Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Zhu, M.*; Romerio, V.*; Steiger, N.*; Nabi, S. D.*; Murai, Naoki; Kawamura, Seiko; Povarov, K. Y.*; Skourski, Y.*; Sibille, R.*; Keller, L.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 133(18), p.186704_1 - 186704_6, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:88.92(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -
- transitions
transitionsYang, Q.*; Yang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Fei, Y.*; Li, F.*; Zheng, H.*; Li, K.*; Han, Y.*; Hattori, Takanori; Zhu, P.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.7778_1 - 7778_9, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:88.46(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Luminescent materials that simultaneously embody bright singlet and triplet excitons hold great potential in optoelectronics, signage, and information encryption. However, achieving high-performance white-light emission is severely hampered by their inherent unbalanced contribution of fluorescence and phosphorescence. Herein, we address this challenge by pressure treatment engineering via hydrogen bonding cooperativity effect to realize the mixture of n- -
- transitions, where the triplet state emission was boosted from 7% to 40% in isophthalic acid (IPA). A superior white-light emission based on hybrid fluorescence and phosphorescence was harvested in pressure-treated IPA, and the photoluminescence quantum yield was increased to 75% from the initial 19% (blue-light emission). In-situ high-pressure IR spectra, X ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction reveal continuous strengthening of the hydrogen bonds with the increase of pressure. Furthermore, this enhanced hydrogen bond is retained down to the ambient conditions after pressure treatment, awarding the targeted IPA efficient intersystem crossing for balanced singlet/triplet excitons population and resulting in efficient white-light emission. This work not only proposes a route for brightening triplet states in organic small molecule, but also regulates the ratio of singlet and triplet excitons to construct high-performance white-light emission.
transitions, where the triplet state emission was boosted from 7% to 40% in isophthalic acid (IPA). A superior white-light emission based on hybrid fluorescence and phosphorescence was harvested in pressure-treated IPA, and the photoluminescence quantum yield was increased to 75% from the initial 19% (blue-light emission). In-situ high-pressure IR spectra, X ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction reveal continuous strengthening of the hydrogen bonds with the increase of pressure. Furthermore, this enhanced hydrogen bond is retained down to the ambient conditions after pressure treatment, awarding the targeted IPA efficient intersystem crossing for balanced singlet/triplet excitons population and resulting in efficient white-light emission. This work not only proposes a route for brightening triplet states in organic small molecule, but also regulates the ratio of singlet and triplet excitons to construct high-performance white-light emission.
Zhu, L.*; He, H.*; Naeem, M.*; Sun, X.*; Qi, J.*; Liu, P.*; Harjo, S.; Nakajima, Kenji; Li, B.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Physical Review Letters, 133(12), p.126701_1 - 126701_6, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:48.32(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Ying, H.*; Yang, X.*; He, H.*; Yan, A.*; An, K.*; Ke, Y.*; Wu, Z.*; Tang, S.*; Zhang, Z.*; Dong, H.*; et al.
Scripta Materialia, 250, p.116181_1 - 116181_7, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:41.92(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Ma, Y.*; Naeem, M.*; Zhu, L.*; He, H.*; Sun, X.*; Yang, Z.*; He, F.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Wang, X.-L.*
Acta Materialia, 270, p.119822_1 - 119822_13, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:95.42(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)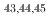 Cl via
Cl via 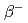 and
and 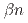 decay
decayTripathi, V.*; Bhattacharya, S.*; Rubino, E.*; Benetti, C.*; Perello, J. F.*; Tabor, S. L.*; Liddick, S. N.*; Bender, P. C.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; Carroll, J. J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(4), p.044320_1 - 044320_15, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Li, X.*; Zhu, R.*; Xin, J.*; Luo, M.*; Shang, S.-L.*; Liu, Z.-K.*; Yin, C.*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Dippenaar, R. J.*; Higo, Yuji*; et al.
CALPHAD; Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry, 84, p.102641_1 - 102641_6, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Thermodynamics) SnSe
SnSe
Ren, Q.*; Gupta, M. K.*; Jin, M.*; Ding, J.*; Wu, J.*; Chen, Z.*; Lin, S.*; Fabelo, O.*; Rodriguez-Velamazan, J. A.*; Kofu, Maiko; et al.
Nature Materials, 22(8), p.999 - 1006, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:76 Percentile:99.20(Chemistry, Physical)Meng, L.*; Wang, B.*; Wang, G.-J.*; Zhu, S.-L.*
Physics Reports; A Review Section of Physics Letters, 1019, p.1 - 149, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:120 Percentile:97.56(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -wave
-wave 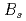 states combining quark model and lattice QCD in the coupled channel framework
states combining quark model and lattice QCD in the coupled channel frameworkYang, Z.*; Wang, G.-J.*; Wu, J.-J.*; Oka, Makoto; Zhu, S.-L.*
Journal of High Energy Physics (Internet), 2023(1), p.058_1 - 058_19, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:74.17(Physics, Particles & Fields)Combining the quark model, the quark-pair-creation mechanism and 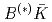 interaction, we have investigated the near-threshold
interaction, we have investigated the near-threshold  -wave
-wave 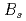 states in the framework of the Hamiltonian effective field theory. With the heavy quark flavor symmetry, all the parameters are determined in the
states in the framework of the Hamiltonian effective field theory. With the heavy quark flavor symmetry, all the parameters are determined in the 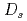 sector by fitting the lattice data. The masses of the bottom-strange partners of the
sector by fitting the lattice data. The masses of the bottom-strange partners of the  and
and 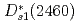 are predicted, which are well consistent with the lattice QCD simulation. The two
are predicted, which are well consistent with the lattice QCD simulation. The two  -wave
-wave 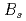 states are the mixtures of the bare
states are the mixtures of the bare 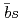 core and
core and 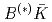 component. Moreover, we find a crossing point between the energy levels with and without the interaction Hamiltonian in the finite volume spectrum in the
component. Moreover, we find a crossing point between the energy levels with and without the interaction Hamiltonian in the finite volume spectrum in the 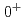 case, which corresponds to a CDD (Castillejo-Dalitz-Dyson) zero in the
case, which corresponds to a CDD (Castillejo-Dalitz-Dyson) zero in the  -matrix of the
-matrix of the 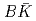 scattering. This CDD zero will help deepen the insights of the near-threshold states and can be examined by future lattice calculation.
scattering. This CDD zero will help deepen the insights of the near-threshold states and can be examined by future lattice calculation.
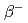 decay of exotic P and S isotopes with neutron number near 28
decay of exotic P and S isotopes with neutron number near 28Tripathi, V.*; Bhattacharya, S.*; Rubino, E.*; Benetti, C.*; Perello, J. F.*; Tabor, S. L.*; Liddick, S. N.*; Bender, P. C.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; Carroll, J. J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(6), p.064314_1 - 064314_14, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:53.47(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
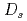 states
statesYang, Z.*; Wang, G.-J.*; Wu, J.-J.*; Oka, Makoto; Zhu, S.-L.*
Physical Review Letters, 128(11), p.112001_1 - 112001_6, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:95.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A novel framework is proposed to extract near-threshold resonant states from finite-volume energy levels of lattice QCD and is applied to elucidate structures of the positive parity 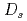 . The quark model, the quark-pair-creation mechanism and
. The quark model, the quark-pair-creation mechanism and 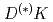 interaction are incorporated into the Hamiltonian effective field theory. The bare
interaction are incorporated into the Hamiltonian effective field theory. The bare 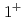
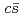 states are almost purely given by the states with heavy-quark spin bases. The physical
states are almost purely given by the states with heavy-quark spin bases. The physical 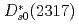 and
and 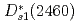 are the mixtures of bare
are the mixtures of bare 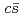 core and
core and 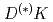 component, while the
component, while the 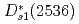 and
and 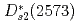 are almost dominated by bare
are almost dominated by bare 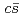 . Furthermore, our model well reproduce the clear level crossing of the
. Furthermore, our model well reproduce the clear level crossing of the 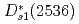 with the scattering state at a finite volume.
with the scattering state at a finite volume.
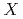 (3872)
(3872)Meng, L.*; Wang, G.-J.*; Wang, B.*; Zhu, S.-L.*
Physical Review D, 104(9), p.094003_1 - 094003_8, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:85.55(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The isospin violating decays of 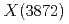 are revisited in a coupled-channel effective field theory. In a cutoff-independent formalism, we relate the coupling constants of
are revisited in a coupled-channel effective field theory. In a cutoff-independent formalism, we relate the coupling constants of 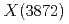 with the two channels to the molecular wave function. The isospin violating decays of
with the two channels to the molecular wave function. The isospin violating decays of 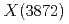 are obtained by two equivalent approaches, which amend some deficiencies about this issue in literature. In the quantum field theory approach, the isospin violating decays arise from the coupling constants of
are obtained by two equivalent approaches, which amend some deficiencies about this issue in literature. In the quantum field theory approach, the isospin violating decays arise from the coupling constants of 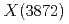 to two di-meson channels. In the quantum mechanics approach, the isospin violating is attributed to wave functions at the origin. We bridge the isospin violating decays of
to two di-meson channels. In the quantum mechanics approach, the isospin violating is attributed to wave functions at the origin. We bridge the isospin violating decays of 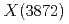 to its inner structure. Our results show that the proportion of the neutral channel in
to its inner structure. Our results show that the proportion of the neutral channel in 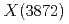 is over 80%. As a by-product, we find that the strong decay width and radiative decay width are about 30 keV and 10 keV, respectively, for the binding energy from -300 keV to -50 keV.
is over 80%. As a by-product, we find that the strong decay width and radiative decay width are about 30 keV and 10 keV, respectively, for the binding energy from -300 keV to -50 keV.
 Bi
BiDoherty, D. T.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Seweryniak, D.*; Woods, P. J.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; Auranen, K.*; Ayangeakaa, A. D.*; Back, B. B.*; Bottoni, S.*; Canete, L.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(20), p.202501_1 - 202501_6, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:64.86(Physics, Multidisciplinary)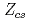 (3985) and
(3985) and 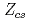 (4000) as two different states
(4000) as two different statesMeng, L.*; Wang, B.*; Wang, G.-J.*; Zhu, S.-L.*
Science Bulletin, 66(20), p.2065 - 2071, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:85.55(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Two recently found tetraquark resonances 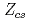 (3985) and
(3985) and 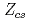 (4000) are studied in a solvable nonrelativistic effective field theory. We include the possible violations of heavy quark spin symmetry and SU(3) flavor symmetry in a comprehensive approach. Our results show that the decay rates can be used to judge whether these resonances can be different states or not.
(4000) are studied in a solvable nonrelativistic effective field theory. We include the possible violations of heavy quark spin symmetry and SU(3) flavor symmetry in a comprehensive approach. Our results show that the decay rates can be used to judge whether these resonances can be different states or not.
Naeem, M.*; Zhou, H.*; He, H.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; Zhu, Y.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Applied Physics Letters, 119(13), p.131901_1 - 131901_7, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:78.00(Physics, Applied)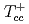 with the strong and electromagnetic decays
with the strong and electromagnetic decaysMeng, L.*; Wang, G.-J.*; Wang, B.*; Zhu, S.-L.*
Physical Review D, 104(5), p.L051502_1 - L051502_8, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:80 Percentile:98.41(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We investigate the kinetically allowed strong and electromagnetic decays of the recently observed 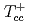 . Our results show that the decay width of
. Our results show that the decay width of 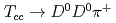 is the largest one, which is just the experimental observation channel. Our theoretical total strong and radiative widths are in favor of the
is the largest one, which is just the experimental observation channel. Our theoretical total strong and radiative widths are in favor of the 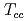 as a
as a 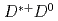 dominated bound state. Our calculation is cutoff-independent and without prior isospin assignment. The absolute partial widths and ratios of the different decay channels can be used to test the structure of
dominated bound state. Our calculation is cutoff-independent and without prior isospin assignment. The absolute partial widths and ratios of the different decay channels can be used to test the structure of 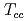 state when the updated experimental results are available.
state when the updated experimental results are available.
 ;
;  In NQR/NMR and
In NQR/NMR and  Co NMR study
Co NMR studySakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Thompson, J. D.*; Ramakrishna, S. K.*; Reyes, A. P.*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 104(8), p.085106_1 - 085106_12, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:30.79(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Antiferromagnetism in a prototypical quantum critical metal CeCoIn is known to be induced by slight substitutions of non-magnetic Zn atoms for In. In nominally 7% Zn substituted CeCoIn
is known to be induced by slight substitutions of non-magnetic Zn atoms for In. In nominally 7% Zn substituted CeCoIn , an antiferromagnetic (AFM) state coexists with heavy fermion superconductivity. Heterogeneity of the electronic states is investigated in Zn doped CeCoIn
, an antiferromagnetic (AFM) state coexists with heavy fermion superconductivity. Heterogeneity of the electronic states is investigated in Zn doped CeCoIn by means of nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonances (NQR and NMR). Site-dependent NQR relaxation rates
by means of nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonances (NQR and NMR). Site-dependent NQR relaxation rates  indicate that the AFM state is locally nucleated around Zn substituents in the matrix of a heavy fermion state, and percolates through the bulk at the AFM transition temperature
indicate that the AFM state is locally nucleated around Zn substituents in the matrix of a heavy fermion state, and percolates through the bulk at the AFM transition temperature  . At lower temperatures, an anisotropic superconducting (SC) gap below the SC transition temperature
. At lower temperatures, an anisotropic superconducting (SC) gap below the SC transition temperature  , and the SC state permeates through the AFM regions via a SC proximity effect. Applying an external magnetic field induces a spin-flop transition near 5 T, reducing the volume of the AFM regions. Consequently, a short ranged inhomogeneous AFM state survives and coexists with a paramagnetic Fermi liquid state at high fields.
, and the SC state permeates through the AFM regions via a SC proximity effect. Applying an external magnetic field induces a spin-flop transition near 5 T, reducing the volume of the AFM regions. Consequently, a short ranged inhomogeneous AFM state survives and coexists with a paramagnetic Fermi liquid state at high fields.
 -wave states
-wave statesWang, G.-J.*; Meng, L.*; Oka, Makoto; Zhu, S.-L.*
Physical Review D, 104(3), p.036016_1 - 036016_15, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:89.41(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Radial excited states and  -wave excited states of the fully charmed tetraquark spectrum was studied in the quark model. In the standard model settings, we find that several states may correspond to the observed X(6900) region. The possible quantum numbers are
-wave excited states of the fully charmed tetraquark spectrum was studied in the quark model. In the standard model settings, we find that several states may correspond to the observed X(6900) region. The possible quantum numbers are 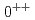 ,
, 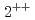 ,
, 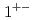 , and
, and 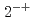 states.
states.
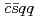 states
statesWang, G.-J.*; Meng, L.*; Xiao, L.-Y.*; Oka, Makoto; Zhu, S.-L.*
European Physical Journal C, 81(2), p.188_1 - 188_12, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:90.93(Physics, Particles & Fields)The mass spectrum and strong decays of the S-wave 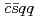 states are studied in the compact tetraquark scenario with the quark model. The model consists of the Coulomb, the linear confinement, and the hyperfine interactions. We calculate their decay amplitudes into the
states are studied in the compact tetraquark scenario with the quark model. The model consists of the Coulomb, the linear confinement, and the hyperfine interactions. We calculate their decay amplitudes into the 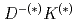 channels using the quark interchange method. The mass and decay width of the
channels using the quark interchange method. The mass and decay width of the 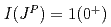 state are
state are 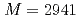 MeV and
MeV and 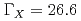 MeV, respectively, which indicates that it might be a good candidate for the recently observed
MeV, respectively, which indicates that it might be a good candidate for the recently observed 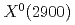 state. We also obtain an isospin partner state
state. We also obtain an isospin partner state 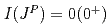 with
with 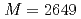 MeV and
MeV and 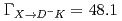 MeV, respectively. Future experimental search for
MeV, respectively. Future experimental search for 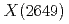 will be very helpful.
will be very helpful.