Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yang, X.*; Che, G.*; Wang, Y.*; Zhang, P.*; Tang, X.*; Lang, P.*; Gao, D.*; Wang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Nano Letters, 25(3), p.1028 - 1035, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:84.76(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Saturated sp -carbon nanothreads (CNTh) have garnered significant interest due to their predicted high Young's modulus and thermal conductivity. While the incorporation of heteroatoms into the central ring has been shown to influence the formation of CNTh and yield chemically homogeneous products, the impact of pendant groups on the polymerization process remains underexplored. In this study, we investigate the pressure-induced polymerization of phenol, revealing two phase transitions occurring below 0.5 and 4 GPa. Above 20 GPa, phenol polymerizes into degree-4 CNThs featuring hydroxyl and carbonyl groups. Hydrogen transfer of hydroxyl groups was found to hinder the formation of degree-6 nanothreads. Our findings highlight the crucial role of the hydroxyl group in halting further intracolumn polymerization and offer valuable insights for future mechanism research and nanomaterial synthesis.
-carbon nanothreads (CNTh) have garnered significant interest due to their predicted high Young's modulus and thermal conductivity. While the incorporation of heteroatoms into the central ring has been shown to influence the formation of CNTh and yield chemically homogeneous products, the impact of pendant groups on the polymerization process remains underexplored. In this study, we investigate the pressure-induced polymerization of phenol, revealing two phase transitions occurring below 0.5 and 4 GPa. Above 20 GPa, phenol polymerizes into degree-4 CNThs featuring hydroxyl and carbonyl groups. Hydrogen transfer of hydroxyl groups was found to hinder the formation of degree-6 nanothreads. Our findings highlight the crucial role of the hydroxyl group in halting further intracolumn polymerization and offer valuable insights for future mechanism research and nanomaterial synthesis.
Liu, P.-F.*; Li, X.*; Li, J.*; Zhu, J.*; Tong, Z.*; Kofu, Maiko*; Nirei, Masami; Xu, J.*; Yin, W.*; Wang, F.*; et al.
National Science Review, 11(12), p.nwae216_1 - nwae216_10, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:94.32(Multidisciplinary Sciences) = 82 shell closure
= 82 shell closureZhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; 10 of others*
Physical Review C, 110(4), p.044301_1 - 044301_7, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)Ying, H.*; Yang, X.*; He, H.*; Yan, A.*; An, K.*; Ke, Y.*; Wu, Z.*; Tang, S.*; Zhang, Z.*; Dong, H.*; et al.
Scripta Materialia, 250, p.116181_1 - 116181_7, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:36.18(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology) -Ti alloy
-Ti alloyZhang, B.*; Xin, S.*; Huang, M.*; Mao, W.; Jia, W.*; Li, Q.*; Li, S.*; Zhang, S.*; Mao, C.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 890, p.145898_1 - 145898_7, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)A significant increase in the recovery strain of a high-Zr  -Ti alloy from 2.25 % to 5.5 % when decreasing the deformation temperature from 300 K to 77 K is reported in this study. It is found that the super-elasticity of this alloy is independent of the
-Ti alloy from 2.25 % to 5.5 % when decreasing the deformation temperature from 300 K to 77 K is reported in this study. It is found that the super-elasticity of this alloy is independent of the  -grain size at 77 K. The results reveal that a coarse-grained specimen exhibited approximately the same super-elasticity as its ultra-fine grain counterpart at 77 K. The relative easiness of deformation-induced martensitic transformation and dislocation slip was substantially changed at 77 K, with a strong suppression of dislocation slip, which overshadowed the effect of grain refinement on the super-elasticity.
-grain size at 77 K. The results reveal that a coarse-grained specimen exhibited approximately the same super-elasticity as its ultra-fine grain counterpart at 77 K. The relative easiness of deformation-induced martensitic transformation and dislocation slip was substantially changed at 77 K, with a strong suppression of dislocation slip, which overshadowed the effect of grain refinement on the super-elasticity.
Zhang, A.*; Deng, K.*; Sheng, J.*; Liu, P.*; Kumar, S.*; Shimada, Kenya*; Jiang, Z.*; Liu, Z.*; Shen, D.*; Li, J.*; et al.
Chinese Physics Letters, 40(12), p.126101_1 - 126101_8, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:85.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Hu, Q.*; Wang, Q. M.*; Zhang, T.*; Zhao, C.*; Iltaf, K. H.*; Liu, S. Q.*; Fukatsu, Yuta
Energy Reports (Internet), 9, p.3661 - 3682, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:64.37(Energy & Fuels)Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Xi, N.*; Gao, Y.-P.*; Ma, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Qi, Z.*; Zhang, S.*; Huang, Z.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(12), p.1883 - 1889, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:93.50(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Ao, N.*; Zhang, H.*; Xu, H. H.*; Wu, S. C.*; Liu, D.*; Xu, P. G.; Su, Y. H.; Kang, Q. H.*; Kang, G. Z.*
Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 281, p.109166_1 - 109166_14, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:82.23(Mechanics) isomer in
isomer in 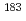 Hg and
Hg and  (
( 2) systematics of neutron transitions across the nuclear chart
2) systematics of neutron transitions across the nuclear chartHuang, H.*; Zhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Liu, Z.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Li, Z. H.*; Guo, C. Y.*; Barzakh, A. E.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Andel, B.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 833, p.137345_1 - 137345_8, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:17.31(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Liu, B.*; Feng, R.*; Busch, M.*; Wang, S.*; Wu, H.*; Liu, P.*; Gu, J.*; Bahadoran, A.*; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; et al.
ACS Nano, 16(9), p.14121 - 14133, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:102 Percentile:98.72(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Wang, Q.*; Hu, Q.*; Zhao, C.*; Yang, X.*; Zhang, T.*; Ilavsky, J.*; Kuzmenko, I.*; Ma, B.*; Tachi, Yukio
International Journal of Coal Geology, 261, p.104093_1 - 104093_15, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:69.82(Energy & Fuels) Bi and
Bi and  Po
PoZhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Liu, Z.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Huang, H.*; 37 of others*
Physical Review C, 106(2), p.024317_1 - 024317_11, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:52.14(Physics, Nuclear)Walter, H.*; Colonna, M.*; Cozma, D.*; Danielewicz, P.*; Ko, C. M.*; Kumar, R.*; Ono, Akira*; Tsang, M. Y. B*; Xu, J.*; Zhang, Y.-X.*; et al.
Progress in Particle and Nuclear Physics, 125, p.103962_1 - 103962_90, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:90 Percentile:95.20(Physics, Nuclear)Transport models are the main method to obtain physics information on the nuclear equation of state and in-medium properties of particles from low to relativistic-energy heavy-ion collisions. The Transport Model Evaluation Project (TMEP) has been pursued to test the robustness of transport model predictions to reach consistent conclusions from the same type of physical model. To this end, calculations under controlled conditions of physical input and set-up were performed by the various participating codes. These included both calculations of nuclear matter in a periodic box, which test individual ingredients of a transport code, and calculations of complete collisions of heavy ions. Over the years, five studies were performed within this project. They show, on one hand, that in box calculations the differences between the codes can be well understood and a convergence of the results can be reached. These studies also highlight the systematic differences between the two families of transport codes, known under the names of Boltzmann-Uehling-Uhlenbeck (BUU) and Quantum Molecular Dynamics (QMD) type codes. On the other hand, there still exist substantial differences when these codes are applied to real heavy-ion collisions. The results of transport simulations of heavy-ion collisions will have more significance if codes demonstrate that they can verify benchmark calculations such as the ones studied in these evaluations.
 Pb
PbZhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Liu, Z.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Huang, H.*; Li, Z. H.*; Li, J. G.*; Guo, C. Y.*; 34 of others*
Physics Letters B, 829, p.137129_1 - 137129_7, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:65.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Zhang, W. Q.*; Yamaguchi, Toshio*; Fang, C. H.*; Yoshida, Koji*; Zhou, Y. Q.*; Zhu, F. Y.*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Li, W.*
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 348, p.118080_1 - 118080_11, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.49(Chemistry, Physical)The ion hydration and association and hydrogen-bonded water structure in an aqueous 3 mol/kg RbCl solution were investigated at 298 K/0.1 MPa, 298 K/1 GPa, 523 K/1 GPa, and 523 K/4 GPa by neutron diffraction combined with EPSR methods. The second hydration layer of Rb and Cl
and Cl becomes evident under elevated pressure and temperature conditions. The average oxygen coordination number of Rb
becomes evident under elevated pressure and temperature conditions. The average oxygen coordination number of Rb (Cl
(Cl ) in the first hydration layer increases from 6.3 (5.9) ambient pressure to 8.9 (9.1) at 4 GPa, while decreasing coordination distance from 0.290 nm (0.322 nm) to 0.288 nm (0.314 nm). The orientation of the water dipole in the first solvation shell of Rb
) in the first hydration layer increases from 6.3 (5.9) ambient pressure to 8.9 (9.1) at 4 GPa, while decreasing coordination distance from 0.290 nm (0.322 nm) to 0.288 nm (0.314 nm). The orientation of the water dipole in the first solvation shell of Rb and a central water molecule is sensitive to pressure, but that in the first solvation shell of Cl
and a central water molecule is sensitive to pressure, but that in the first solvation shell of Cl does not change very much. The number of contact-ion pairs Rb
does not change very much. The number of contact-ion pairs Rb -Cl
-Cl decreases with elevated temperature and increases with elevated pressure. Water molecules are closely packed, and the tetrahedral hydrogen-bonded network of water molecules no longer exists in extreme conditions.
decreases with elevated temperature and increases with elevated pressure. Water molecules are closely packed, and the tetrahedral hydrogen-bonded network of water molecules no longer exists in extreme conditions.

Hao, Y. Q.*; Wo, H. L.*; Gu, Y. M.*; Zhang, X. W.*; Gu, Y. Q.*; Zheng, S. Y.*; Zhao, Y.*; Xu, G. Y.*; Lynn, J. W.*; Nakajima, Kenji; et al.
Science China; Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 64(3), p.237411_1 - 237411_6, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:69.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Wang, Y.*; Jia, G.*; Cui, X.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, Q.*; Gu, L.*; Zheng, L.*; Li, L. H.*; Wu, Q.*; Singh, D. J.*; et al.
Chem, 7(2), p.436 - 449, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:297 Percentile:99.75(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) decay of
decay of 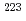 U
USun, M. D.*; Liu, Z.*; Huang, T. H.*; Zhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Ding, B.*; Wang, J. G.*; Liu, X. Y.*; Lu, H. Y.*; Hou, D. S.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 800, p.135096_1 - 135096_5, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:75.82(Astronomy & Astrophysics) resonances in a box
resonances in a boxOno, Akira*; Xu, J.*; Colonna, M.*; Danielewicz, P.*; Ko, C. M.*; Tsang, M. B.*; Wang, Y,-J.*; Wolter, H.*; Zhang, Y.-X.*; Chen, L.-W.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 100(4), p.044617_1 - 044617_35, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:75 Percentile:98.53(Physics, Nuclear)International comparison of heavy-ion induced reaction models were discussed in the international conference "Transport2017" held in April 2017. Owing to their importance for safety assessment of heavy-ion accelerators and dosimetry of astronauts, various models to simulate heavy-ion induced reaction models are developed. This study is intended to clarify the difference among them to pinpoint their problems. In the comparison study, 320 protons and neutrons were packed in a 20-fm-large cube to calculate the number and energies of collisions during the time evolution. The author contributed to this study by running calculation using JQMD (JAERI Quantum Molecular Dynamics). This study showed that time step in the calculation is one of the biggest causes of the discrepancies. For example, the calculation by JQMD comprises 1-fm/c time steps, each of which is composed of transport, scattering and decay phases. Therefore a sequence of scattering, and decay followed by another scattering in 1 fm/c cannot be considered. Moreover, in JQMD particles are labeled by sequential numbers and scattering reactions are simulated by the order. Therefore scattering between low ID numbers, that between high ID numbers and that between the first (low ID) pair is overlooked in JQMD. Above indications obtained in this study must be kept in our mind for future JQMD upgrades.