladder wall. S values derived from the simple assumption were found to be conservative for beta-ray emitters within the urinary bladder.
Tl for a MIRD 5 type phantom using Monte Carlo simulation. S values were also evaluated on the adult voxel phantoms developed at JAERI and were compared with those for the MIRD 5 type phantom. Furthermore, each of the S values was compared with those derived from the simple assumption (ICRP 30). Consequently, it was found that the absorbed dose to the urinary bladder wall for those radionuclides are not one-half of the absorbed dose in bladder content and largely depend on the mass of the urinary bladder wall. S values derived from the simple assumption were found to be conservative for beta-ray emitters within the urinary bladder.
Kinase, Sakae; Zankl, M.*; Funabiki, Jun*; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Saito, Kimiaki
KEK Proceedings 2003-15, p.45 - 52, 2004/02
no abstracts in English
Kinase, Sakae; Zankl, M.*; Kuwabara, Jun; Sato, Kaoru; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Funabiki, Jun*; Saito, Kimiaki
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 105(1-4), p.557 - 563, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:83.75(Environmental Sciences)There exists a need to calculate specific absorbed fractions (SAFs) in voxel phantoms for internal dosimetry. For this purpose, an EGS4 user code for calculating SAFs using voxel phantoms was developed on the basis of an existing EGS4 user code for external dosimetry (UCPIXEL). In the developed code, the transport of photons, electrons and positrons in voxel phantoms can be simulated, particularly the transport simulations of secondary electrons in voxel phantoms can be made. The evaluated SAFs for the GSF Child voxel phantom using the developed code were found to be in good agreement with the GSF evaluated data. In addition, SAFs in adult voxel phantoms developed at JAERI were evaluated using the developed code and were compared with several published data. It was found that SAFs for organ self-absorption depend on the organ masses and would be affected by differences in the structure of the human body.
Saito, Kimiaki; Wittmann, A.*; Koga, Sukehiko*; Ida, Yoshihiro*; Kamei, Tetsuya*; Funabiki, Jun*; Zankl, M.*
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 40(1), p.69 - 76, 2001/04
Times Cited Count:93 Percentile:89.95(Biology)no abstracts in English
Kinase, Sakae; Zankl, M.*; Kuwabara, Jun; Sato, Kaoru; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Funabiki, Jun*; Saito, Kimiaki
Radiation Risk Assessment Workshop Proceedings, p.118 - 127, 2001/00
There exists a need to calculate specific absorbed fractions (SAFs) in voxel phantoms for internal dosimetry. For the purpose, an EGS4 user code for calculating SAFs using voxel phantoms was developed on the basis of the EGS4 user code (UCPIXEL). In the developed code, the transport of photons, electrons and positrons in voxel phantoms can be simulated, particularly the transport simulations of secondary electrons in voxel phantoms can be made. The evaluated SAFs for the GSF "Child" voxel phantom using the developed code were found to be in good agreement with the GSF evaluated data. In addition, SAFs in voxel phantoms developed at JAERI were evaluated using the developed code and were compared with several published data. It was found that SAFs depend on the organ masses and would be affected by differences in the structure of the human body.
Saito, Kimiaki; N.Petoussi*; Zankl, M.*
Health Physics, 74(6), p.698 - 706, 1998/06
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:94.78(Environmental Sciences)no abstracts in English
Saito, Kimiaki; N.Petoussi*; Zankl, M.*; R.Veit*; P.Jacob*; G.Drexler*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 28(7), p.627 - 641, 1991/07
no abstracts in English
Saito, Kimiaki; N.Petoussi*; Zankl, M.*; R.Veit*; P.Jacob*; G.Drexler*
GSF-2-90, 119 Pages, 1990/01
no abstracts in English
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Endo, Akira; Petoussi-Henss, N.*; Zankl, M.*; Niita, Koji*
no journal, ,
The fluence to organ-dose and effective-dose conversion coefficients for neutrons and protons with energies up to 100 GeV was calculated using the PHITS code coupled to male and female adult reference computational phantoms.
Endo, Akira; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Petoussi-Henss, N.*; Zankl, M.*; Niita, Koji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Endo, Akira; Zankl, M.*; Petoussi-Henss, N.*; Niita, Koji*
no journal, ,
We calculated the conversion coefficients from fluence to organ dose equivalents for neutrons, protons and heavy ions up to Z=28 (Ni) and E=100 GeV/nucleon for the isotropic irradiation geometry, using the PHITS code and the ICRP/ICRU adult reference computational phantoms, developed under the supervision of ICRP Task Group on Dose Calculations (DOCAL).
Petoussi-Henss, N.*; Schlattl, H.*; Zankl, M.*; Becker, J.*; Saito, Kimiaki; Endo, Akira
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English