Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takizuka, Tomonori; Urano, Hajime; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oyama, Naoyuki
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(6), p.799 - 806, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:44.73(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Dependence of the ELMy H-mode confinement on the beta has been investigated for a long time, but a common conclusion has not yet been obtained.The IPB98(y,2) scaling shows a strong degradation with beta, while DIII-D and JET experiments exhibited the absence of the beta degradation. Recent JT-60U experiment demonstrated that the strong beta degradation really exists for the ELMy H-mode. In the present paper, we analyze the JT-60U ELMy H-mode confinement database and confirm the strong power degradation of the confinement time, which corresponds to the strong beta degradation consistent with the above result. We analyze also the ITPA H-mode confinement database in detail. How the beta dependence of the confinement time is changed by the externally given parameters, such as the shape parameters, are investigated.
Miyato, Naoaki; Kishimoto, Yasuaki; Li, J.*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(5A), p.A335 - A340, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:63.29(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)It is well known that drift wave turbulence such as ion temperature gradient (ITG) driven turbulence and zonal flows nonlinearly generated from it play an important role in anomalous transport in tokamak plasmas. The zonal flows can regulate turbulent transport and trigger formation of transport barriers. In toroidal plasmas there are two kinds of zonal flows. One is stationary zonal flow which is dominant in a low safety factor ( ) region. The other is oscillatory ones appearing in a high
) region. The other is oscillatory ones appearing in a high  region. Global ITG turbulence simulations have shown that the frequencies of the oscillatory zonal flows do not vary continuously with a radius, but the oscillatory zonal flows have the same frequency over a certain radial region. It is considered that the nonlocal behaviour becomes weak for small
region. Global ITG turbulence simulations have shown that the frequencies of the oscillatory zonal flows do not vary continuously with a radius, but the oscillatory zonal flows have the same frequency over a certain radial region. It is considered that the nonlocal behaviour becomes weak for small 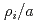 , where
, where 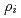 is an ion Larmor radius and
is an ion Larmor radius and  is a minor radius of a torus. In this research effects of
is a minor radius of a torus. In this research effects of 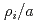 on the nonlocal behaviour of the zonal flows are investigated by global Landau fluid ITG simulations.
on the nonlocal behaviour of the zonal flows are investigated by global Landau fluid ITG simulations.
Yoshida, Maiko; Kobayashi, Shinji*; Urano, Hajime; Oyama, Naoyuki; Koide, Yoshihiko; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60 Team
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(5A), p.A209 - A215, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:35.81(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Kamada, Yutaka; Oyama, Naoyuki; Ide, Shunsuke; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Isayama, Akihiko; Fujita, Takaaki; Urano, Hajime; Suzuki, Takahiro; Yoshida, Maiko
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(5A), p.A419 - A427, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:46.96(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Ide, Shunsuke; Yoshida, Maiko; Koide, Yoshihiko; Fujita, Takaaki; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Kamada, Yutaka
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(5A), p.A63 - A70, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:72.94(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamada, Yutaka; Ide, Shunsuke; Koide, Yoshihiko
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(5A), p.A55 - A61, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:23.82(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Oyama, Naoyuki; Gohil, P.*; Horton, L. D.*; Hubbard, A. E.*; Hughes, J. W.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Kamiya, Kensaku; Leonard, A. W.*; Loarte, A.*; Maingi, R.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(5A), p.A171 - A181, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:93 Percentile:92.88(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oyama, Naoyuki; Bruskin, L. G.*; Mase, Atsushi*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Fujita, Takaaki
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(5A), p.A401 - A408, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:20.78(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Kensaku; Urano, Hajime; Koide, Yoshihiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60 Team
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(5A), p.A131 - A139, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:57.49(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Effects of plasma rotation and ripple loss on the Type-I ELMs have systematically studied in the JT-60U tokamak, scanning combinations of NBI at the three kinds of plasma volumes. New findings on the Type-I ELMs confirm to be smaller ELM energy loss per pedestal stored energy, DWELM/Wped, and faster ELM frequency, fELM, in the counter-NBI than co-NBI, keeping the power of ELM, PELM, per heating power crossing the separatrix, PSEP, constant. Balanced-NBI case is also intermediate between co- and counter-NBI. In addition, the product of PELM/PSEP decreases according to increase in the plasma volume, suggesting an increase in the inter-ELM transport due mainly to an enhancement in the ripple loss of fast ion.
Urano, Hajime; Kamiya, Kensaku; Koide, Yoshihiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60 Team
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(5A), p.A193 - A199, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:33.19(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The characteristics of the H-mode pedestal structure were investigated by conducting the power scans for a variation of the toroidal momentum sources at different toroidal field ripple in JT-60U. It was found that the pedestal pressure is increased by reduced loss power of fast ions, independently of toroidal rotation. However, the energy confinement is improved with the CO-directed toroidal momentum source at H-mode plasmas with small ripple loss.
Hubbard, A. E.*; Kamiya, Kensaku; Oyama, Naoyuki; Basse, N.*; Biewer, T.*; Edlund, E.*; Hughes, J. W.*; Lin, L.*; Porkolab, M.*; Rowan, W.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(5A), p.A121 - A129, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:46.96(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Dedicated experiments were carried out to compare the properties, fluctuation behaviour and access conditions of these regimes. A common shape was developed which scaled the plasma boundary except for aspect ratio. Scans of density and input power were carried out at several values of q95, so as to achieve ranges of dimensionless parameters. A striking similarity of access conditions was seen. These results suggest common physical mechanisms for the H-mode regimes, which do not depend critically on aspect ratio over this range. On the other hand, several differences in the details of the edge fluctuations were found, and will be reported. The effect of wall conditioning via boronization on the H-mode regimes will also be discussed.
Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Ito, Kimitaka*; Ito, Sanae*; Hoshino, Katsumichi; Fujisawa, Akihide*; Ejiri, Akira*; Takase, Yuichi*; Yagi, Masatoshi*; Shinohara, Koji; Uehara, Kazuya; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(5A), p.A377 - A386, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:61.77(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A bispector analysis and envelope moduration analysis of the potential oscillations of a low frequency (1kHz) oscillation, a high frequency (10-15kHz) oscillation and background turbulence are presented. The low frequency mode and the high frequency mode are considered to be a low frequency zonal flow and a geodesic acoustic mode respectively. We could found that the low frequency oscillation has a three wave interaction with the background turbulence as well as the high frequency oscillation does from the bicoherence (nonlinear coupling coefficient), biphase and envelope moduration relation. Apparently, the modulation of the high frequency mode by the low frequency mode was suggested, but it was found that the bicoherence between them is small and the modulation relation was not concluded. Therefore, it is concluded that the nonlinear interaction between the zonal flow - zonal flow system does not exist or the interaction of them is linear if any. Thus it was found that the marked nonlinear interaction occurs only in the turbulence - zonal flow system and not in the zonal flow - zonal flow system.