Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Co
Co )Sn studied by
)Sn studied by  SR
SRCai, Y.*; Yoon, S.*; Sheng, Q.*; Zhao, G.*; Seewald, E. F.*; Ghosh, S.*; Ingham, J.*; Pasupathy, A. N.*; Queiroz, R.*; Lei, H.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 111(21), p.214412_1 - 214412_17, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0Li, F.*; Tang, X.*; Fei, Y.*; Zhang, J.*; Liu, J.*; Lang, P.*; Che, G.*; Zhao, Z.*; Zheng, Y.*; Fang, Y.*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 147(17), p.14054 - 14059, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We synthesized a crystalline graphane nanoribbon (GANR) via pressure-induced polymerization of 2,2'-bipyrazine (BPZ). By performing Rietveld refinement of in situ neutron diffraction data, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, infrared spectra, and theoretical calculation, we found that BPZ experienced Diels-Alder polymerization between the 

 stacked aromatic rings, and formed extended boat-GANR structures with exceptional long-range order. The unreacted -C=N- groups bridge the two ends of the boat, and ready for further functionalization. The GANR has a bandgap of 2.25 eV, with booming photoelectric response (
stacked aromatic rings, and formed extended boat-GANR structures with exceptional long-range order. The unreacted -C=N- groups bridge the two ends of the boat, and ready for further functionalization. The GANR has a bandgap of 2.25 eV, with booming photoelectric response (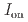 /
/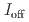 =18.8). Our work highlights that the high-pressure topochemical polymerization is a promising method for the precise synthesis of graphane with specific structure and desired properties.
=18.8). Our work highlights that the high-pressure topochemical polymerization is a promising method for the precise synthesis of graphane with specific structure and desired properties.
Ling, B.-K.*; Chang, M.*; Zhai, Y.-Q.*; Deng, J.*; Kofu, Maiko*; Guo, H.*; Zhao, J.*; Fu, Z.*; Zheng, Y.-Z.*
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 147(13), p.10935 - 10942, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:83.04(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Che, G.*; Fei, Y.*; Tang, X.*; Zhao, Z.*; Hattori, Takanori; Abe, Jun*; Wang, X.*; Ju, J.*; Dong, X.*; Wang, Y.*; et al.
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 27(2), p.1112 - 1118, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:75.15(Chemistry, Physical)Pressure-induced polymerization (PIP) of aromatic molecules has emerged as an effective method for synthesizing various carbon-based materials. In this work, PIP of 1,4-difluorobenzene (1,4-DFB) was investigated.  high-pressure investigations of 1,4-DFB reveal a phase transition at approximately 12.0 GPa and an irreversible chemical reaction at 18.7 GPa. Structural analysis of the product and the kinetics of the reaction uncovered the formation of pseudohexagonal stacked fluoro-diamond nanothreads with linear growth. Compared to the crystal structures of benzene under high pressure, 1,4-DFB exhibits higher compression along the [001] axis. The anisotropic compression is attributed to the stronger H
high-pressure investigations of 1,4-DFB reveal a phase transition at approximately 12.0 GPa and an irreversible chemical reaction at 18.7 GPa. Structural analysis of the product and the kinetics of the reaction uncovered the formation of pseudohexagonal stacked fluoro-diamond nanothreads with linear growth. Compared to the crystal structures of benzene under high pressure, 1,4-DFB exhibits higher compression along the [001] axis. The anisotropic compression is attributed to the stronger H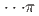 interaction along the [01
interaction along the [01 ] axis and the potential compression-inhibiting H
] axis and the potential compression-inhibiting H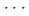 F interactions along the [100] and [010] axes, and it facilitates a possible reaction pathway along the [01
F interactions along the [100] and [010] axes, and it facilitates a possible reaction pathway along the [01 ] axis. This work emphasizes the crucial role of functionalization in modulating molecular stacking and influencing the reaction pathway.
] axis. This work emphasizes the crucial role of functionalization in modulating molecular stacking and influencing the reaction pathway.
 -
- transitions
transitionsYang, Q.*; Yang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Fei, Y.*; Li, F.*; Zheng, H.*; Li, K.*; Han, Y.*; Hattori, Takanori; Zhu, P.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.7778_1 - 7778_9, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:88.19(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Luminescent materials that simultaneously embody bright singlet and triplet excitons hold great potential in optoelectronics, signage, and information encryption. However, achieving high-performance white-light emission is severely hampered by their inherent unbalanced contribution of fluorescence and phosphorescence. Herein, we address this challenge by pressure treatment engineering via hydrogen bonding cooperativity effect to realize the mixture of n- -
- transitions, where the triplet state emission was boosted from 7% to 40% in isophthalic acid (IPA). A superior white-light emission based on hybrid fluorescence and phosphorescence was harvested in pressure-treated IPA, and the photoluminescence quantum yield was increased to 75% from the initial 19% (blue-light emission). In-situ high-pressure IR spectra, X ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction reveal continuous strengthening of the hydrogen bonds with the increase of pressure. Furthermore, this enhanced hydrogen bond is retained down to the ambient conditions after pressure treatment, awarding the targeted IPA efficient intersystem crossing for balanced singlet/triplet excitons population and resulting in efficient white-light emission. This work not only proposes a route for brightening triplet states in organic small molecule, but also regulates the ratio of singlet and triplet excitons to construct high-performance white-light emission.
transitions, where the triplet state emission was boosted from 7% to 40% in isophthalic acid (IPA). A superior white-light emission based on hybrid fluorescence and phosphorescence was harvested in pressure-treated IPA, and the photoluminescence quantum yield was increased to 75% from the initial 19% (blue-light emission). In-situ high-pressure IR spectra, X ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction reveal continuous strengthening of the hydrogen bonds with the increase of pressure. Furthermore, this enhanced hydrogen bond is retained down to the ambient conditions after pressure treatment, awarding the targeted IPA efficient intersystem crossing for balanced singlet/triplet excitons population and resulting in efficient white-light emission. This work not only proposes a route for brightening triplet states in organic small molecule, but also regulates the ratio of singlet and triplet excitons to construct high-performance white-light emission.

Gu, Y. Q.*; Gu, Y. M.*; Liu, F.*; Kawamura, Seiko; Murai, Naoki; Zhao, J.*
Physical Review Letters, 132(24), p.246702_1 - 246702_7, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:64.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -MgAgSb
-MgAgSbLi, J.*; Li, X.*; Zhang, Y.*; Zhu, J.*; Zhao, E.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Avdeev, M.*; Liu, P.-F.*; Sui, J.*; et al.
Applied Physics Reviews (Internet), 11(1), p.011406_1 - 011406_8, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:89.71(Physics, Applied)Nara, Yoshitaka*; Kashiwaya, Koki*; Oketani, Kazuki*; Fujii, Hirokazu*; Zhao, Y.*; Kato, Masaji*; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ozaki, Yusuke; Matsui, Hiroya; Kono, Masanori*
Zairyo, 73(3), p.220 - 225, 2024/03
The fractures in the rock are the main pass of groundwater flow and solute transport. The filling of fine-grained particle, such as clay minerals, was confirmed to decrease the permeability of rock by laboratory experiment. This research aimed to verify the occurrence of the phenomena in the field. The water containing the clay minerals was injected into the rock at the 200m stage of the Mizunami Underground research laboratory. The hydraulic conductivity decreased two order before and after the injection. This result suggested that the decrease of hydraulic conductivity by the filling of fine-grained particle in the fractures occurred in the real field.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionZhou, Y.*; Song, W.*; Zhang, F.*; Wu, Y.*; Lei, Z.*; Jiao, M.*; Zhang, X.*; Dong, J.*; Zhang, Y.*; Yang, M.*; et al.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 971, p.172635_1 - 172635_7, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.52(Chemistry, Physical) titanium alloys strong and ductile
titanium alloys strong and ductileChong, Y.*; Gholizadeh, R.*; Guo, B.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Zhao, G.*; Yoshida, Shuhei*; Mitsuhara, Masatoshi*; Godfrey, A.*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 257, p.119165_1 - 119165_14, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:98.38(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Metastable  titanium alloys possess excellent strain-hardening capability, but suffer from a low yield strength. As a result, numerous attempts have been made to strengthen this important structural material in the last decade. Here, we explore the contributions of grain refinement and interstitial additions in raising the yield strength of a Ti-12Mo (wt.%) metastable
titanium alloys possess excellent strain-hardening capability, but suffer from a low yield strength. As a result, numerous attempts have been made to strengthen this important structural material in the last decade. Here, we explore the contributions of grain refinement and interstitial additions in raising the yield strength of a Ti-12Mo (wt.%) metastable  titanium alloy. Surprisingly, rather than strengthening the material, grain refinement actually lowers the ultimate tensile strength in this alloy. This unexpected and anomalous behavior is attributed to a significant enhancement in strain-induced
titanium alloy. Surprisingly, rather than strengthening the material, grain refinement actually lowers the ultimate tensile strength in this alloy. This unexpected and anomalous behavior is attributed to a significant enhancement in strain-induced  martensite phase transformation, where in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction analysis reveals, for the first time, that this phase is much softer than the parent
martensite phase transformation, where in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction analysis reveals, for the first time, that this phase is much softer than the parent  phase. Instead, a combination of both oxygen addition and grain refinement is found to realize an unprecedented strength-ductility synergy in a Ti-12Mo-0.3O (wt.%) alloy. The advantageous effect of oxygen solutes in this ternary alloy is twofold. Firstly, solute oxygen largely suppresses strain-induced transformation to the
phase. Instead, a combination of both oxygen addition and grain refinement is found to realize an unprecedented strength-ductility synergy in a Ti-12Mo-0.3O (wt.%) alloy. The advantageous effect of oxygen solutes in this ternary alloy is twofold. Firstly, solute oxygen largely suppresses strain-induced transformation to the  martensite phase, even in a fine-grained microstructure, thus avoiding the softening effect of excessive amounts of
martensite phase, even in a fine-grained microstructure, thus avoiding the softening effect of excessive amounts of  martensite. Secondly, oxygen solutes readily segregate to twin boundaries, as revealed by atom probe tomography. This restricts the growth of
martensite. Secondly, oxygen solutes readily segregate to twin boundaries, as revealed by atom probe tomography. This restricts the growth of 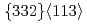 deformation twins, thereby promoting more extensive twin nucleation, leading to enhanced microstructural refinement. The insights from our work provide a cost-effective rationale for the design of strong yet tough metastable
deformation twins, thereby promoting more extensive twin nucleation, leading to enhanced microstructural refinement. The insights from our work provide a cost-effective rationale for the design of strong yet tough metastable  titanium alloys, with significant implications for more widespread use of this high strength-to-weight structural material.
titanium alloys, with significant implications for more widespread use of this high strength-to-weight structural material.
Bao, S.*; Gu, Z.-L.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, B.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Wang, W.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.6093_1 - 6093_9, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:92.84(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Esser, S. P.*; Rahlff, J.*; Zhao, W.*; Predl, M.*; Plewka, J.*; Sures, K.*; Wimmer, F.*; Lee, J.*; Adam, P. S.*; McGonigle, J.*; et al.
Nature Microbiology (Internet), 8(9), p.1619 - 1633, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:74.53(Microbiology)Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Xi, N.*; Gao, Y.-P.*; Ma, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Qi, Z.*; Zhang, S.*; Huang, Z.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(12), p.1883 - 1889, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:93.50(Physics, Multidisciplinary) X-ray synchrotron diffraction
X-ray synchrotron diffractionLi, H.*; Liu, Y.*; Zhao, W.*; Liu, B.*; Tominaga, Aki; Shobu, Takahisa; Wei, D.*
International Journal of Plasticity, 165, p.103612_1 - 103612_20, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:94.81(Engineering, Mechanical)In order to clarify the strength properties of Co-free maraging steel,  tensile experiment using high energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction was performed. Diffraction profiles from the martensitic and austenitic phases were obtained, and their strength and width were observed to vary as loading. Analysis of the diffraction profiles showed that the content of martensite in the as-aged material decreased slowly at low stress levels and decreased rapidly at high stress levels. On the other hand, the austenite phase in the as-solution materials was significantly transformed the martensite phase as the stress increased. It was clarified to be responsible for their respective strength properties.
tensile experiment using high energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction was performed. Diffraction profiles from the martensitic and austenitic phases were obtained, and their strength and width were observed to vary as loading. Analysis of the diffraction profiles showed that the content of martensite in the as-aged material decreased slowly at low stress levels and decreased rapidly at high stress levels. On the other hand, the austenite phase in the as-solution materials was significantly transformed the martensite phase as the stress increased. It was clarified to be responsible for their respective strength properties.
Wu, P.*; Murai, Naoki; Li, T.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Xia, K.*; Peng, K.*; Zhang, Y.*; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 25(1), p.013032_1 - 013032_11, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary) BaCo(PO
BaCo(PO )
)
Sheng, J.*; Wang, L.*; Candini, A.*; Jiang, W.*; Huang, L.*; Xi, B.*; Zhao, J.*; Ge, H.*; Zhao, N.*; Fu, Y.*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 119(51), p.e2211193119_1 - e2211193119_9, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:93.63(Multidisciplinary Sciences) ;
;  SR studies and charge-spin percolation model
SR studies and charge-spin percolation modelSheng, Q.*; Kaneko, Tatsuya*; Yamakawa, Kohtaro*; Guguchia, Z.*; Gong, Z.*; Zhao, G.*; Dai, G.*; Jin, C.*; Guo, S.*; Fu, L.*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 4(3), p.033172_1 - 033172_14, 2022/09
 K
K (Zn
(Zn Mn
Mn )
) As
As studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonant inelastic X-ray scattering
studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonant inelastic X-ray scatteringSuzuki, Hakuto*; Zhao, G.*; Okamoto, Jun*; Sakamoto, Shoya*; Chen, Z.-Y.*; Nonaka, Yosuke*; Shibata, Goro; Zhao, K.*; Chen, B.*; Wu, W.-B.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(6), p.064710_1 - 064710_5, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Zhao, Y.*; Suzuki, T.*; Iimori, T.*; Kim, H.-W.*; Ahn, J. R.*; Horio, Masafumi*; Sato, Yusuke*; Fukaya, Yuki; Kanai, T.*; Okazaki, K.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 105(11), p.115304_1 - 115304_8, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.98(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 Cu
Cu TeO
TeO
Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Cai, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Huang, Z.*; Ma, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; et al.
Physical Review B, 104(22), p.224430_1 - 224430_8, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10.46(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)