Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Brumm, S.*; Gabrielli, F.*; Sanchez Espinoza, V.*; Stakhanova, A.*; Groudev, P.*; Petrova, P.*; Vryashkova, P.*; Ou, P.*; Zhang, W.*; Malkhasyan, A.*; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 211, p.110962_1 - 110962_16, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:93.24(Nuclear Science & Technology)Liu, P.-F.*; Li, X.*; Li, J.*; Zhu, J.*; Tong, Z.*; Kofu, Maiko*; Nirei, Masami; Xu, J.*; Yin, W.*; Wang, F.*; et al.
National Science Review, 11(12), p.nwae216_1 - nwae216_10, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:91.22(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Fang, W.*; Liu, C.*; Zhang, J.*; Xu, P. G.; Peng, T.*; Liu, B.*; Morooka, Satoshi; Yin, F.*
Scripta Materialia, 249, p.116046_1 - 116046_6, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:63.37(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Zhang, Z.*; Hattori, Takanori; Song, R.*; Yu, D.*; Mole, R.*; Chen, J.*; He, L.*; Zhang, Z.*; Li, B.*
Journal of Applied Physics, 136(3), p.035105_1 - 035105_8, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:40.97(Physics, Applied)Solid-state refrigeration using barocaloric materials is environmentally friendly and highly efficient, making it a subject of global interest over the past decade. Here, we report giant barocaloric effects in sodium hexafluorophosphate (NaPF ) and sodium hexafluoroarsenate (NaAsF
) and sodium hexafluoroarsenate (NaAsF ) that both undergo a cubic-to-rhombohedral phase transition near room temperature. We have determined that the low-temperature phase structure of NaPF
) that both undergo a cubic-to-rhombohedral phase transition near room temperature. We have determined that the low-temperature phase structure of NaPF is a rhombohedral structure with space group R
is a rhombohedral structure with space group R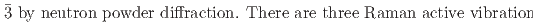 and NaAsF
and NaAsF , i.e., F
, i.e., F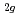 , E
, E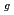 , and A
, and A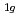 . The phase transition temperature varies with pressure at a rate of dT
. The phase transition temperature varies with pressure at a rate of dT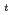 /dP = 250 and 310 K/GPa for NaPF
/dP = 250 and 310 K/GPa for NaPF and NaAsF
and NaAsF . The pressure-induced entropy changes of NaPF
. The pressure-induced entropy changes of NaPF and NaAsF
and NaAsF are determined to be around 45.2 and 35.6J kg
are determined to be around 45.2 and 35.6J kg K
K , respectively. The saturation driving pressure is about 40 MPa. The pressure-dependent neutron powder diffraction suggests that the barocaloric effects are related to the pressure-induced cubic-to-rhombohedral phase transitions.
, respectively. The saturation driving pressure is about 40 MPa. The pressure-dependent neutron powder diffraction suggests that the barocaloric effects are related to the pressure-induced cubic-to-rhombohedral phase transitions.

Liao, J.*; Huang, Z.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Zhang, B.*; Cheng, S.*; Xu, H.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Bao, S.*; Wen, J.*
Physical Review B, 109(22), p.224411_1 - 224411_10, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Baccou, J.*; Glantz, T.*; Ghione, A.*; Sargentini, L.*; Fillion, P.*; Damblin, G.*; Sueur, R.*; Iooss, B.*; Fang, J.*; Liu, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 421, p.113035_1 - 113035_16, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:97.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)Guo, B.*; Chen, H.*; Chong, Y.*; Mao, W.; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Zhang, Z.*; Jonas, J. J.*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 268, p.119780_1 - 119780_11, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:92.77(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Li, X.*; Zhu, R.*; Xin, J.*; Luo, M.*; Shang, S.-L.*; Liu, Z.-K.*; Yin, C.*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Dippenaar, R. J.*; Higo, Yuji*; et al.
CALPHAD; Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry, 84, p.102641_1 - 102641_6, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Thermodynamics) -Ti alloy
-Ti alloyZhang, B.*; Xin, S.*; Huang, M.*; Mao, W.; Jia, W.*; Li, Q.*; Li, S.*; Zhang, S.*; Mao, C.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 890, p.145898_1 - 145898_7, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)A significant increase in the recovery strain of a high-Zr  -Ti alloy from 2.25 % to 5.5 % when decreasing the deformation temperature from 300 K to 77 K is reported in this study. It is found that the super-elasticity of this alloy is independent of the
-Ti alloy from 2.25 % to 5.5 % when decreasing the deformation temperature from 300 K to 77 K is reported in this study. It is found that the super-elasticity of this alloy is independent of the  -grain size at 77 K. The results reveal that a coarse-grained specimen exhibited approximately the same super-elasticity as its ultra-fine grain counterpart at 77 K. The relative easiness of deformation-induced martensitic transformation and dislocation slip was substantially changed at 77 K, with a strong suppression of dislocation slip, which overshadowed the effect of grain refinement on the super-elasticity.
-grain size at 77 K. The results reveal that a coarse-grained specimen exhibited approximately the same super-elasticity as its ultra-fine grain counterpart at 77 K. The relative easiness of deformation-induced martensitic transformation and dislocation slip was substantially changed at 77 K, with a strong suppression of dislocation slip, which overshadowed the effect of grain refinement on the super-elasticity.
Lloveras, P.*; Zhang, Z.*; Zeng, M.*; Barrio, M.*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Yu, D.*; Lin, S.*; Li, K.*; Moya, X.*; Tamarit, J.-L.*; et al.
Barocaloric Effects in the Solid State; Materials and methods, p.7_1 - 7_30, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:232 Percentile:99.37(Multidisciplinary Sciences)As Chapter 1 of the ebook entitled as "Barocaloric Effects in the Solid State", various plastic crystals (PC) showing colossal barocaloric (BC) effect are introduced. A method to determine the BC response in PCs, thermodynamic origin of BC effects, spectroscopic insights from quasi-elastic neutron scattering and application of PCs are explained.
Bao, S.*; Gu, Z.-L.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, B.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Wang, W.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.6093_1 - 6093_9, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:92.93(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Xi, N.*; Gao, Y.-P.*; Ma, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Qi, Z.*; Zhang, S.*; Huang, Z.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(12), p.1883 - 1889, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:94.19(Physics, Multidisciplinary) neutron diffraction study on the deformation behavior of the plastic inorganic semiconductor Ag
neutron diffraction study on the deformation behavior of the plastic inorganic semiconductor Ag S
SWang, Y.*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; Zhang, K.*; Zhang, Z. D.*; Li, B.*
Applied Physics Letters, 123(1), p.011903_1 - 011903_6, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:50.15(Physics, Applied)Jiang, X.*; Hattori, Takanori; Xu, X.*; Li, M.*; Yu, C.*; Yu, D.*; Mole, R.*; Yano, Shinichiro*; Chen, J.*; He, L.*; et al.
Materials Horizons, 10(3), p.977 - 982, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:93.43(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)As a promising environment-friendly alternative to current vapor-compression refrigeration, solid-state refrigeration based on the barocaloric effect has been attracting world wide attention. Generally, both phases in which a barocaloric effect occurs are present at ambient pressure. Here, instead, we demonstrate that KPF exhibits a colossal barocaloric effect due to the creation of a high-pressure rhombohedral phase. The phase diagram is constructed based on pressure-dependent calorimetric, Raman scattering, and neutron diffraction measurements. The present study is expected to provide an alternative routine to colossal barocaloric effects through the creation of a high-pressure phase.
exhibits a colossal barocaloric effect due to the creation of a high-pressure rhombohedral phase. The phase diagram is constructed based on pressure-dependent calorimetric, Raman scattering, and neutron diffraction measurements. The present study is expected to provide an alternative routine to colossal barocaloric effects through the creation of a high-pressure phase.
 isomer in
isomer in  Hg and
Hg and  (
( 2) systematics of neutron transitions across the nuclear chart
2) systematics of neutron transitions across the nuclear chartHuang, H.*; Zhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Liu, Z.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Li, Z. H.*; Guo, C. Y.*; Barzakh, A. E.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Andel, B.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 833, p.137345_1 - 137345_8, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:18.16(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Liu, B.*; Feng, R.*; Busch, M.*; Wang, S.*; Wu, H.*; Liu, P.*; Gu, J.*; Bahadoran, A.*; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; et al.
ACS Nano, 16(9), p.14121 - 14133, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:97 Percentile:98.70(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Wang, Q.*; Hu, Q.*; Zhao, C.*; Yang, X.*; Zhang, T.*; Ilavsky, J.*; Kuzmenko, I.*; Ma, B.*; Tachi, Yukio
International Journal of Coal Geology, 261, p.104093_1 - 104093_15, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:71.33(Energy & Fuels) decay of the 8
decay of the 8 isomer in
isomer in  U
UZhang, M. M.*; Tian, Y. L.*; Wang, Y. S.*; Zhang, Z. Y.*; Gan, Z. G.*; Yang, H. B.*; Huang, M. H.*; Ma, L.*; Yang, C. L.*; Wang, J. G.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(2), p.024305_1 - 024305_6, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:61.57(Physics, Nuclear)Brumm, S.*; Gabrielli, F.*; Sanchez-Espinoza, V.*; Groudev, P.*; Ou, P.*; Zhang, W.*; Malkhasyan, A.*; Bocanegra, R.*; Herranz, L. E.*; Berda , M.*; et al.
, M.*; et al.
Proceedings of 10th European Review Meeting on Severe Accident Research (ERMSAR 2022) (Internet), 13 Pages, 2022/05
Gatera, A.*; Belmans, J.*; Boussa, S.*; Davin, F.*; De Cock, W.*; De Florio, V.*; Doucet, F.*; Parez, L.*; Pompon, F.*; Ponton, A.*; et al.
Proceedings of 64th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High Intensity and High Brightness Hadron Beams (HB2021), p.186 - 190, 2022/04