Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wei, P.; Xu, Y.; Nagata, Shinji*; Narumi, Kazumasa; Naramoto, Hiroshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206(1-4), p.233 - 236, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.64(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Okamura, Masachika*; Yasuno, Noriko*; Otsuka, Masako*; Tanaka, Atsushi; Shikazono, Naoya; Hase, Yoshihiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206, p.574 - 578, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:93 Percentile:97.62(Instruments & Instrumentation)Resent studies indicate that the ion beams have higher mutation frequency than low-LET radiations in plants but the difference in mutation spectrum still remains to be characterized. We investigated the efficiency of ion-beam irradiation combined with tissue culture in obtaining floral mutants. Leaves collected from carnation plants, cultivar Vital (cherry pink flowers with frilly petals), were irradiated with carbon ions or X-rays. They were cultured till the shoots regenerated. Sixteen mutants were obtained from 705 regenerated plants by carbon-ion irradiation. Those mutants were rich in variety, i.e., pink, dark pink, light pink, salmon, red, complex- and striped-color, and round and Dianthus-type petals were obtained. In contrast, 7 mutants obtained from 556 regenerated plants by X-rays were only pink, light pink and red. These results indicate that the ion beams could induce wider variety of flower-color and shape mutant than X-rays, and also indicate that the combined method of ion-beam irradiation with tissue culture is useful to obtain commercial varieties in a short time.
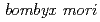
Tu, Z.; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Kiguchi, Kenji*; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206, p.591 - 595, 2003/05
no abstracts in English
Vacik, J.; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Narumi, Kazumasa; Yamamoto, Shunya; Abe, Hiroaki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206, p.395 - 398, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:52.47(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Umebayashi, Tsutomu; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Sumita, Taishi*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Tanaka, Shigeru; Asai, Keisuke*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206, p.264 - 267, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:82.19(Instruments & Instrumentation)Chromium (Cr) and niobium (Nb) were implanted into single-crystalline titanium dioxide (TiO ; rutile). After annealing at 600
; rutile). After annealing at 600 C for the Cr-implanted sample or at 1000
C for the Cr-implanted sample or at 1000 C for the Nb-implanted sample, the radiation damage was recovered. The implanted metals occupied titanium (Ti) sites in TiO
C for the Nb-implanted sample, the radiation damage was recovered. The implanted metals occupied titanium (Ti) sites in TiO to form metal-oxygen bonds. According to the ultraviolet-ray photoelectron spectra, a localized level due to the implanted metals was formed in band gap of both the crystals. This position was close to the VB edge for the Cr-doped TiO
to form metal-oxygen bonds. According to the ultraviolet-ray photoelectron spectra, a localized level due to the implanted metals was formed in band gap of both the crystals. This position was close to the VB edge for the Cr-doped TiO , while the Nb-doped TiO
, while the Nb-doped TiO had the small peak far from the edge. This is in good agreement with the ab-initio band calculation results. It is considered that the midgap states of Cr- and Nb-doped TiO
had the small peak far from the edge. This is in good agreement with the ab-initio band calculation results. It is considered that the midgap states of Cr- and Nb-doped TiO consist of the Cr t
consist of the Cr t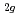 or Ti t
or Ti t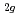 state, respectively.
state, respectively.
Nakanishi, Yasuo*; Wakahara, Akihiro*; Okada, Hiroshi*; Yoshida, Akira*; Oshima, Takeshi; Ito, Hisayoshi; Nakao, Setsuo*; Saito, Kazuo*; Kim, Y. T.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206, p.1033 - 1036, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:73.56(Instruments & Instrumentation)Photo luminescence properties of GaN implanted with Eu ions were studied. The GaN was epitaxialy grown on sapphire substrate. Multiple-implantation at RT was done to form box profile of Eu at a mean Eu concentration from 2.8 10
10 to 2.8
to 2.8 10
10 /cm
/cm . Samples were annealed in NH
. Samples were annealed in NH , N
, N at 900-1050
at 900-1050 C for 5-30 min after implantation. As the result, sharp emission peaks around 621nm which is assigned as 4f-4f transition were observed. The intensity of peaks increases with increasing Eu concentration and saturate at Eu concentrations around 2.8
C for 5-30 min after implantation. As the result, sharp emission peaks around 621nm which is assigned as 4f-4f transition were observed. The intensity of peaks increases with increasing Eu concentration and saturate at Eu concentrations around 2.8 10
10 /cm
/cm .
.
Oshima, Takeshi; Lee, K. K.; Onoda, Shinobu; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Laird, J. S.; Hirao, Toshio; Ito, Hisayoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206(1-4), p.979 - 983, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.76(Instruments & Instrumentation)Ion beam induced current for pn SiC diode was observed by using MeV range ion beams.The diodes used in this study were pn diode fabricated on n-type epitaxial 6H-SiC. The p region was formed using Al-ion implantation at 800 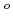 C and subsequent annealing at 1800
C and subsequent annealing at 1800  C. The value of charge collection for diode applied to 30V by 12MeV-Ni microbeam irradiationis estimated to be (1.7-1.8)
C. The value of charge collection for diode applied to 30V by 12MeV-Ni microbeam irradiationis estimated to be (1.7-1.8) 10
10 Q from the analyzing transient-IBIC measurement.The efficiency of the charge collection is 85-93%.
Q from the analyzing transient-IBIC measurement.The efficiency of the charge collection is 85-93%.
Isoya, Junichi*; Oshima, Takeshi; Oi, Akihiko; Morishita, Norio; Ito, Hisayoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206, p.965 - 968, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.76(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Matsunami, Noriaki*; Ito, Masaharu*; Takai, Yoshiaki*; Tazawa, Masato*; Sataka, Masao
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206, p.282 - 286, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:81.09(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Sumita, Taishi*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Matsuda, Sumio*; Oshima, Takeshi; Oi, Akihiko; Ito, Hisayoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206, p.448 - 451, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:95.13(Instruments & Instrumentation)Proton irradiation effects of triple-junction (InGaP/GaAs/Ge) solar cells for space use were studied. The changes in electrical and optical properties of the solar cells irradiated with protons at energies between 20 keV and 10 MeV were examined. As the result of analyzing the relationship between proton projection range and the degradation of their properties, the largest degradation of the properties was observed when proton projection range is near the junction of GaAs sub-cells. This indicates that improvement of the radiation resistance of GaAs is necessary to enhance radiation resistance of tliple-junction solar cells.
Choi, Y.; Yamamoto, Shunya; Saito, Hiroshi*; Sumita, Taishi*; Ito, Hisayoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206(1-4), p.241 - 244, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:46.40(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Abe, Hiroshi; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Azuma, Yorito*; Uedono, Akira*; Chen, Z. Q.*; Ito, Hisayoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206(1-4), p.224 - 227, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:77.57(Instruments & Instrumentation)Palladium(Pd) is used for the purification of H gas and as a catalyst for the dissociation of H
gas and as a catalyst for the dissociation of H molecules. Therefore, much work has been made until now. Since low energy ion irradiation, i.e., ion implantation is quite useful for surface modification of materials, the hydrogen absorption properties of Pd is expected to be improved by ion irradiation. In this work, we aimed at investigating the effect of ion irradiation on the hydrogen absorption rate of Pd. Ion irradiation was made with H
molecules. Therefore, much work has been made until now. Since low energy ion irradiation, i.e., ion implantation is quite useful for surface modification of materials, the hydrogen absorption properties of Pd is expected to be improved by ion irradiation. In this work, we aimed at investigating the effect of ion irradiation on the hydrogen absorption rate of Pd. Ion irradiation was made with H , He
, He and Ar
and Ar in an acceleration energy rage from 30 to 350keV up to a dose of 1 x 10
in an acceleration energy rage from 30 to 350keV up to a dose of 1 x 10 /cm
/cm . As a result, ion irradiated Pd sample was found to induce a higher absorption rate than that of the unirradiated one. The initial hydrogen results suggest that defects introduced in Pd by ion irradiation facilitate tha rate of nucleation and growth of hydride.
. As a result, ion irradiated Pd sample was found to induce a higher absorption rate than that of the unirradiated one. The initial hydrogen results suggest that defects introduced in Pd by ion irradiation facilitate tha rate of nucleation and growth of hydride.
Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Saito, Takeru
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206(1-4), p.42 - 46, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:66.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 Xe-fullerene by ion implantation
Xe-fullerene by ion implantationWatanabe, Satoshi; Ishioka, Noriko; Shimomura, Haruhiko*; Muramatsu, Hisakazu*; Sekine, Toshiaki
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206(1-4), p.399 - 402, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.76(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 films by RBS/channeling
films by RBS/channelingYamamoto, Shunya; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Tanaka, Shigeru
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206(1-4), p.268 - 271, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:63.54(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Umebayashi, Tsutomu; Sumita, Taishi*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Ito, Hisayoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206(1-4), p.254 - 258, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:139 Percentile:98.82(Instruments & Instrumentation)Single crystalline titanium dioxide (TiO ) rutile were implanted with 200keV F
) rutile were implanted with 200keV F at a nominal fluence of 1
at a nominal fluence of 1 10
10 to 1
to 1 10
10 ions cm
ions cm and then thermally annealed in air up to 1200
and then thermally annealed in air up to 1200 for 5h. The radiation damage and its recovery during the subsequent annealing were analyzed by Rutherford backscattering spectrometry in channeling geometry and variable-energy positron annihilation spectroscopy. The lattice disorder was completely annealed at 1200
for 5h. The radiation damage and its recovery during the subsequent annealing were analyzed by Rutherford backscattering spectrometry in channeling geometry and variable-energy positron annihilation spectroscopy. The lattice disorder was completely annealed at 1200 by the diffusion of point defects to the surface acting as a sink. According to the secondary ion mass spectrometry, the F depth profile was shifted to a shallower region along with the damage recovery, finally producing an F-doped layer where the impurity concentration increased steadily towards the surface. The F doping proved to provide a small modification to the conduction-band edge of TiO
by the diffusion of point defects to the surface acting as a sink. According to the secondary ion mass spectrometry, the F depth profile was shifted to a shallower region along with the damage recovery, finally producing an F-doped layer where the impurity concentration increased steadily towards the surface. The F doping proved to provide a small modification to the conduction-band edge of TiO , as assessed by theoretical band calculations.
, as assessed by theoretical band calculations.
 TiO
TiO irradiated with high energy ions
irradiated with high energy ionsNakazawa, Tetsuya; Grismanovs, V.*; Yamaki, Daiju; Katano, Yoshio*; Aruga, Takeo
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206, p.166 - 170, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:87.49(Instruments & Instrumentation)Li TiO
TiO samples with high energy oxygen ions were examined by the use of Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The Raman spectra of the irradiated samples do not show any evidence of destruction of Li
samples with high energy oxygen ions were examined by the use of Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The Raman spectra of the irradiated samples do not show any evidence of destruction of Li TiO
TiO structure. On the other hand, the Bragg peak intensity of XRD is decreased with the increasing the ion fluence. Especially, the intensity of (002) supercell peak is drastically reduced after the irradiation to 1.2E+19 ions/m
structure. On the other hand, the Bragg peak intensity of XRD is decreased with the increasing the ion fluence. Especially, the intensity of (002) supercell peak is drastically reduced after the irradiation to 1.2E+19 ions/m . This result implies that partial site mixing between Li and Ti atoms is induced by the irradiation. The transition to such a disordering is observed also by SEM examination; the grain structure at surface layer is vanished after the irradiation.
. This result implies that partial site mixing between Li and Ti atoms is induced by the irradiation. The transition to such a disordering is observed also by SEM examination; the grain structure at surface layer is vanished after the irradiation.
 -FeSi
-FeSi fabricated by ion beam sputter deposition method
fabricated by ion beam sputter deposition methodSaito, Takeru; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Hojo, Kiichi; Haraguchi, Masaharu*; Imamura, Motoyasu*; Matsubayashi, Nobuyuki*; Tanaka, Tomoaki*; Shimada, Hiromichi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206, p.321 - 325, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:46.40(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 thin film formed by ion beam sputter deposition method
thin film formed by ion beam sputter deposition methodHaraguchi, Masaharu*; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Saito, Takeru; Sasase, Masato*; Hojo, Kiichi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206, p.313 - 316, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:71.86(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Kitazawa, Shinichi; Putra, P.; Sakai, Seiji; Narumi, Kazumasa; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Shunya; Chiba, Atsuya
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206, p.952 - 955, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.64(Instruments & Instrumentation)Pulsed energy impacts are expected to generate the elastic waves reflecting the elastic properties of impacted substances. Among the generated waves, the surface acoustic waves (SAW) can be more specific to the surface structures and can be used effectively in the characterization of thin films in a non-destructive way. In the present study, pulsed laser impacts were employed to generate SAWs on a thin film and the SAWs are detected with a laser reflection technique. To test the effectiveness of this method, an amorphous carbon films were irradiated with 13 keV Ar ions at room temperature in a broad range and the SAW propagation velocity was evaluated as a function of Ar ion dose. The present preliminary experiment using pulsed laser suggests the successful detection of SAW from typical substances with different modulus of elasticity such as fcc metals, oxides and semi conducting materials.