Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Noguchi, Yuto; Maruyama, Takahito; Ueno, Kenichi; Komai, Masafumi; Takeda, Nobukazu; Kakudate, Satoshi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 109-111(Part B), p.1291 - 1295, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.46(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper reports the impact hammer test of the full-scale mock-up of ITER Blanket Remote Handling system (BRHS). Since the BRHS, which is composed of the articulated rail and the vehicle manipulator which travels on the rail deployed in the vacuum vessel, is subjected to the floor response spectrum with 14 G peak at 8 Hz, evaluation of dynamic response of the system is of essential importance. Recently impact hammer testing on the full-scale mock-up of the BRHS was carried out to verify the finite element method seismic analysis and to experimentally obtain the damping ratio of the system. The results showed that the mock-up has a vertical major natural mode with a natural frequency of 7.5 Hz and a damping ratio of 0.5%. While higher structural damping ratios is predicted in a high amplitude excitation such as major earthquake, it was confirmed that the experimental natural major frequencies are in agreement with the major frequencies obtained by elastic dynamic analysis.
Kim, Jae-Hwan; Nakamichi, Masaru
Fusion Engineering and Design, 109-111(Part B), p.1764 - 1768, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:76.68(Nuclear Science & Technology)Shirai, Hiroshi; Barabaschi, P.*; Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60SA Team
Fusion Engineering and Design, 109-111(Part B), p.1701 - 1708, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:89.37(Nuclear Science & Technology)The JT-60SA Project has shown steady progress toward the first plasma in 2019. JT-60SA is a superconducting tokamak designed to operate in the break-even conditions for a long pulse duration with a maximum plasma current of 5.5 MA. Design and fabrication of JT-60SA components shared by EU and Japan started in 2007. Assembly in the torus hall started in January 2013, and welding work of the vacuum vessel sectors is currently on going on the cryostat base. Other components such as TF coils, PF coils, power supplies, cryogenic system, cryostat vessel, thermal shields and so forth were or are being delivered to Naka site for installation, assembly and commissioning. This paper gives technical progress on fabrication, installation and assembly of tokamak components and ancillary systems, as well as progress of JT-60SA Research Plan being developed jointly by EU and Japanese fusion communities.
Konno, Chikara; Sato, Satoshi; Ota, Masayuki; Kwon, Saerom; Ochiai, Kentaro
Fusion Engineering and Design, 109-111(Part B), p.1649 - 1652, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:59.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)Recently we have examined KERMA factors and DPA cross section data in the latest official ACE files of JENDL-4.0, ENDF/B-VII.1, JEFF-3.2 and FENDL-3.0 in more detail and we found out the following new problems on the KERMA factors and DPA cross section data. (1) NJOY bugs and incorrect nuclear data generated KERMA factors and DPA cross section data of no increase with decreasing neutron energy in low neutron energy. (2) Huge helium production data caused drastically large KERMA factors and DPA cross section data in low neutron energy. (3) It seemed that NJOY could not adequately process capture cross section data in File 6, not File 12-15. (4) KERMA factors with the kinematics method are not correct for nuclear data libraries without detailed secondary particle data (energy-angular distribution data). These problems should be resolved based on our study.
Uto, Hiroyasu; Takase, Haruhiko; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Tobita, Kenji; Mori, Kazuo; Kudo, Tatsuya; Someya, Yoji; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Hoshino, Kazuo; Nakamura, Makoto; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 103, p.93 - 97, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:59.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)Conceptual design of in-vessel component including conducting shell has been investigated in Broader Approach (BA) DEMO design activities, in order to propose feasible DEMO reactor from plasma vertical stability and engineering viewpoint. The conducting shell for the plasma vertical stability will be incorporated behind blanket module, while the location must be close to the plasma surface as possible for the plasma stabilization. We evaluated dependence of the plasma vertical stability on the conducing shell parameters by using a 3-dimensional eddy current analysis code (EDDYCAL). The calculation results showed that the conducting shell requires more than 0.01 m thickness of Cu-alloy on DEMO. On the other hand, the electromagnetic force at the plasma disruption is a few times larger than no conducting shell case because of larger eddy current on conducting shell. The engineering design issues of in-vessel components for plasma vertical stability are presented.
Rivas, J. C.*; Nakamura, Makoto; Someya, Yoji; Takase, Haruhiko; Tobita, Kenji; Dies, J.*; Blas, A. de*; Fabbri, M.*; Riego, A.*
no journal, ,
In the frame of JAPAN-EU collaborative work for development of AINA code in 2014-2016, a version of AINA code has been developed for the Japanese DEMO WCPB design. During 2014, the AINA code was adapted from ITER to this new mission. A breeding blanket model was implemented in code. The configuration was changed to implement the design parameters of DEMO reactor. Finally, safety studies of plasma-wall transients affecting blanket region were performed. During 2015, plasma models were improved both for plasma core and for divertor (improved SOL model). Safety analyses affecting divertor were performed, considering thermohydraulic accidents and plasma transients where loss of control function was assumed. First analyses performed for the Japanese DEMO design show the behavior of the reactor during Ex-Vessel LOCA and during overpower events. The preliminary conclusions point to the possibility of considering the plasma control system as a safety important component.
Takase, Haruhiko; Uto, Hiroyasu; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Mori, Kazuo; Kudo, Tatsuya; Tobita, Kenji
no journal, ,
Pre-conceptual design of DEMO reactor has been preceded under collaboration Japan and Europe (Broader Approach activities (BA)). In the case of DEMO reactor, it is important for design of plasma position control to take into account the actual shape of vacuum vessel and in-vessel components precisely since the design condition of DEMO reactor is different from current tokamak devices and ITER (for example, installation of maintenance ports). To consider the DEMO design condition, the numerical simulation that consists of three modules has been developed. As results, (1) The time constants of eddy current in the breeding blankets are less than 10ms and there is no influence to passive stabilization effect. (2) The stabilization effect of conducting components decreases by considering installation of vertical maintenance port. The adoption of vertical port is related to the choice of the maintenance scenario.
Maruyama, Takahito; Noguchi, Yuto; Ueno, Kenichi; Takeda, Nobukazu; Kakudate, Satoshi
no journal, ,
In the vacuum vessel of ITER, the blanket modules will be handled by a huge robotic manipulator that travels on a rail which has been deployed into the vessel. This system is called the ITER blanket remote handling system. A robot vision system using two cameras was developed for rough positioning of that system. Previous testing confirmed that the manipulator satisfies the required positioning accuracy with that robot vision system. However, these tests also showed that camera calibration and edge detection take quite some time since precise camera positioning is needed to calibrate the cameras, and parameters need to be adjusted during operations for edge detection. To improve camera calibration, software image transformation to correct the misalignment of cameras was adopted. Using this method, positioning of cameras does not affect accuracy of the robot vision system, and thus precise positioning of cameras is not necessary. To improve edge detection, we adopted smaller apertures for a wider depth of field, edge dilation for connecting edges, and the Sobel operator for detecting the edges of the modules. These methods make edge detection robust and the adjustment of parameters unnecessary. Through testing we confirmed that these methods make the robot vision system more efficient.
Seki, Yohji; Ezato, Koichiro; Suzuki, Satoshi; Yokoyama, Kenji; Yamada, Hirokazu; Hirayama, Tomoyuki
no journal, ,
Through R&D for a plasma facing unit (PFU) of an ITER full-tungsten (W) divertor, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) succeeded in demonstrating the durability of the cyclic heat loaded W divertor which was shaped by an electrical discharge machining (EDM). To prevent melting of W, an adequate technology to meet requirements of a geometrical shape and tolerance of the PFU is one of the most important key issues in a manufacturing process. JAEA has evaluated the EDM to control the final shape tolerance of  0.25 mm. In order to examine an effect on durability of the micro-crack due to EDM, one polished W armor without the EDM and three W armors with the EDM were exposed to cyclic thermal loads. As the result, all of the W armors endured the repetitive heat load of 20 MW/m
0.25 mm. In order to examine an effect on durability of the micro-crack due to EDM, one polished W armor without the EDM and three W armors with the EDM were exposed to cyclic thermal loads. As the result, all of the W armors endured the repetitive heat load of 20 MW/m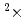 1000 cycles without any macro-cracks, which strongly encourages the realization of the PFU of ITER full-W divertor with various geometrical shape and high accuracy tolerance.
1000 cycles without any macro-cracks, which strongly encourages the realization of the PFU of ITER full-W divertor with various geometrical shape and high accuracy tolerance.