Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 using vibrational spectroscopies
using vibrational spectroscopiesSakurai, Yoko; Machida, Akihiko; Aoki, Katsutoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Yasuoka, Hiroshi; Haga, Yoshinori; Onuki, Yoshichika
no journal, ,
T-dependence and anisotropy of Knight shift and spin-lattice relaxation time T1 of In-NMR have been determined in heavy fermion superconductor CeIrIn . Knight shift and T1 show a strong anisotropy. Knight shift versus static susceptibility plot is non-linear at low temperatures, indicating that the hyperfine coupling depends on temperature. The origin of hyperfine interaction and anisotropy of spin fluctuations will be discussed.
. Knight shift and T1 show a strong anisotropy. Knight shift versus static susceptibility plot is non-linear at low temperatures, indicating that the hyperfine coupling depends on temperature. The origin of hyperfine interaction and anisotropy of spin fluctuations will be discussed.
Hosaka, Koichi; Itakura, Ryuji; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yamanouchi, Kaoru*; Yokoyama, Atsushi
no journal, ,
In intense laser fields, molecules are decomposed into fragments through a number of competing dissociative ionization pathways. We investigate the dissociative ionization dynamics of ethanol in intense laser fields with photoelectron-photoion coincidence momentum imaging. The channel-specific photoelectron spectra reveal the electronic states prepared just after ionization, depending both on the decomposition pathways and on the temporal profile of laser pulses.
Sato, Shinichiro; Sai, Hitoshi*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Shimazaki, Kazunori*; Oshima, Takeshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kawasuso, Atsuo; Maekawa, Masaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Maekawa, Fujio
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 1s X-ray resonant emission spectroscopy of LuFe
1s X-ray resonant emission spectroscopy of LuFe O
O single crystal
single crystalAgui, Akane; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Kuroda, Tomoko*; Hayakawa, Hironori*; Maeda, Daisuke*; Michiuchi, Takamasa*; Ikeda, Naoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yokota, Terufumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Igarashi, Takahiro; Nakazawa, Tetsuya; Tsuru, Tomohito; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Fe
Fe (C
(C O
O )
) (H
(H O)
O)
Matsuda, Masaaki; Honda, Zentaro*
no journal, ,
We performed neutron inelastic scattering experiments in Na Fe
Fe (C
(C O
O )
) (H
(H O)
O) that consists of two-leg spin ladders of Fe
that consists of two-leg spin ladders of Fe ions. We observed sharp magnetic excitation peaks around
ions. We observed sharp magnetic excitation peaks around  3.5 meV and
3.5 meV and  5.3 meV. This result shows that the magnetic excitations originate from almost isolated dimers, indicating that the interaction along the leg direction is negligibly small.
5.3 meV. This result shows that the magnetic excitations originate from almost isolated dimers, indicating that the interaction along the leg direction is negligibly small.
 O
O
Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Fukunaga, Mamoru*; Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Noda, Yukio*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Sr
Sr NiO
NiO and La
and La Ba
Ba CuO
CuO
Wakimoto, Shuichi; Ishii, Kenji; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Mizuki, Junichiro; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Noda, Yukio*; Adachi, Tadashi*; Koike, Yoji*; Fujita, Masaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -BaTiO
-BaTiO solid solution
solid solutionYoneda, Yasuhiro; Yoshii, Kenji; Mori, Shigeo*
no journal, ,
Local structure analysis of 0.75BiFeO -0.25BaTiO
-0.25BaTiO solid solution was carried out by a synchrotron radiation X-ray pair-distribution function (PDF) method with the temperature range from room temperature to 900
solid solution was carried out by a synchrotron radiation X-ray pair-distribution function (PDF) method with the temperature range from room temperature to 900 C. The 0.75BiFeO
C. The 0.75BiFeO -0.25BaTiO
-0.25BaTiO occurred two phase transitions. The average structure of changed from low-temperature rhombohedral structure to pseudo-cubic structure at 500
occurred two phase transitions. The average structure of changed from low-temperature rhombohedral structure to pseudo-cubic structure at 500 C, but the local structure unchanged. The local structure changed at second phase transition from pseudo cubic structure to cubic structure at 800
C, but the local structure unchanged. The local structure changed at second phase transition from pseudo cubic structure to cubic structure at 800 C. The local structure of the pseudo-cubic phase can be reproduced not by the average cubic structure but by the distorted rhombohedral structure.
C. The local structure of the pseudo-cubic phase can be reproduced not by the average cubic structure but by the distorted rhombohedral structure.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Takahashi, Nobuaki; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Ito, Shinichi*; Aizawa, Kazuya; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -ray spectroscopy of
-ray spectroscopy of 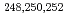 Cf using neutron-transfer reactions
Cf using neutron-transfer reactionsTakahashi, Ryuta; Ishii, Tetsuro; Nagae, Daisuke; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Ishii, Yasuo; Matsuda, Makoto; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Makii, Hiroyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fujimori, Shinichi; Okochi, Takuo; Okane, Tetsuo; Saito, Yuji; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Fujimori, Atsushi; Aoki, Dai*; Ikeda, Shugo*; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Haga, Yoshinori; et al.
no journal, ,
We have performed synchrotron radiation photoemission study on UFeGa , UB
, UB , UPd
, UPd , UPd
, UPd Al
Al , UNi
, UNi Al
Al , URu
, URu Si
Si , UPt
, UPt , UGe
, UGe , UIr, UPtGa
, UIr, UPtGa , USb
, USb , and UN. Their electronic structures are discussed based on their valence band and core-level photoelectron spectra.
, and UN. Their electronic structures are discussed based on their valence band and core-level photoelectron spectra.
Nakatani, Takeshi; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Ito, Takayoshi; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Aoyagi, Tetsuo; Ohara, Takashi; Otomo, Toshiya*; Yasu, Yoshiji*; Suzuki, Jiro*; Morishima, Takahiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have started the commissioning of the neutron scattering experiment instruments since May 2008 in MLF, J-PARC. Simultaneously, we have started the commissioning of the data acquisition and analysis software. Experimental users operate this software through the software framework which we have developed. The software framework was developed based on Python which is an object oriented script language. The system implemented with the software framework can seamlessly measure, analyze and visualize with some modules which are experimental control and data analysis. In this presentation, we report the process of the construction and the current status of the software.
Maruyama, Ryuji; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Soyama, Kazuhiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Yasuyuki; Narumi, Kazumasa; Chiba, Atsuya; Saito, Yuichi; Yamada, Keisuke; Ishikawa, Norito; Sugai, Hiroyuki; Maeda, Yoshihito
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English