Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
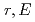 ) analysis
) analysisNakamura, Mitsutaka; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Kawakita, Yukinobu
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 551, p.351 - 354, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.97(Physics, Condensed Matter)The dynamic structure function in real space G(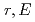 ) is deduced from the dynamical structure factor S(
) is deduced from the dynamical structure factor S(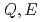 ) which can be obtained from inelastic neutron scattering measurement. In this study, we applied the G(
) which can be obtained from inelastic neutron scattering measurement. In this study, we applied the G(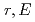 ) analysis to NaI which is a typical alkali halide crystal. The optic and acoustic phonons of NaI are widely separated in energy because the difference in mass between the constituent atoms is large. These characteristic properties certainly help us to evaluate the G(
) analysis to NaI which is a typical alkali halide crystal. The optic and acoustic phonons of NaI are widely separated in energy because the difference in mass between the constituent atoms is large. These characteristic properties certainly help us to evaluate the G(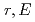 ) features associated with the phonon modes. We measured the S(
) features associated with the phonon modes. We measured the S(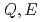 ) for NaI powder using the Fermi chopper spectrometer 4SEASONS at J-PARC, and converted S(
) for NaI powder using the Fermi chopper spectrometer 4SEASONS at J-PARC, and converted S(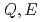 ) into G(
) into G(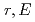 ) by newly developed software which utilizes the maximum entropy method. Our analysis clearly demonstrated the G(
) by newly developed software which utilizes the maximum entropy method. Our analysis clearly demonstrated the G(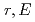 ) of TO mode oscillates out of phase with that of LA mode, which is physically reasonable. Further analyses will be given in the presentation.
) of TO mode oscillates out of phase with that of LA mode, which is physically reasonable. Further analyses will be given in the presentation.
Kawasaki, Takuro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Gong, W.*; Oikawa, Kenichi
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 551, p.460 - 463, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.97(Physics, Condensed Matter)Kawakita, Yukinobu; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Tahara, Shuta*; Maruyama, Kenji*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro*; Chiba, Kaori*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 551, p.291 - 296, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:43.16(Physics, Condensed Matter)There are elemental liquid metals with complex structures far from the hard sphere (HS) packing model. Liquid Bi has an asymmetric first peak in the structure factors S(Q). The pair distribution function g(r) exhibits strange distance ratio of 1:2 between the first and the second peaks. Since a HS model with two kinds of radius produces asymmetry of the main peak in S(Q), existence of short-lived covalent bonds was discussed. Contrarily, modulation of the atomic distribution by the Friedel oscillations of shielding electrons around metallic ions was discussed. To examine its bonding nature from viewpoints of dynamic correlation functions, we have measured neutron quasielastic scattering of liquid Bi by using cold disk chopper spectrometer installed at MLF of J-PARC. The van Hove function revealed that the shoulder structure located at a longer side of the first peak in g(r) exhibits a longer relaxation time than the main structures such as the first and second peaks.
Seki, Yoshichika; Shinohara, Takenao; Ueno, Wakana; Parker, J. D.*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 551, p.512 - 516, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:17.88(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Oikawa, Kenichi; Su, Y. H.; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Kawasaki, Takuro; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Hiroi, Kosuke; Harjo, S.; Parker, J. D.*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 551, p.436 - 442, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:26.43(Physics, Condensed Matter)Nakajima, Kenji; Kajimoto, Ryoichi
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 551, p.142 - 145, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)Hiroi, Kosuke; Shinohara, Takenao; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Parker, J. D.*; Su, Y. H.; Oikawa, Kenichi; Kai, Tetsuya; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 551, p.146 - 151, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:34.08(Physics, Condensed Matter)Kai, Tetsuya; Sato, Setsuo*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Su, Y. H.; Segawa, Mariko; Parker, J. D.*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Shinohara, Takenao; Oikawa, Kenichi; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 551, p.496 - 500, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:17.88(Physics, Condensed Matter)Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kambara, Wataru*; Iida, Kazuki*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Aoyama, Kazuhiro*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 551, p.480 - 483, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:34.08(Physics, Condensed Matter)Recently there has been an increasing need for inelastic neutron scattering experiments under some special environments such as magnetic fields, pressure and high temperatures. In order to obtain high quality data, the unnecessary scattering caused by sample environmental apparatus should be suppressed as much as possible. We have developed an oscillating radial collimator with a view to satisfying users' needs, which is specialized for the Fermi chopper spectrometer 4SEASONS at J-PARC.4SEASONS provides relatively high incident energies, and thus we chose hydrogen free metal sheets as the collimator blades. The control system of this oscillating radial collimator enables us to flexibly tune the oscillating pattern, such as the oscillating speed and oscillating angle. In this presentation, we report the performances and remaining issues of the newly developed oscillating radial collimator for 4SEASONS.
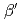 -(BEDT-TTF)
-(BEDT-TTF) ICl
ICl by inelastic neutron scattering
by inelastic neutron scatteringKawamura, Seiko; Matsuura, Masato*; Iguchi, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; Taniguchi, Hiromi*; Kubota, Aiko*; Sato, Kazuhiko*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Nakajima, Kenji
no journal, ,
It has been reported that in a molecular dimer-Mott insulator 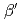 -(BEDT-TTF)
-(BEDT-TTF) ICl
ICl shows a relaxor-like dielectric response. The system exhibits a glassy ferroelectric state associated with charge disproportionation within the dimer, where a hole (
shows a relaxor-like dielectric response. The system exhibits a glassy ferroelectric state associated with charge disproportionation within the dimer, where a hole ( = 1/2) is localized, below
= 1/2) is localized, below  = 62K, and a long-range antiferromagnetic order below
= 62K, and a long-range antiferromagnetic order below  = 22K. For such molecule-based materials, it is expected that low-energy phonon modes are coupled with spin/charge degrees of freedom. In order to observe the phonon modes in this system, we have performed inelastic neutron scattering measurements in a wide wave-vector and energy region using a chopper spectrometer AMATERAS at J-PARC MLF. The lowest energy mode shows remarkable temperature dependence of its intensity, while any softening is not observed. The result suggests that this phonon mode reflects changes in the spin/charge dynamics.
= 22K. For such molecule-based materials, it is expected that low-energy phonon modes are coupled with spin/charge degrees of freedom. In order to observe the phonon modes in this system, we have performed inelastic neutron scattering measurements in a wide wave-vector and energy region using a chopper spectrometer AMATERAS at J-PARC MLF. The lowest energy mode shows remarkable temperature dependence of its intensity, while any softening is not observed. The result suggests that this phonon mode reflects changes in the spin/charge dynamics.
 =7/2 family Eu
=7/2 family Eu In
In (
( =Ni, Pd, Pt)
=Ni, Pd, Pt)Kaneko, Koji; Ikeda, Shugo*; Frontzek, M. D.*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Nakao, Akiko*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Ohara, Takashi; Homma, Yoshiya*; Kobayashi, Hisao*; Yamagami, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
Kofu, Maiko; Faraone, A.*; Tyagi, M.*; Nagao, Michihiro*; Yamamuro, Osamu*
no journal, ,
The self-diffusion of molecules in a liquid is basically governed by Fick's law. It is known that the self-part of the van Hove correlation function is written as the Gaussian function with respect to  and decays exponentially with time (Debye relaxation). In the case, the relaxation time obeys the relation
and decays exponentially with time (Debye relaxation). In the case, the relaxation time obeys the relation 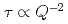 . In glass-forming materials, however, the relaxation process is often described by the non-Debye KWW function,
. In glass-forming materials, however, the relaxation process is often described by the non-Debye KWW function, ![$$exp [-(t/tau)^{beta}]$$](/search/images/EROGK4DQEBNS0KDUF3OHIYLVFFPHWXDCMV0GC5K3EQ.gif) . A natural question arises as to whether the relation
. A natural question arises as to whether the relation 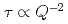 is valid for the non- Debye diffusion process. To address this issue, we have investigated in detail the
is valid for the non- Debye diffusion process. To address this issue, we have investigated in detail the  -dependence of the relaxation times for two different types of liquid, a molecular liquid (3-methylpentane) and an ionic liquid (C4mimTFSI). The measurements were done using neutron spin echo, backscattering and chopper spectrometers at NIST. Two crossover points were clearly found. The first crossover can be due to coupling with structural relaxation and the second one is Gaussian to non-Gaussian transition. This is the first clear experimental evidence for the two crossover.
-dependence of the relaxation times for two different types of liquid, a molecular liquid (3-methylpentane) and an ionic liquid (C4mimTFSI). The measurements were done using neutron spin echo, backscattering and chopper spectrometers at NIST. Two crossover points were clearly found. The first crossover can be due to coupling with structural relaxation and the second one is Gaussian to non-Gaussian transition. This is the first clear experimental evidence for the two crossover.
Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Iida, Kazuki*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Murai, Naoki
no journal, ,
Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Shibata, Kaoru; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Matsuura, Masato*; Endo, Hitoshi*; Seto, Hideki*; Ito, Shinichi*; Nakajima, Kenji; et al.
no journal, ,
Li, B.
no journal, ,
I will attend International Conference of Neutron Scattering 2017 in Daejeon, South Korea. The conference is the most popular one among the international neutron scattering community. The main content of this trip is as follows. To introduce the neutron scattering user program in J-PARC. This conference is great chance to introduce our facilities to the attendees from all over the world. It is expected to have broad discussion with those who are interested in our facilities. To report our latest study of AgCrSe . In this work, by combining X-ray and neutron scattering as well as density-functional-theory calculations, we provide a comprehensive picture of atomic dynamics. Most importantly, we have found a crystal can behave as a liquid in its thermal conduction. This property is brand new and may be helpful for future design of thermoelectric materials.
. In this work, by combining X-ray and neutron scattering as well as density-functional-theory calculations, we provide a comprehensive picture of atomic dynamics. Most importantly, we have found a crystal can behave as a liquid in its thermal conduction. This property is brand new and may be helpful for future design of thermoelectric materials.
Soyama, Kazuhiko; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Yamazaki, Dai; Miyata, Noboru*; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Kasai, Satoshi*; Suzuki, Junichi*
no journal, ,
Ohara, Takashi; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Oikawa, Kenichi; Kawasaki, Takuro; Kaneko, Koji; Tamura, Itaru; Nakao, Akiko*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Munakata, Koji*
no journal, ,
Shamoto, Shinichi; Matsuura, Masato*; Akatsu, Mitsuhiro*; Ito, Takashi; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Mori, Michiyasu; Onishi, Hiroaki; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kawamura, Seiko; Shibata, Kaoru; et al.
no journal, ,
We have studied the magnon density of state in yttrium iron garnet ranging from 0.02 meV to 20 meV by using spectrometers, DNA, AMATERAS, and 4SEASONS, at J-PARC/MLF. The E-dependence is well reproduced by a simple square-root function in this energy range.