Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamashita, Susumu; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Takase, Kazuyuki
no journal, ,
In the Fukushima accidents, fuel assemblies which were installed in the reactors were reached a high temperature by stop of the core cooling system with a power station black-out. As a result, it is considered that the core degradation has been introduced because the melting of the fuel rods occurred and the melting behavior was expanded. In order to elucidate a progress of the melting phenomena in the reactor core, a numerical simulation code which can be precisely evaluated the melting phenomena is required. Then, the melting behavior of the fuel assemblies in the reactor core was analyzed numerically using the three-dimensional multi-phase thermal-hydraulic simulation code. In the presentation, the numerical results on the melting behavior of the simulated fuel assemblies and reactor structures are reported for several different initial conditions.
Ozu, Akira; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Takase, Misao; Kurata, Noritaka; Haruyama, Mitsuo; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Kureta, Masatoshi; Seya, Michio
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ozawa, Kazumi; Koyanagi, Takaaki*; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Nozawa, Takashi; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Kondo, Sosuke*; Hinoki, Tatsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationMotooka, Takafumi; Sato, Tomonori; Tsukada, Takashi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Matsunaga, Junji*; Kashibe, Shinji*; Serizawa, Hiroyuki; Oishi, Yuji*; Yamanaka, Shinsuke*
no journal, ,
In the developing MA-MOX fuel, the accumulation of helium should be serious problem since minor actinides are  -emitter. In this paper, we will discuss a mechanism of inter-granular gas bubble produced by the helium injected into UO
-emitter. In this paper, we will discuss a mechanism of inter-granular gas bubble produced by the helium injected into UO using HIP.
using HIP.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Kubo, Shigenobu; Nishino, Hiroyuki; Sakai, Takaaki; Tani, Akihiro*
no journal, ,
The importance in safety measures against external events becomes more significant recently and investigation for the design measures is inevitable. Thus conditions for external event were established in order to investigate safety measures for JSFR. In this paper, we report a screening method and definition method for postulating condition for the design.
Fujimoto, Ikuo; Yanagibashi, Futoshi; Yamamoto, Kohei; Sato, Takehiko; Obu, Tomoyuki; Taki, Kiyotaka
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kikuchi, Hirohito; Tanai, Kenji; Sawada, Sumiyuki; Maekawa, Keisuke
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Harada, Masahide; Niita, Koji*
no journal, ,
Irradiation damage for the accelerator materials is estimated by using the Displacement per Atom (DPA) which is expressed by the particle flux and the displacement cross section. For the displacement cross section, Harada's data is available, but there are some problems. For example, there is lack of important nucleus such as Si and Mo for the accelerator, no available data below 20 MeV for protons and no data for deuterons. In this work, we calculated the displacement cross sections for the accelerator materials irradiated with neutrons, protons, and deuterons. For thick Cu target, we calculated DPA distribution by using our data and PHITS code and it was found that DPA values for protons was higher than that for neutrons within the stopping length of protons. We concluded that PHITS with our displacement cross sections can give information of irradiation damage for the large accelerator facilities.
Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Amamoto, Ippei; Yokozawa, Takuma; Yamashita, Teruo; Nagai, Takayuki; Kitamura, Naoto*; Takebe, Hiromichi*; Mitamura, Naoki*; Tsuzuki, Tatsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iijima, Masashi; Takahara, Shogo; Homma, Toshimitsu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Morita, Keisuke; Yamagishi, Isao; Nishihara, Kenji; Tsubata, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Noda, Shusaku; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Fukahori, Tokio; Chiba, Satoshi; Niita, Koji*
no journal, ,
The author has developed the quasideuteron model in the PHITS code.
Kimura, Yoshiki; Shinohara, Nobuo; Sato, Kaneaki; Toda, Nobufumi; Shinoda, Yoshiharu; Watahiki, Masaru; Kuno, Yusuke
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nagai, Haruyasu; Katata, Genki; Ota, Masakazu; Ina, Takuya; Kakefuda, Toyokazu; Endo, Akira
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ambai, Hiromu; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Hoshi, Masayuki; Sakauchi, Nobuyuki; Aose, Shinichi; Ogino, Hideki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Akabori, Mitsuo; Takano, Masahide; Nakada, Masami; Kawashima, Hidenori*; Komamine, Satoshi*; Ochi, Eiji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Takuya; Nagai, Haruyasu; Chino, Masamichi; Kawamura, Hideyuki
no journal, ,
The source term of the atmospheric release of I-131 and Cs-137 due to the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident estimated by previous studies was validated and refined by coupling atmospheric and oceanic dispersion simulations with observed Cs-134 in seawater collected from the Pacific Ocean.
Okubo, Kiyoshi; Suyama, Kenya; Kashima, Takao; Tonoike, Kotaro; Takada, Tomoyuki*
no journal, ,
Criticality safety analysis is necessary for the damaged-fuel handling in the Fukushima Daiichi NPP decommissioning. This presentation show influence of structural materials such as Zry-2, Fe, concrete expected to be present in the damaged fuel. Multiplication factor (kinf) decreases most by replacing moisture, in the damaged fuel, with iron. Replacement of all moisture with Zry-2 gives the same influence as iron, although decrease rate of kinf is lower because of the smaller absorb cross section of Zry-2. Concrete has much less influence due to the neutron moderation by hydrogen contained in concrete, which calls attention on handling of the concrete-fuel mixture. Effect as reflector of the materials is also evaluated.
Shibata, Keiichi
no journal, ,
Although JENDL-4.0 was relased in 2010, the high-energy cross sections of about 40 FP nuclides were not re-examined due to the time limit. Ruthenium is one of such data which were not revised in the high-energy region. Considering the significance of the activation cross sections of ruthenium, the present work was undertaken to evaluate the neutron cross sections of 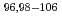 Ru in the energy from 10
Ru in the energy from 10 eV to 20 MeV. The statistical model code POD, which was based on the Hauser-Feshbach theory, was used to evaluate cross sections above 10 eV. Parameters required as input to the POD code were determined by reflecting the latest knowledge on nuclear physics. As for the neutron optical model parameters, we employed the values obtained by Kunieda
eV to 20 MeV. The statistical model code POD, which was based on the Hauser-Feshbach theory, was used to evaluate cross sections above 10 eV. Parameters required as input to the POD code were determined by reflecting the latest knowledge on nuclear physics. As for the neutron optical model parameters, we employed the values obtained by Kunieda  using the coupled-channel method. The evaluated results reproduce existing experimental data very well.
using the coupled-channel method. The evaluated results reproduce existing experimental data very well.