Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Lee, K. K.*; Laird, J. S.*; Oshima, Takeshi; Onoda, Shinobu; Hirao, Toshio; Ito, Hisayoshi
Materials Science Forum, 645-648, p.1013 - 1016, 2010/04
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Yasunori*; Onoda, Shinobu; Takatsuka, Akio*; Oshima, Takeshi; Yatsuo, Tsutomu*
Materials Science Forum, 645-648, p.941 - 944, 2010/04
no abstracts in English
Tomita, Takuro*; Iwami, Masahiro*; Yamamoto, Minoru*; Deki, Manato*; Matsuo, Shigeki*; Hashimoto, Shuichi*; Nakagawa, Yoshinori*; Kitada, Takahiro*; Isu, Toshiro*; Saito, Shingo*; et al.
Materials Science Forum, 645-648, p.239 - 242, 2010/04
no abstracts in English
 - and He
- and He -implantation or by irradiation with high-energy electrons
-implantation or by irradiation with high-energy electronsWeidner, M.*; Trapaidze, L.*; Pensl, G.*; Reshanov, S. A.*; Sch ner, A.*; Ito, Hisayoshi; Oshima, Takeshi; Kimoto, Tsunenobu*
ner, A.*; Ito, Hisayoshi; Oshima, Takeshi; Kimoto, Tsunenobu*
Materials Science Forum, 645-648, p.439 - 442, 2010/00
Intrinsic defects in 3C-SiC generated by implantation of H and He
and He ions or by irradiation of high energy electrons were investigated using DLTS (Deep Level Transient Spectroscopy). The defect parameters and the thermal stability of the observed defects are determined. The dominant DLTS peak was named W6-center and its capture-cross-section was directly measured by variation of the filling pulse length. The charge state of the W6-center is obtained from double-correlated DLTS investigations according to the Poole-Frenkel effect.
ions or by irradiation of high energy electrons were investigated using DLTS (Deep Level Transient Spectroscopy). The defect parameters and the thermal stability of the observed defects are determined. The dominant DLTS peak was named W6-center and its capture-cross-section was directly measured by variation of the filling pulse length. The charge state of the W6-center is obtained from double-correlated DLTS investigations according to the Poole-Frenkel effect.
Son, N. T.*; Carlsson, P.*; Isoya, Junichi*; Morishita, Norio; Oshima, Takeshi; Magnusson, B.*; Janz n, E.*
n, E.*
Materials Science Forum, 645-648, p.399 - 402, 2010/00
Defects in high-purity semi-insulating 4H SiC irradiated with 2 MeV electrons at room temperature were studied using Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR). The EPR signal named EI4 defect increased with annealing temperature up to 750  C. Additional large-splitting
C. Additional large-splitting  Si hyperfine (hf) structures and
Si hyperfine (hf) structures and  C hf lines by the interaction with one
C hf lines by the interaction with one  C nucleus were investigated. Based on the observed hf structures, the C
C nucleus were investigated. Based on the observed hf structures, the C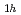 symmetry as well as the annealing behaviour, the EI4 defects is determined to be the complex between two carbon vacancies and a carbon antisite in the neutral charge state, V
symmetry as well as the annealing behaviour, the EI4 defects is determined to be the complex between two carbon vacancies and a carbon antisite in the neutral charge state, V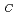 V
V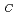 C
C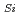
 . The formation of the complex is interpreted in terms of the migration of the silicon vacancy and the formation of the carbon vacancy-carbon antisite pair next to a carbon vacancy.
. The formation of the complex is interpreted in terms of the migration of the silicon vacancy and the formation of the carbon vacancy-carbon antisite pair next to a carbon vacancy.
Reshanov, S. A.*; Beljakowa, S.*; Zippelius, B.*; Pensl, G.*; Danno, Katsunori*; Alfieri, G.*; Kimoto, Tsunenobu*; Onoda, Shinobu; Oshima, Takeshi; Yan, F.*; et al.
Materials Science Forum, 645-648, p.423 - 426, 2010/00
n- and p-type 4H-SiC epilayers were irradiated with electrons at 170 keV or 1 MeV. Subsequent annealing (in Ar, 30 min) up to 1700  C was carried out. Defects in the samples were investigated using DLTS (Deep Level Transient Spectroscopy). As a results, for n-type, dominant defects were Z1/Z2 and EH7, and they can observed for both 170 keV- and 1 MeV-irradiated samples. Both defects decreased with increasing temperature up to 1100
C was carried out. Defects in the samples were investigated using DLTS (Deep Level Transient Spectroscopy). As a results, for n-type, dominant defects were Z1/Z2 and EH7, and they can observed for both 170 keV- and 1 MeV-irradiated samples. Both defects decreased with increasing temperature up to 1100  C, although they appeared again at 1400
C, although they appeared again at 1400  C. Then they disappeared at 1600
C. Then they disappeared at 1600  C. For p-type, defects named UK1 and HK2 were observed and they were very stable. No significant decrease was observed after 1700
C. For p-type, defects named UK1 and HK2 were observed and they were very stable. No significant decrease was observed after 1700  C annealing.
C annealing.
Matsushita, Yoshinori*; Kato, Masashi*; Ichimura, Masaya*; Hatayama, Tomoaki*; Oshima, Takeshi
Materials Science Forum, 645-648, p.207 - 210, 2010/00
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a promising material for radiation hardness devices. In this study, we evaluated excess carrier decay curves in both as-grown and electron-irradiated p-type 4H-SiC layers by the microwave photoconductivity decay ( -PCD) method. The samples used in this study were an Al-doped p-type epitaxial layer grown on a Si-face B doped bulk p-type 4H-SiC. The samples were irradiated with electrons at an energy of 160 keV and at a doses of 1
-PCD) method. The samples used in this study were an Al-doped p-type epitaxial layer grown on a Si-face B doped bulk p-type 4H-SiC. The samples were irradiated with electrons at an energy of 160 keV and at a doses of 1 10
10 cm
cm (ele-16) and 1
(ele-16) and 1 10
10 cm
cm (ele-17). As a results of
(ele-17). As a results of  -PCD measurements, the lifetimes of free carriers for as-grown, ele-16 and ele-17 were estimated to be 0.14
-PCD measurements, the lifetimes of free carriers for as-grown, ele-16 and ele-17 were estimated to be 0.14  s, 0.07
s, 0.07  s and 0.04
s and 0.04  s, respectively. This result indicates that defects acting as recombination centers were introduced by the electron irradiation.
s, respectively. This result indicates that defects acting as recombination centers were introduced by the electron irradiation.
 He ion irradiated 4H SiC
He ion irradiated 4H SiCYan, F.*; Devaty, R. P.*; Choyke, W. J.*; Kimoto, Tsunenobu*; Oshima, Takeshi; Pensl, G.*; Gali, A.*
Materials Science Forum, 645-648, p.411 - 414, 2010/00
Silicon Carbide (SiC) samples were irradiated with electron, proton and  He ions and defects in the irradiated SiC were investigated by Low Temperature Photo Luminescence (LTPL). After irradiation, PL spectra between 2.48 and 2.62 eV were measured at 7 K. As a results, several PL lines were observed. These lines showed the same annealing behavior and were annealed out between 1300 and 1400
He ions and defects in the irradiated SiC were investigated by Low Temperature Photo Luminescence (LTPL). After irradiation, PL spectra between 2.48 and 2.62 eV were measured at 7 K. As a results, several PL lines were observed. These lines showed the same annealing behavior and were annealed out between 1300 and 1400 C. Therefore, it is concluded that these line have the same origin. In addition, as a result of simulation, the structure of the defect is determined to be di-carbon antisite.
C. Therefore, it is concluded that these line have the same origin. In addition, as a result of simulation, the structure of the defect is determined to be di-carbon antisite.
 -implnated Al-doped 4H-SiC epilayers
-implnated Al-doped 4H-SiC epilayersBeljakowa, S.*; Reshanov, S. A.*; Zippelius, B.*; Krieger, M.*; Pensl, G.*; Danno, Katsunori*; Kimoto, Tsunenobu*; Onoda, Shinobu; Oshima, Takeshi; Yan, F.*; et al.
Materials Science Forum, 645-648, p.427 - 430, 2010/00
Defects in Al-doped p-type 4H-SiC were investigated using admittance spectroscopy (AS). Also, defects in 4H-SiC irradiated with electrons and He ions were studied using AS. As a result, a shallow level with activation energy at 170 meV was found and is has the capture cross section of 3.5 10
10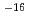 /cm
/cm which is extremely low value. The concentration of the defect did not change even after electron and He irradiations. Also, the defect can be found after annealing at 1800
which is extremely low value. The concentration of the defect did not change even after electron and He irradiations. Also, the defect can be found after annealing at 1800  C. Therefore, we can conclude that the defect is a very stable intrinsic defect in SiC.
C. Therefore, we can conclude that the defect is a very stable intrinsic defect in SiC.
Yan, F.*; Devaty, R. P.*; Choyke, W. J.*; Danno, Katsunori*; Alfieri, G.*; Kimoto, Tsunenobu*; Onoda, Shinobu; Oshima, Takeshi; Reshanov, S. A.*; Beljakowa, S.*; et al.
Materials Science Forum, 645-648, p.419 - 422, 2010/00
Defects in n- and p-type 4H-SiC epitaxial layer were investigated by low temperature photoluminescence spectroscopy (LTPL) and deep level transient spectroscopy (DLTS). Defects were introduced by either 170 keV or 1 MeV electron irradiation into samples at RT. The samples were annealed from 25 C to 1700
C to 1700 C in 100
C in 100 C steps. As a result of LTPL measurements, L
C steps. As a result of LTPL measurements, L line was observed after irradiation. In previous studies, L
line was observed after irradiation. In previous studies, L line is thought to correlate with Z
line is thought to correlate with Z /Z
/Z centers in DLTS measurements. However, in this study, no correlation between L
centers in DLTS measurements. However, in this study, no correlation between L and Z
and Z 1/Z
1/Z was observed.
was observed.
Beyer, F. C.*; Hemmingsson, C.*; Pedersen, H.*; Henry, A.*; Isoya, Junichi*; Morishita, Norio; Oshima, Takeshi; Janz n, E.*
n, E.*
Materials Science Forum, 645-648, p.435 - 438, 2010/00
By low-energy electron irradiation of epitaxial n-type 4H-SiC, the Deep Level Transient Spectroscopy (DLTS) peaks called the defects Z1/2 and EH6/7 were observed, which were also observed in as-grown layer and the commonly found peaks EH1 and EH3 (M-center) also appeared. New defect named the EB-centers increased after annealing out of EH1 and EH3. Since low energy electron irradiation (less than 220 keV) affects mainly the carbon atom in SiC, both the M- and EB-centers might be carbon related defects.
 N diodes degraded by low-energy electron irradiation
N diodes degraded by low-energy electron irradiationIwamoto, Naoya; Onoda, Shinobu; Oshima, Takeshi; Kojima, Kazutoshi*; Koizumi, Atsushi*; Uchida, Kazuo*; Nozaki, Shinji*
Materials Science Forum, 645-648, p.921 - 924, 2010/00
Electron irradiation effects on the charge collection efficiency (CCE) of the 6H-SiC p n diodes were investigated. The diodes were irradiated with electrons at energies from 100 keV to 1 MeV. The value of CCE of the diodes using alpha particles compared before and after the electron irradiations. In the case of 100 keV electron, no significant change in CCE was observed. On the other hand, above 200 keV, the values of CCE decreased with increasing fluence. The degradation was larger with increasing incident electron energy.
n diodes were investigated. The diodes were irradiated with electrons at energies from 100 keV to 1 MeV. The value of CCE of the diodes using alpha particles compared before and after the electron irradiations. In the case of 100 keV electron, no significant change in CCE was observed. On the other hand, above 200 keV, the values of CCE decreased with increasing fluence. The degradation was larger with increasing incident electron energy.