Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Artikova, S.; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1004 - 1007, 2015/09
Sawabe, Yuki; Maruta, Tomofumi*; Liu, Y.*; Miura, Akihiko; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Ishiyama, Tatsuya; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Hayashi, Naoki
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1202 - 1205, 2015/09
no abstracts in English
Tamura, Fumihiko; Shimada, Taihei; Yoshii, Masahito*; Omori, Chihiro*; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Nomura, Masahiro; Toda, Makoto*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Hara, Keigo*
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.639 - 642, 2015/09
In the J-PARC RCS, magnetic alloy (MA) loaded rf cavities are employed to achieve a high accelerating voltage and to realize the dual harmonic operation, where a single cavity is driven by the fundamental accelerating rf and the second harmonic. The cavity is driven by a class-AB push-pull tetrode amplifier. R&D for a high power balun to mitigate the unbalanced output voltages of two tubes is undergoing. The balun is a rf transformer, which consists of a MA core and high voltage cables. In application to the RCS rf system, the maximum rf voltage is very high in the order of 15kV and suppression of corona dischages is a key. We presentthe techniques to suppress corona discharges. Also, the R&D status of cooling of the MA core and cables.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Higashi, Yasuo*; Kumada, Hiroaki*; Kurokawa, Shinichi*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Naito, Fujio*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.948 - 950, 2015/09
An accelerator based boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) facility is being planned at Okinawa institute of science and technology (OIST). The proton accelerator consists of a radio frequency quadrupole (RFQ) linac and a drift tube linac (DTL). The reqired beam power is 60 kW. The present beam energy and current are 10 MeV and 30 mA, respectively. The pulse length is 3.3 ms and the repetition rate is 60 Hz, therefore, the duty factor is 20%. In this paper, present designof this compact, midium current, high duty proton linac is presented.
Kawase, Masato; Takahashi, Hiroki
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.764 - 766, 2015/09
In most cases, the legacy method of the design and development of control systems starts after the production of devices. Therefore the control system design has been receiving a lower priority. And because constructing control processes unique for each device increases the number of types of the processes, such control systems lack maintainability, scalability and flexibility. To overcome these problems, the common control system using the model called "Machine Model" has been developed for the needs of constructing a unified control system. It also controls procedure-type processes for device status transitions. It allows us to unify control systems of different kinds of devices. In addition, because this method hides the procedural control of each device from upper application levels, it is possible to reduce the correction time of the application when it's modified or upgraded. This report is about development of the accelerator device control system using the machine model.
Otani, Masashi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Yoshida, Mitsuhiro*; Saito, Naohito; Kitamura, Ryo*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Kondo, Yasuhiro
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.56 - 61, 2015/09
We are developing a linac dedicated to the muon acceleration. It enables us to measure the muon anomalous magnetic moment with an accuracy of 0.1 ppm and search for electric dipole moment with a sensitivity of 10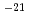 e
e cm to explore beyond Standard Model of elementary particle physics. As a first step for demonstration of the muon acceleration, we are developing the source of slow muon with which RFQ acceleration is conducted. This paper described status of these developments.
cm to explore beyond Standard Model of elementary particle physics. As a first step for demonstration of the muon acceleration, we are developing the source of slow muon with which RFQ acceleration is conducted. This paper described status of these developments.
Hori, Toshihiko; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Sato, Fumiaki; Fukui, Yuji*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.643 - 646, 2015/09
We are making efforts to decrease the fault rate of the high voltage power supplies for 324 MHz klystron. A new Veto module has been developed to prevent the 25 Hz trigger fan out module from malfunction due to the klystron discharge. As the result of installing the Veto module to the SDTL#16 klystron station, the klystron had never stopped for two months operation although the discharge occurred forty-two times during the operation. It confirmed that the installation of the Veto module is extremely useful to operate the klystron stably.
Usami, Hiroki; Takahashi, Hiroki; Komukai, Satoshi*
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.760 - 763, 2015/09
EU and JAEA are advancing development of Linear IFMIF Prototype Accelerator (LIPAc) control system jointly, but JAEA keeps developing central control system (CCS) mainly. Data transfer during an equipment control system of CCS and EU is performed through EPICS. JAEA is using PostgreSQL as 1 of development elements in CCS and is advancing development of the system to record the whole EPICS data of LIPAc (the data acquisition system). On the other hand, a data acquisition is performed using BEAUTY (Best Ever Archive Toolset, yet) in an element test of equipment at Europe. Therefore "1 client refers to collected data by more than one server machine" with "compatibility securement of data with BEAUTY" in case of development of the data acquisition system of CCS, and, it's necessary to consider "To do a data acquisition and backup work at the same time". For the moment, former 2 are in progress. And a demonstration of the data acquisition system is being performed simultaneously with commissioning in injector. The data acquisition system is collecting data of injector other ones, and the data reference by a monitor with CSS (Control System Studio) is also possible. We will report on the current state of the development of the data acquisition system by making reference to a result of the test by injector commissioning.
Shinoe, Kenji*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Umemori, Kensei*; Enami, Kazuhiro*; Sawamura, Masaru; Egi, Masato*; Furuya, Takaaki*
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.548 - 552, 2015/09
no abstracts in English
Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ueno, Akira; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Asano, Hiroyuki; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1040 - 1044, 2015/09
In order to satisfy the requirements of the J-PARC second stage, which will produce a 1MW beam, the Cs-free LaB -filament-driven H
-filament-driven H ion source was replaced to a cesiated RF-driven H
ion source was replaced to a cesiated RF-driven H ion source (RF ion source) during the summer shutdown period in 2014. By developing and testing the RF ion source on an off-line test-stand for about five years, it successfully and stably produced a peak current of more than 60mA within the acceptance of the following RFQ linac with the required beam duty-factor of more than 1.25% (500
ion source (RF ion source) during the summer shutdown period in 2014. By developing and testing the RF ion source on an off-line test-stand for about five years, it successfully and stably produced a peak current of more than 60mA within the acceptance of the following RFQ linac with the required beam duty-factor of more than 1.25% (500 s
s  25Hz). For about one year, the RF ion source has been operated with a peak current of 33mA routinely, which causes low beam loss in the J-PARC operated with a 500kW beam. It has been also operated with a peak current of 55mA for a few weeks in each two months for the J-PARC beam study striving toward the 1MW beam operation. The beam current is controlled within the error of
25Hz). For about one year, the RF ion source has been operated with a peak current of 33mA routinely, which causes low beam loss in the J-PARC operated with a 500kW beam. It has been also operated with a peak current of 55mA for a few weeks in each two months for the J-PARC beam study striving toward the 1MW beam operation. The beam current is controlled within the error of  0.1mA by feed-backing the RF power and the Cs density during the operation. Except for the only one failure of the internal RF-antenna in the beginning of the operation, there was no serious trouble. The RF ion source with the 33mA peak current operation is successfully operated for approximately 1100 hours.
0.1mA by feed-backing the RF power and the Cs density during the operation. Except for the only one failure of the internal RF-antenna in the beginning of the operation, there was no serious trouble. The RF ion source with the 33mA peak current operation is successfully operated for approximately 1100 hours.
Numata, Naoto*; Asakawa, Tomoyuki*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Umemori, Kensei*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Shinoe, Kenji*; Enami, Kazuhiro*; Egi, Masato*; Sakanaka, Shogo*; Michizono, Shinichiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.566 - 570, 2015/09
no abstracts in English
Yuyama, Takahiro; Ishibori, Ikuo; Kurashima, Satoshi; Yoshida, Kenichi; Ishizaka, Tomohisa; Chiba, Atsuya; Yamada, Keisuke; Yokoyama, Akihito; Usui, Aya; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; et al.
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.302 - 304, 2015/09
no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Masanobu; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Nomura, Masahiro; Omori, Chihiro*; Shimada, Taihei; Tamura, Fumihiko; Toda, Makoto*; Yoshii, Masahito*
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1008 - 1012, 2015/09
A harmonic number of J-PARC RCS is two, and when all RF buckets are filled with bunches, the major parts of the beam Fourier components are the even harmonics. However, the particle tracking simulation suggests that the odd harmonics promote asymmetry on each bunch shape and they rapidly increase under some conditions. When the asymmetry becomes larger and larger monotonously, it causes severe beam loss. Furthermore, although the odd harmonics remain small amplitude, an amplitude modulation of them makes a beam halo and causes small beam loss. We describe the particle tracking simulation results to investigate the odd harmonics.
Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kobayashi, Tetsuya*; Sato, Fumiaki; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Chishiro, Etsuji; Hirano, Koichiro; Fang, Z.*; Fukui, Yuji*; Hori, Toshihiko; Michizono, Shinichiro*
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1317 - 1320, 2015/09
In the J-PARC linac, an RF deflector installed in 3-MeV Medium Energy Beam Transport (MEBT1) is used to kick the unnecessary beam and the intermediate-pulse like a comb is created. The kicked beam leads to a scraper downstream the RF deflector and lose all kinetic energy. When the beam current increases to 50 mA of the design value, the heat load of a scraper to irradiate the kicked beam increases and its surface is predicted to be damaged. Therefore, we are preparing the tandem scrapers to reduce the damage. The half of the kicked beam leads to a scraper and the residual is to the other. The chopping operation is achieved by rotating the phase of the RF deflector in the periodic cycles by the LLRF system. We will introduce the phase rotation system and the test results.
Suganuma, Kazuaki; Shimoyama, Nobuyoshi*; Yonekyu, Naoyuki*; Taki, Yukina*; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.686 - 688, 2015/09
no abstracts in English
Hotchi, Hideaki
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.103 - 107, 2015/09
The J-PARC 3-GeV RCS have successfully achieved a 1-MW beam acceleration in January 2015. In this beam test, a major part of beam loss, such as space-charge induced beam loss, was well minimized by the injection painting technique. In addition, in the recent beam test in June, 2015, the transverse painting area was successfully expanded by correcting beta function beating during injection with the newly installed quadrupole corrector system. By this effort, a foil scattering part of beam loss during charge-exchange injection was further reduced. In this talk, recent progress of RCS beam commissioning will be reported especially focusing on our approaches to beam loss issues that we faced on the process of the beam power ramp-up.
Okabe, Kota; Maruta, Tomofumi*; Hotchi, Hideaki; Saha, P. K.; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Miura, Akihiko; Liu, Y.*; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.933 - 937, 2015/09
In a high power proton accelerator such as the 3-GeV rapid cycle synchrotron (RCS), small ratio of the beam loss such as beam halo can cause serious radiation dose. The suppression of the transverse beam halo is a key issue to provide high intensity beam for routine user operation at the RCS. If the transverse twiss parameter of the injection beam is not matched to the RCS optics, it will generates beam halo during the multi-turn injection. In order to suppress such beam halo, twiss parameters and dispersion matching are performed at the RCS injection point. In the beam matching process, we use the rms envelope equation solver with space charge effect to predict high intensity beam behavior. The beam profile measurement is done with wire scanner monitors at the downstream of the L3BT as well as multi-wire profile monitors at the RCS injection section. In this presentation, we introduce the transverse twiss parameter matching scheme at the RCS injection points.
Horino, Koki; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Tobita, Norimitsu; Ueno, Tomoaki*; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1175 - 1179, 2015/09
no abstracts in English
Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Ueno, Tomoaki*; Horino, Koki; Tobita, Norimitsu; Hayashi, Naoki; Kinsho, Michikazu; Irie, Yoshiro*; Okabe, Kota; Tani, Norio; Naito, Shingo*; et al.
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1169 - 1174, 2015/09
The new injection bump power supply for the shift bump magnet of the beam injection sub-systems at the J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex) 3-GeV RCS (Rapid Cycling Synchrotron) has been developed and manufactured. The power capacity of the new power supply was more than doubled with the injection beam energy upgrading of the LINAC (Linear Accelerator) from 181 MeV to 400 MeV. Furthermore, the low ripple noise on the output current was required to prevent the resonance of the RF shield loop at the ceramic duct with the excitation magnetic field. The power supply newly adopted a capacitor commutation method to form the trapezoid waveform pattern (bump waveform). This paper reports characteristic about the new power supply.
Tobita, Norimitsu; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Takeda, Osamu; Saeki, Riuji; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Kinsho, Michikazu; Muto, Masayoshi*
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1350 - 1354, 2015/09
no abstracts in English