Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Liu, P.-F.*; Li, X.*; Li, J.*; Zhu, J.*; Tong, Z.*; Kofu, Maiko*; Nirei, Masami; Xu, J.*; Yin, W.*; Wang, F.*; et al.
National Science Review, 11(12), p.nwae216_1 - nwae216_10, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:94.32(Multidisciplinary Sciences) = 82 shell closure
= 82 shell closureZhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; 10 of others*
Physical Review C, 110(4), p.044301_1 - 044301_7, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear) -Ti alloy
-Ti alloyZhang, B.*; Xin, S.*; Huang, M.*; Mao, W.; Jia, W.*; Li, Q.*; Li, S.*; Zhang, S.*; Mao, C.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 890, p.145898_1 - 145898_7, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)A significant increase in the recovery strain of a high-Zr  -Ti alloy from 2.25 % to 5.5 % when decreasing the deformation temperature from 300 K to 77 K is reported in this study. It is found that the super-elasticity of this alloy is independent of the
-Ti alloy from 2.25 % to 5.5 % when decreasing the deformation temperature from 300 K to 77 K is reported in this study. It is found that the super-elasticity of this alloy is independent of the  -grain size at 77 K. The results reveal that a coarse-grained specimen exhibited approximately the same super-elasticity as its ultra-fine grain counterpart at 77 K. The relative easiness of deformation-induced martensitic transformation and dislocation slip was substantially changed at 77 K, with a strong suppression of dislocation slip, which overshadowed the effect of grain refinement on the super-elasticity.
-grain size at 77 K. The results reveal that a coarse-grained specimen exhibited approximately the same super-elasticity as its ultra-fine grain counterpart at 77 K. The relative easiness of deformation-induced martensitic transformation and dislocation slip was substantially changed at 77 K, with a strong suppression of dislocation slip, which overshadowed the effect of grain refinement on the super-elasticity.
Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Xi, N.*; Gao, Y.-P.*; Ma, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Qi, Z.*; Zhang, S.*; Huang, Z.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(12), p.1883 - 1889, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:93.50(Physics, Multidisciplinary) isomer in
isomer in 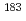 Hg and
Hg and  (
(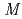 2) systematics of neutron transitions across the nuclear chart
2) systematics of neutron transitions across the nuclear chartHuang, H.*; Zhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Liu, Z.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Li, Z. H.*; Guo, C. Y.*; Barzakh, A. E.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Andel, B.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 833, p.137345_1 - 137345_8, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:17.31(Astronomy & Astrophysics) Bi and
Bi and  Po
PoZhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Liu, Z.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Huang, H.*; 37 of others*
Physical Review C, 106(2), p.024317_1 - 024317_11, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:52.14(Physics, Nuclear) Pb
PbZhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Liu, Z.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Huang, H.*; Li, Z. H.*; Li, J. G.*; Guo, C. Y.*; 34 of others*
Physics Letters B, 829, p.137129_1 - 137129_7, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:65.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Zhang, W. Q.*; Yamaguchi, Toshio*; Fang, C. H.*; Yoshida, Koji*; Zhou, Y. Q.*; Zhu, F. Y.*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Li, W.*
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 348, p.118080_1 - 118080_11, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.49(Chemistry, Physical)The ion hydration and association and hydrogen-bonded water structure in an aqueous 3 mol/kg RbCl solution were investigated at 298 K/0.1 MPa, 298 K/1 GPa, 523 K/1 GPa, and 523 K/4 GPa by neutron diffraction combined with EPSR methods. The second hydration layer of Rb and Cl
and Cl becomes evident under elevated pressure and temperature conditions. The average oxygen coordination number of Rb
becomes evident under elevated pressure and temperature conditions. The average oxygen coordination number of Rb (Cl
(Cl ) in the first hydration layer increases from 6.3 (5.9) ambient pressure to 8.9 (9.1) at 4 GPa, while decreasing coordination distance from 0.290 nm (0.322 nm) to 0.288 nm (0.314 nm). The orientation of the water dipole in the first solvation shell of Rb
) in the first hydration layer increases from 6.3 (5.9) ambient pressure to 8.9 (9.1) at 4 GPa, while decreasing coordination distance from 0.290 nm (0.322 nm) to 0.288 nm (0.314 nm). The orientation of the water dipole in the first solvation shell of Rb and a central water molecule is sensitive to pressure, but that in the first solvation shell of Cl
and a central water molecule is sensitive to pressure, but that in the first solvation shell of Cl does not change very much. The number of contact-ion pairs Rb
does not change very much. The number of contact-ion pairs Rb -Cl
-Cl decreases with elevated temperature and increases with elevated pressure. Water molecules are closely packed, and the tetrahedral hydrogen-bonded network of water molecules no longer exists in extreme conditions.
decreases with elevated temperature and increases with elevated pressure. Water molecules are closely packed, and the tetrahedral hydrogen-bonded network of water molecules no longer exists in extreme conditions.

Hao, Y. Q.*; Wo, H. L.*; Gu, Y. M.*; Zhang, X. W.*; Gu, Y. Q.*; Zheng, S. Y.*; Zhao, Y.*; Xu, G. Y.*; Lynn, J. W.*; Nakajima, Kenji; et al.
Science China; Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 64(3), p.237411_1 - 237411_6, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:69.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Wang, Y.*; Jia, G.*; Cui, X.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, Q.*; Gu, L.*; Zheng, L.*; Li, L. H.*; Wu, Q.*; Singh, D. J.*; et al.
Chem, 7(2), p.436 - 449, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:297 Percentile:99.75(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) decay of
decay of 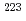 U
USun, M. D.*; Liu, Z.*; Huang, T. H.*; Zhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Ding, B.*; Wang, J. G.*; Liu, X. Y.*; Lu, H. Y.*; Hou, D. S.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 800, p.135096_1 - 135096_5, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:75.82(Astronomy & Astrophysics) resonances in a box
resonances in a boxOno, Akira*; Xu, J.*; Colonna, M.*; Danielewicz, P.*; Ko, C. M.*; Tsang, M. B.*; Wang, Y,-J.*; Wolter, H.*; Zhang, Y.-X.*; Chen, L.-W.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 100(4), p.044617_1 - 044617_35, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:75 Percentile:98.53(Physics, Nuclear)International comparison of heavy-ion induced reaction models were discussed in the international conference "Transport2017" held in April 2017. Owing to their importance for safety assessment of heavy-ion accelerators and dosimetry of astronauts, various models to simulate heavy-ion induced reaction models are developed. This study is intended to clarify the difference among them to pinpoint their problems. In the comparison study, 320 protons and neutrons were packed in a 20-fm-large cube to calculate the number and energies of collisions during the time evolution. The author contributed to this study by running calculation using JQMD (JAERI Quantum Molecular Dynamics). This study showed that time step in the calculation is one of the biggest causes of the discrepancies. For example, the calculation by JQMD comprises 1-fm/c time steps, each of which is composed of transport, scattering and decay phases. Therefore a sequence of scattering, and decay followed by another scattering in 1 fm/c cannot be considered. Moreover, in JQMD particles are labeled by sequential numbers and scattering reactions are simulated by the order. Therefore scattering between low ID numbers, that between high ID numbers and that between the first (low ID) pair is overlooked in JQMD. Above indications obtained in this study must be kept in our mind for future JQMD upgrades.
 Ge
Ge
Wo, H.*; Wang, Q.*; Shen, Y.*; Zhang, X.*; Hao, Y.*; Feng, Y.*; Shen, S.*; He, Z.*; Pan, B.*; Wang, W.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 122(21), p.217003_1 - 217003_5, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:46.81(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Yang, P.-J.*; Li, Q.-J.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Ogata, Shigenobu*; Zhang, J.-W.*; Sheng, H.-W.*; Shan, Z.-W.*; Sha, G.*; Han, W.-Z.*; Li, J.*; et al.
Acta Materialia, 168, p.331 - 342, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:83 Percentile:96.81(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Body-centred-cubic metallic materials, such as niobium (Nb) and other refractory metals, are prone to embrittlement due to low levels of oxygen solutes. The mechanisms responsible for the oxygen-induced rampant hardening and damage are unclear. Here we illustrate that screw dislocations moving through a random repulsive force field imposed by impurity oxygen interstitials readily form cross-kinks and emit excess vacancies in Nb. The vacancies bind strongly with oxygen and screw dislocation in a three-body fashion, rendering dislocation motion difficult and hence pronounced dislocation storage and hardening. This leads to unusually high strain hardening rates and fast breeding of nano-cavities that underlie damage and failure.
Zhang, Y.-X.*; Wang, Y,-J.*; Colonna, M.*; Danielewicz, P.*; Ono, Akira*; Tsang, M. B.*; Wolter, H.*; Xu, J.*; Chen, L.-W.*; Cozma, D.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 97(3), p.034625_1 - 034625_20, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:117 Percentile:98.99(Physics, Nuclear)International comparison of heavy-ion induced reaction models were discussed in the international conference "Transport2017" held in April 2017. Owing to their importance for safety assessment of heavy-ion accelerators and dosimetry of astronauts, various models to simulate heavy-ion induced reaction models are developed. This study is intended to clarify the difference among them to pinpoint their problems. In the comparison study, 320 protons and 320 neutrons were packed in a 20-fm-large cube to calculate the number of particle-particle collisions as well as the energies of collisions during the time evolution. In addition to the calculation, their algorithms were compared. The author contributed to this study by running calculation using JQMD (JAERI Quantum Molecular Dynamics). The results were compared with those calculated by the other 15 codes from over the world. Algorithm comparison showed that JQMD calculates collision probabilities from protons at first and collisions by neutrons are simulated later, which might be unreasonable. On the other hand, it was clarified that the calculation by JQMD agrees with those by the others. Despite the fact that some codes deviate from the average by a factor of 2, JQMD exhibited stable performance.
Wang, Y.-Q.*; Gai, W.-Z.*; Zhang, X.-Y.*; Pan, H.-Y.*; Cheng, Z.-X.*; Xu, P. G.; Deng, Z.-Y.*
RSC Advances (Internet), 7(4), p.2103 - 2109, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:63.30(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)
Li, B.; Luo, X. H.*; Wang, H.*; Ren, W. J.*; Yano, S.*; Wang, C.-W.*; Gardner, J. S.*; Liss, K.-D.*; Miao, P.*; Lee, S.-H.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 93(22), p.224405_1 - 224405_6, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:56 Percentile:87.40(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Deng, Z.*; Zhao, K.*; Gu, B.; Han, W.*; Zhu, J. L.*; Wang, X. C.*; Li, X.*; Liu, Q. Q.*; Yu, R. C.*; Goko, Tatsuo*; et al.
Physical Review B, 88(8), p.081203_1 - 081203_5, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:77 Percentile:91.56(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) /SrTiO
/SrTiO (110) interface
(110) interfaceAnnadi, A.*; Zhang, Q.*; Renshaw Wang, X.*; Tuzla, N.*; Gopinadhan, K.*; L , W. M.*; Roy Barman, A.*; Liu, Z. Q.*; Srivastava, A.*; Saha, S.*; et al.
, W. M.*; Roy Barman, A.*; Liu, Z. Q.*; Srivastava, A.*; Saha, S.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 4, p.1838_1 - 1838_7, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:103 Percentile:94.51(Multidisciplinary Sciences) [503] band of
[503] band of  Pt
PtLi, G. S.*; Zhou, X. H.*; Zhang, Y. H.*; Zheng, Y.*; Liu, M. L.*; Hua, W.*; Zhou, H. B.*; Ding, B.*; Wang, H. X.*; Lei, X. G.*; et al.
Journal of Physics G; Nuclear and Particle Physics, 38(9), p.095105_1 - 095105_9, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.38(Physics, Nuclear)High-spin states in  Pt have been investigated by means of in beam
Pt have been investigated by means of in beam  -ray spectroscopic method at the JAEA tandem facility. Low-spin signature inversion is revealed in the 7/2
-ray spectroscopic method at the JAEA tandem facility. Low-spin signature inversion is revealed in the 7/2 [503] band. The inversion can be interpreted as a configuration change from the 7/2
[503] band. The inversion can be interpreted as a configuration change from the 7/2 [503] orbital to the 7/2
[503] orbital to the 7/2 [514] orbital with increasing spin, which is supported by a theoretical calculation of the semi-classical Donau and Frauendorf approach.
[514] orbital with increasing spin, which is supported by a theoretical calculation of the semi-classical Donau and Frauendorf approach.