Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ozu, Akira; Kureta, Masatoshi; Kobayashi, Nozomi*; Takase, Misao*; Kurata, Noritaka*; Tobita, Hiroshi; Haruyama, Mitsuo; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Suzuki, Hiroyuki; Sakasai, Kaoru; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ota, Masayuki; Kwon, Saerom; Ochiai, Kentaro; Sato, Satoshi; Konno, Chikara
no journal, ,
We perform a benchmark experiment with a Mo assembly and the DT neutron source at JAEA/FNS to validate recent nuclear data of Mo. A rectangular Mo assembly, the size of which is 253 mm  253 mm
253 mm  354 mm, is covered with 51, 202 and 253 mm thick Li2O blocks around the front, side and back surfaces in order to eliminate background neutrons in the measuring points, respectively. The assembly is placed at a distance of 150 mm from the DT neutron source. Several dosimetry reaction rates and fission rates measured in the assembly are compared to those calculated with the Monte Carlo neutron transport code MCNP5-1.40 and the recent nuclear data libraries of ENDF/B-VII.1, JEFF-3.2 and JENDL-4.0 (FENDL-3.0). The ratios of the calculated reaction rates to the experimental ones generally decrease with the increasing distance from the front surface of the assembly. Reasons of the discrepancies are discussed in the presentation.
354 mm, is covered with 51, 202 and 253 mm thick Li2O blocks around the front, side and back surfaces in order to eliminate background neutrons in the measuring points, respectively. The assembly is placed at a distance of 150 mm from the DT neutron source. Several dosimetry reaction rates and fission rates measured in the assembly are compared to those calculated with the Monte Carlo neutron transport code MCNP5-1.40 and the recent nuclear data libraries of ENDF/B-VII.1, JEFF-3.2 and JENDL-4.0 (FENDL-3.0). The ratios of the calculated reaction rates to the experimental ones generally decrease with the increasing distance from the front surface of the assembly. Reasons of the discrepancies are discussed in the presentation.
Kwon, Saerom; Ota, Masayuki; Ochiai, Kentaro; Sato, Satoshi; Konno, Chikara
no journal, ,
A benchmark experiment on copper with DT neutron source was performed 20 years ago at JAEA/FNS. However, the calculated results tended to underestimate the measured data related to lower energy neutrons below a few keV in the experiment, which suggested that the measured data might be affected by neutrons scattered in the concrete wall of the experiment room or other surroundings. Therefore, we have carried out an additional integral experiment on copper, where a copper assembly was covered with Li O blocks to reduce neutrons scattered in the concrete wall. We used the Monte Carlo neutron transport code, MCNP5-1.40 and the recent nuclear data libraries, ENDF/B-VII.1, JEFF-3.2, JENDL-4.0 and FENDL-3.0 (ENDF/B-VII.0) for the experiment analysis. JENDL/D-99 was used as dosimetry cross section data. The calculated reaction rates of the
O blocks to reduce neutrons scattered in the concrete wall. We used the Monte Carlo neutron transport code, MCNP5-1.40 and the recent nuclear data libraries, ENDF/B-VII.1, JEFF-3.2, JENDL-4.0 and FENDL-3.0 (ENDF/B-VII.0) for the experiment analysis. JENDL/D-99 was used as dosimetry cross section data. The calculated reaction rates of the  Au(n,
Au(n, )
)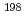 Au reaction with all the nuclear data libraries still underestimate the measured data, although the underestimation was improved compared to the previous result with JENDL-4.0 in particular. We found out that the nuclear data of copper caused this underestimation problem.
Au reaction with all the nuclear data libraries still underestimate the measured data, although the underestimation was improved compared to the previous result with JENDL-4.0 in particular. We found out that the nuclear data of copper caused this underestimation problem.
Motooka, Takafumi; Suzuki, Miho; Tomita, Takeshi; Kimura, Yasuhiko; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
no journal, ,
To investigate the migration of seawater components to a spent fuel cladding tube, cross-sectional observation for spent fuel cladding tube immersed in diluted artificial seawater at 80 for 300 hours was conducted with EPMA. Spent fuel cladding tube having crud layer and zirconium oxide layer showed the adhesion of seawater components (Mg, Cl) on the cladding and no penetration of seawater components into the cladding.
Goto, Minoru; Okumura, Keisuke; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Matsuura, Hideaki*; Nakaya, Hiroyuki*; Katayama, Kazunari*
no journal, ,
A feasibility study of a High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) for tritium production using  Li(n,
Li(n, )T reaction for fusion reactors has been conducted. In this study, the burn-up chain was modified to treat
)T reaction for fusion reactors has been conducted. In this study, the burn-up chain was modified to treat  Li(n,a)T reaction directory in neutronics calculations, and then the feasibility study was performed from the view point of nuclear characteristics using SRAC code system, which has experience in neutronics analysis of HTGRs.
Li(n,a)T reaction directory in neutronics calculations, and then the feasibility study was performed from the view point of nuclear characteristics using SRAC code system, which has experience in neutronics analysis of HTGRs.
Tochio, Daisuke; Fujimoto, Nozomu
no journal, ,
Helium gas used in future HTGR should be mixed in the cooling system from the view point of structure integrity and temperature control. Primary helium gas flows from 4 helium gas circulators (HGCs) to the reactor in HTTR. The primary helium gas from circulator has different temperature. It affect to reactor inlet coolant temperature control due to the lack of helium gas mixing. Now the problem is cleared by using of the mean mixing temperature with the temperature at each HGCs. From this experience, there is the possibility that the lack of helium mixing affect to the turbine inlet temperature control. In this report, thermal-hydraulic analysis in the primary cooling system of the HTTR was conducted and the mixing behavior in the primary cooling system is clarified.
Nishihara, Tetsuo
no journal, ,
Research and development for commercialization of the high temperature gas cooled reactor (HTGR) as the generation IV nuclear system is carried out in the world because the HTGR has inherent safety features and can supply high temperature heat for electricity generation as well as hydrogen production and desalination. Heat application system of the HTGR shall provide adequate safety from the viewpoint of nuclear safety and the economic competitiveness to conventional hydrogen plants. This report describes the safety requirement of the HTGR coupled with a hydrogen plant and the safety design requirement to categorize the hydrogen plant as a conventional chemical plant.

Nagai, Takayuki; Sasage, Kenichi; Oyama, Koichi; Sato, Nobuaki*; Inose, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Inose, Takehiko*; Nishizawa, Daiji*; Miyauchi, Atsushi; Oyama, Koichi; Yamakawa, Atsushi*; Nagai, Takayuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakayama, Mariko*; Kobayashi, Masato*; Kawakubo, Masahiro*; Suzuki, Kei*; Eto, Jiro*; Nakayama, Masashi; Ono, Hirokazu; Asano, Hidekazu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Kiwamu; Ueno, Takashi; Yasuda, Mari; Shimada, Asako; Hoshi, Akiko; Kameo, Yutaka
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 in aqueous hydrogen peroxide solution
in aqueous hydrogen peroxide solutionKumagai, Yuta; Takano, Masahide; Watanabe, Masayuki
no journal, ,
In the severe accident at Fukushima, the reactor cores of Units 1, 2 and 3 overheated and largely melted. The molten fuel debris possibly dissolves in water due to the intense ionizing radiations in the reactors. Ionizing radiations decompose water and generate hydrogen peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide may oxidize uranium in the debris from tetravalent to more soluble hexavalent. In order to understand the effect of hydrogen peroxide on dissolution of the fuel debris, leaching of uranium from simulated fuel debris in aqueous hydrogen peroxide solution was studied. The simulated debris used in this study was solid solution of UO and ZrO
and ZrO ((U,Zr)O
((U,Zr)O ). The leaching experiments were performed on (U,Zr)O
). The leaching experiments were performed on (U,Zr)O and on UO
and on UO for comparison. The observed leaching rate of uranium from (U,Zr)O
for comparison. The observed leaching rate of uranium from (U,Zr)O was lower than that measured for UO
was lower than that measured for UO . The uranium concentration leached from (U,Zr)O
. The uranium concentration leached from (U,Zr)O was only about 1 % of consumed hydrogen peroxide, whereas that from UO
was only about 1 % of consumed hydrogen peroxide, whereas that from UO was as high as 70 % of consumed hydrogen peroxide. The results suggest that dissolution of uranium from (U,Zr)O
was as high as 70 % of consumed hydrogen peroxide. The results suggest that dissolution of uranium from (U,Zr)O was inhibited due to decomposition of hydrogen peroxide on (U,Zr)O
was inhibited due to decomposition of hydrogen peroxide on (U,Zr)O without oxidation of uranium.
without oxidation of uranium.
Wu, H.; Udagawa, Yutaka; Narukawa, Takafumi; Amaya, Masaki
no journal, ,
Sato, Shunsuke*; Nauchi, Yasushi*; Hayakawa, Takehito; Kimura, Yasuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
no journal, ,
The  ray spectrum measurement was conducted for a sample taken from a PWR lead used assembly and photon spectrum data for higher energy region than usual case was obtained. Burnup calculation adopting MVP-BURN code was carried out for the sample and the agreement between experimental data and the calculation results was confirmed.
ray spectrum measurement was conducted for a sample taken from a PWR lead used assembly and photon spectrum data for higher energy region than usual case was obtained. Burnup calculation adopting MVP-BURN code was carried out for the sample and the agreement between experimental data and the calculation results was confirmed.
Ashida, Takashi; Sakata, Hideaki; Miyamoto, Kazuyuki; Nakamura, Toshiyuki; Ito, Hideaki; Tobita, Koichi; Koga, Kazuhiro*; Ohara, Norikazu*; Ino, Hiroichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Eguchi, Shohei; Takemoto, Noriyuki; Tanimoto, Masataka; Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Ito, Haruhiko; Araki, Masanori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,
We used laser-induced fluorescence imaging with a varying beam focal point to observe ablation plumes from metal and oxide samples of gadolinium. The plumes expand vertically when the focal point is far from the sample surface. In contrast, the plume becomes hemispherical when the focal point is on the sample surface. In addition, the internal plume structure and the composition of the ablated atomic and ionic particles also vary significantly. The fluorescence intensity of a plume from a metal sample is greater than that from an oxide sample, which suggests that the number of monatomic species produced in each plume differs. For both the metal and oxide samples, the most intense fluorescence from atomic (ionic) species is observed with the beam focal point at 3-4 mm (2 mm) from the sample surface.
Tamura, Koji; Ishigami, Ryoya*
no journal, ,
The laser cutting of thick steel plates with 30 kW fiber laser has been developed. Output of the introduced fiber laser (30 kW, IPG YLS-30000) was collimated with a pair of focusing lens, and was irradiated to stainless steel and carbon steel plates, which were transferred at a constant speed. Assist gas of air at a flow rate of about 500 l/min was used. It was demonstrated in this experiment that thick stainless steel plates up to 300 mm and carbon steel plates up to 300 mm were successfully cut. These results are quite promising for the application of laser cutting to the actual nuclear decommissioning.
Tada, Kenichi; Nagaya, Yasunobu
no journal, ,
JAEA has been developed the nuclear data processing system FRENDY (FRom Evaluated Nuclear Data librarY to any application). In this presentation, verification of scattering cross section generation in the thermal energy range is described.