Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hamasaki, Manabu*; Yoshinaka, Kazuyuki
no journal, ,
In 2008, the Atomic Energy Society of Japan (AESJ) launched its own Continuing Professional Development (CPD) registration system. But the system was not largely used by the Society members, which obliged to cease it only one year after the launch. In 2015 the AESJ Education Committee renewed and resumed its CPD registration system under the "Sunshine Policy", reflecting the lessons learned from the past failure. The renewed system has already attracted many users. On the other hand, some issues are emerging, including that the repeat users are quite limited.
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Enoto, Teruaki*; Wada, Yuki*; Furuta, Yoshihiro*; Nakazawa, Kazuhiro*; Yuasa, Takayuki*; Okuda, Kazufumi*; Makishima, Kazuo*; Sato, Mitsuteru*; Sato, Yosuke*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Furutachi, Naoya; Minato, Futoshi; Iwamoto, Osamu
no journal, ,
Except for extremely light nuclei and neutron rich nuclei, generally the density of nuclear excited states around neutron threshold energy is very high, and therefore it is very difficult to predict energy and width of resonance precisely. On the other hand, it has been known that the resonance parameters have statistical property with high density of excited states. There is a theoretical method to calculate cross section in resonance region by generating resonance parameters randomly utilizing the statistical properties of the resonance parameters. Such a method can reflect a theoretical information of resonance on a nuclear data evaluation for nuclei with no experimental data, such as fission products. However, studies for how to determine a representative value of the cross section randomly calculated, and what is an uncertainty from the randomness, are insufficient. Therefore, in this study, we calculated the cross section in the resonance region using randomly generated resonance parameters, and derived the probability distribution of the cross section by calculating cross section repetitively using resonance parameter sets generated from different random seeds. By using this density distribution, we discuss the behavior of the statistically reasonable cross section, and uncertainty from statistical fluctuation.
Ichihara, Akira
no journal, ,
In JAEA we are in charge of the revision of the Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library, JENDL-4.0. An evaluation activity of the next JENDL project is being carried out for structural materials in nuclear power plants. Zirconium is an important element which is used in the fuel rods and the channel boxes of fuel assemblies in light-water reactors. In this study, we calculated neutron cross sections theoretically in the incident energy range between 0.1 and 20 MeV. In the next JENDL, metastable state production data will be supplemented substantially in order to contribute to the evaluation of radioactivities. By adjusting parameters of nuclear reaction models, we could obtain the metastable state production cross sections which are consistent with the experimental data in the (n,2n) and (n,p) reactions of Zr-90.
Kimura, Yoshiki; Tomikawa, Hirofumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takeuchi, Masayuki; Miyazaki, Yasunori; Kofuji, Hirohide
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Goto, Takahiro*; Matsubara, Ryuta*; Hamamoto, Takafumi*; Fujisaki, Kiyoshi*; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Taniguchi, Naoki
no journal, ,
For the purpose of improvement of long-term glass corrosion model, we conducted immersion tests with specimens of carbon steel and simulated waste glass at 50 C and 80
C and 80 C under nitrogen gas atmosphere. We also conducted control immersion tests with a specimen of carbon steel or simulated waste glass under the same conditions. After the immersion tests, we determined glass corrosion rates and secondary phases on the surface of carbon steel specimen. Glass corrosion rates for the immersion tests with specimens of carbon steel and simulated waste glass were three times larger than those for the control immersion tests with simulated waste glass specimen. With X-ray diffraction, several peaks associated with an iron silicate mineral were identified. This observation is consistent with the results of geochemical calculation based on solution data and published study using carbon steel and simulated waste glass.
C under nitrogen gas atmosphere. We also conducted control immersion tests with a specimen of carbon steel or simulated waste glass under the same conditions. After the immersion tests, we determined glass corrosion rates and secondary phases on the surface of carbon steel specimen. Glass corrosion rates for the immersion tests with specimens of carbon steel and simulated waste glass were three times larger than those for the control immersion tests with simulated waste glass specimen. With X-ray diffraction, several peaks associated with an iron silicate mineral were identified. This observation is consistent with the results of geochemical calculation based on solution data and published study using carbon steel and simulated waste glass.
Yamamoto, Masahiko; Do, V. K.; Taguchi, Shigeo; Inada, Satoshi; Takamura, Yuzuru*; Kuno, Takehiko
no journal, ,
In this research, we focused on liquid electrode plasma optical emission spectrometry(LEP-OES), which is effective method to minimize the analytical device, to determine technetium (Tc) in reprocessing solution. Measurement conditions such as applied voltage, output pulse sequence and nitric acid concentration were optimized. Consequently, measurement condition at voltage of 1000V, pulse width of 2ms, pulse interval of 8ms, pulse number of 50 and nitric acid concentration of 0.4M offers the high peak intensity with good reproducibility. Also, interference of coexisting elements in sample from reprocessing steam was investigated for Tc peak at 254.3nm, 261.0nm, 264.7nm. The spectral interference of iron was observed at Tc peak of 254.3nm and 261.0nm although no spectral interference were observed at 264.7nm peak. It was found that determination of Tc by LEP-OES can be possible using this peak.
Yokoyama, Keisuke; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Tanno, Takashi; Oka, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Amamoto, Ippei; Oyama, Koichi; Nagano, Yuichi*; Jantzen, T.*; Hack, K.*; Fukayama, Daigen*
no journal, ,
As the vitrified study of the high-level radioactive waste is usually carried out under the high-temperature circumstance, it spends a lot of time and effort. The actual experiments and/or measurement, therefore, should be undertaken rationally after ascertaining the behaviors of target materials by the theoretical calculation, if possible. From such point of view, the construction of phase diagrams is considered after obtaining necessary thermodynamic properties from existing phase diagrams by CALPHAD method and/or published data. In this paper, several phase diagrams are presented such as the borosilicate glass which is currently used as the vitrified medium for the HLW, the iron-phosphate glass which will be potential vitrified medium for various wastes. Some phase diagrams are also prepared for the vitrified wastes which was loaded fission products such as molybdenum, palladium, etc..
 4.1 with TOF experiments at OKTAVIAN
4.1 with TOF experiments at OKTAVIANIsobe, Yuta*; Yoshida, Shigeo*; Konno, Chikara
no journal, ,
A benchmark test of ENDF/B-VIII 4.1 being developed in US were carried out with Co and Cu experiments in the OKTAVIAN TOF experiments. For the comparison, ENDF/B-VII.1 and JENDL-4.0 were also used. As a result, it is found out that the analysis results with ENDF/B-VIII
4.1 being developed in US were carried out with Co and Cu experiments in the OKTAVIAN TOF experiments. For the comparison, ENDF/B-VII.1 and JENDL-4.0 were also used. As a result, it is found out that the analysis results with ENDF/B-VIII 4.1 agreed the measured data better than those with the other nuclear data in the Co experiment, while they are in worse agreement with the measured data than those with the other nuclear data in the Cu experiment. It is also demonstrated that the differences between the analysis results with ENDF/B-VIII
4.1 agreed the measured data better than those with the other nuclear data in the Co experiment, while they are in worse agreement with the measured data than those with the other nuclear data in the Cu experiment. It is also demonstrated that the differences between the analysis results with ENDF/B-VIII 4.1 and ENDF/B-VII.1 come from the inelastic scattering data to continuum states in
4.1 and ENDF/B-VII.1 come from the inelastic scattering data to continuum states in  Co and all the inelastic scattering data in
Co and all the inelastic scattering data in  Cu and
Cu and  Cu.
Cu.
Kwon, Saerom*; Konno, Chikara; Ota, Masayuki*; Ochiai, Kentaro*; Suzuki, Hiromitsu*
no journal, ,
We have studied reasons of an unphysical dip around 20 MeV in the DPA energy spectrum calculated with FENDL-3.1c for the A-FNS design. It was found out that recoil nuclei data etc. in  Fe of FENDL-3.1c had some problems around 20 MeV. The unphysical dip around 20 MeV in the DPA energy spectrum was resolve by modifying the problems. This issue occurred in not only
Fe of FENDL-3.1c had some problems around 20 MeV. The unphysical dip around 20 MeV in the DPA energy spectrum was resolve by modifying the problems. This issue occurred in not only  Fe but also a lot of nuclei of FENDL-3.1c. FENDL-3.1c should be revised.
Fe but also a lot of nuclei of FENDL-3.1c. FENDL-3.1c should be revised.
Imoto, Jumpei; Miwa, Shuhei; Takano, Masahide; Osaka, Masahiko
no journal, ,
In order to improve the boron release model from the molten BWR control blade under LWR severe accident, chemical reaction during the boron release was investigated experimentally. Thermal analysis of the Fe-B compound formed in molten control blade was carried out and the reaction products were analyzed. Fe-B-O compound was detected as reaction product at oxidation of the Fe B compound in 1200-1400K using X-ray diffraction. It was found that B release from Fe
B compound in 1200-1400K using X-ray diffraction. It was found that B release from Fe B occurred via oxidation formation of B
B occurred via oxidation formation of B O
O and stable Fe-B-O compound.
and stable Fe-B-O compound.
Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko
no journal, ,
Many neutrons are produced in forward directions by intermediate-energy proton-induced reactions. While it is known that collective motion in a target nucleus plays important role in this neutron production, validity of theoretical model and nuclear-data library has not been examined well due to a lack of experimental data. Hence, we obtained systematic data of neutron-production double-differential cross section in the most-forward direction. The experiment was performed at TIARA of Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute, QST. 20-, and 34-MeV proton beams were bombarded upon carbon, aluminum, iron, and lead target, and the neutrons produced in the most-forward direction were led to experimental room passing through a collimator. A scintillation detector was used to the neutron detection. In comparison with the calculation results of PHITS using a theoretical model INCL and a nuclear-data library JENDL-4.0/HE, it was found that JENDL-4.0/HE reproduces the experimental data better than the INCL does.
Ho, H. Q.; Honda, Yuki; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Ishii, Toshiaki; Ishitsuka, Etsuo
no journal, ,
Miyahara, Naoya; Suzuki, Eriko; Uesawa, Shinichiro; Sato, Isamu*; Matsuura, Haruaki*; Hagura, Naoto*; Koshigoe, Koki*; Osaka, Masahiko
no journal, ,
We have started the fundamental research on detailed aerosol deposition phenomena at the walls of containment vessel and reactor building to develop a reasonable evaluation model of aerosol deposition amount which have a large influence on release amount to the environment. In this study, an aerosol deposition test onto various materials was conducted to investigate the physical and chemical phenomena related to aerosol deposition. As a result, important phenomena such as aerosol penetration into concrete pore were observed, which should be considered in the aerosol deposition model.
Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Sato, Tatsuhiko
no journal, ,
More and more attention is payed to neutrino-induced nuclear reactions recently in terms of fundamental studies such as neutrino oscillation and application technologies such as remote observation of nuclear reactors. On the other hand, the general purpose radiation transport code PHITS does not have nuclear reaction models or nuclear data dedicated to neutrino-induced reactions therefore neutrinos penetrated materials without any reactions. In this study, the reaction model for the reaction most important for neutrino detection,  H(
H(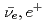 )n is developed. The reaction cross section was taken from the Strumia's systematics which ranges up to 200 MeV of incident energy. The momenta of produced positron and neutron were determined based on the conservation laws and the fluctuation given in the Strumia's systematics. The result of demonstration mocking a reactor activity monitoring device showed that 3
)n is developed. The reaction cross section was taken from the Strumia's systematics which ranges up to 200 MeV of incident energy. The momenta of produced positron and neutron were determined based on the conservation laws and the fluctuation given in the Strumia's systematics. The result of demonstration mocking a reactor activity monitoring device showed that 3 10
10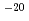 (count/
(count/ decay) is expected and therefore the model is working. This model will play a promising role to promote PHITS in the field of fundamental physics experiments and neutrino application engineering.
decay) is expected and therefore the model is working. This model will play a promising role to promote PHITS in the field of fundamental physics experiments and neutrino application engineering.
Yamashita, Susumu; Tada, Kenichi; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Suyama, Kenya
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Kubo, Shigenobu; Hayafune, Hiroki; Shimakawa, Yoshio*; Uzawa, Masayuki*; Miyagawa, Takayuki*; Uchita, Masato*
no journal, ,
A loop-type sodium-cooled reactor which considers reduction of development load and utilization of international collaboration has been studied based on the next generation sodium-cooled reactor studied in the FaCT project.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Yamamoto, Akio*; Kitada, Takanori*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English