Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Fukano, Yoshitaka; Onoda, Yuichi; Sato, Ikken; Charpenel, J.*
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 13 Pages, 2009/10
Yamano, Hidemasa; Tanaka, Masaaki; Kimura, Nobuyuki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Kamide, Hideki; Watanabe, Osamu*
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 18 Pages, 2009/09
This paper describes the current status of flow-induced vibration evaluation methodology development for the primary cooling pipings in JSFR, in particular emphasizing on R&D activities that investigate unsteady hydraulic characteristics in a short-elbow piping. Experimental efforts have been made using 1/3-scale and 1/10-scale single-elbow test sections for the hot-leg piping and 1/4-scale and 1/7-scale triple-elbow test sections for the cold-leg piping. Simulation activities include Unsteady Reynolds Averaged Naviar Stokes equation (U-RANS) approach with Reynolds Stress Model (RSM) using a CFD code and Large Eddy Simulation (LES) approach using in-house codes. Numerical results appears in this paper, focusing on its applicability to the hot-leg piping experiments. The numerical results could be provided to the input data for the structural vibration evaluation of the piping. The procedure of the flow-induced vibration evaluation is also described in this paper.
Yuki, Kazuhisa*; Hasegawa, Shunsuke*; Sato, Tsukasa*; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2009/09
In this study, the flow structures in a 3-dimentionally connected dual elbow, which simulates a part of the cold leg, are visualized by PIV measurement, and it is discussed on the detailed flow transition from the 1st elbow to the 2nd elbow and the generation of unsteady flow such as a separation that influences flow-induced vibration. Experimental apparatus has a 1/15 scale test section of actual design whose inner diameter and curvature radius ratio are 56mm and 1.0, respectively. For visualization without any image distortion, matched refractive-index PIV measurement is carried out using NaI solution as the working fluid. The Reynolds number is 50,000, and the inlet flow condition to the test section is a fully developed turbulent flow. It is confirmed that it generates a separation along the inner wall of the 1st elbow and one large swirling flow in the 2nd elbow. Furthermore, unsteady flow formed in and/or behind the separation region is transported downstream and flows into the center area of the 2nd elbow.
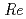 -number short-elbow pipe flow
-number short-elbow pipe flowEguchi, Yuzuru*; Murakami, Takahiro*; Tanaka, Masaaki; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 14 Pages, 2009/09
Since unsteady force possibly generated by fluid motion in a short-elbow pipe needs evaluating in the JSFR plant design, applicability of large-eddy simulation (LES) method to a high 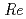 number water test is studied with an in-house LES code in the paper. First, requirement for mesh subdivision at high-
number water test is studied with an in-house LES code in the paper. First, requirement for mesh subdivision at high-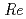 LES computation is theoretically studied. Then, the effects of turbulence model and boundary conditions are numerically studied using the Smagorinsky model and the WALE (Wall-adapting local eddy-viscosity) model with various inlet and outlet boundary conditions at
LES computation is theoretically studied. Then, the effects of turbulence model and boundary conditions are numerically studied using the Smagorinsky model and the WALE (Wall-adapting local eddy-viscosity) model with various inlet and outlet boundary conditions at 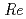 = 1.2
= 1.2 10
10 . It has turned out that the Smagorinsky model excels the WALE model and that an inlet velocity profile has a considerable impact on the separation features at the elbow curvature. It was also revealed that the outlet boundary condition is likely to have an effect on the separation features especially if the distance between the elbow and the outlet is rather short, which is the case of the present computation. Basic features of the pressure and the wall force fluctuations are also discussed with the aid of computational visualization and spectral analysis.
. It has turned out that the Smagorinsky model excels the WALE model and that an inlet velocity profile has a considerable impact on the separation features at the elbow curvature. It was also revealed that the outlet boundary condition is likely to have an effect on the separation features especially if the distance between the elbow and the outlet is rather short, which is the case of the present computation. Basic features of the pressure and the wall force fluctuations are also discussed with the aid of computational visualization and spectral analysis.
Suzuki, Mitsuhiro; Nakamura, Hideo
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 17 Pages, 2009/09
Presented are experiment results on performance of core exit thermocouple (CET) and applicability to PWR accident management (AM) during 12 tests of small-break loss-of-coolant accident (SBLOCA) and abnormal transient conducted at the Large Scale Test Facility (LSTF) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, which is the largest PWR simulator with full-height and 1/48 volume scaling. General CET performances are derived including (1) CETs are capable in most cases to detect core overheating with delay of time and temperature increase from core heat-up, (2) one of the reasons of this delay is attributed to cooling effects of structural materials at the core exit and peripheral region, (3) CETs were incapable to detect core overheating in a very small break under steam generator depressurization action as well as a 10% cold leg break due to significant water fall-back from hot legs, and (4) an alternative indication by CET superheat is necessary in extremely high and low pressure conditions.
Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2009/09
Xenon spatial oscillations on the cylindrical cores used in light water reactors such as BWR and PWR have already been theoretically and experimentally much-studied. On the other hand, evaluations of the oscillations on annular cores applied to VHTR have still not been fully evaluated. It is essential to investigate the relationship among the oscillations, annular core geometry and feedback effect with temperature coefficient. In this paper, a neutron binding parameter related to core geometry as one of dimensionless parameters are proposed and these parameters are useful for the evaluation of xenon spatial oscillations in annular cores.
Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Suzuki, Takayuki*; Takase, Kazuyuki
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2009/09
Kimura, Nobuyuki; Ono, Ayako; Miyakoshi, Hiroyuki; Kamide, Hideki
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 16 Pages, 2009/09
A quantitative evaluation on high cycle thermal fatigue due to temperature fluctuation in fluid is of importance for structural integrity in the reactor. It is necessary for the quantitative evaluation to investigate occurrence and propagate processes of temperature fluctuation, e. g. decay of temperature fluctuation near structures and transfer of temperature fluctuation from fluid to structures. In this study, a water experiment using T-junction was performed to evaluate the transfer characteristics of temperature fluctuation from fluid to structure. In the experiment, temperatures and local velocities were measured simultaneously to evaluate the correlation between the temperature and velocity under the non-stationary fields. The large heat transfer coefficients were registered at the region where the local velocity was high.
Onoda, Yuichi; Fukano, Yoshitaka; Sato, Ikken; Marquie, C.*; Duc, B.*
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 15 Pages, 2009/09
Matsumoto, Toshinori*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Kurihara, Akikazu; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2009/09
When a heat transfer tube fails in steam generator (SG) of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), sodium-water reaction (SWR) would take place. It is significant for estimation of the heat transfer from the fluid to the tube wall during SWR region to evaluate the possibility of the secondary tube failure in case of overheating rupture. In the present study, thermal hydraulics simulation of the fluid around the tube is conducted. The heat transfer coefficient is computed, the correlation diagram between the heat transfer coefficient and the void fraction has been obtained. The void fraction around the heat transfer tube in the SWR has been evaluated.
Sato, Hiroyuki; Kobayashi, Jun; Miyakoshi, Hiroyuki; Kamide, Hideki
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 13 Pages, 2009/09
A sodium cooled fast reactor is designed to attain a high burn-up core in a feasibility study on commercialized fast reactor cycle systems. It is of importance to obtain the flow velocity distribution in a wire wrapped pin bundle for the high burn-up core. A 2.5 times enlarged 7-pin bundle water model was applied to investigate the detailed velocity distribution in an inner subchannel surrounded by 3 pins with wrapping wire. The velocity distribution in an inner subchannel with the wrapping wire was measured by Particle Image Velocimetry. In the vertical velocity distribution in a narrow space between the pins, the wrapping wire decreased the velocity downstream of the wire and asymmetrical flow distribution was formed between the pin and wire. In the horizontal velocity distribution, swirl flow around the wrapping wire was obviously observed.
Ezato, Koichiro; Seki, Yohji; Tanigawa, Hisashi; Hirose, Takanori; Tsuru, Daigo; Nishi, Hiroshi; Dairaku, Masayuki; Yokoyama, Kenji; Suzuki, Satoshi; Enoeda, Mikio
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2009/09
In-vessel components such as Blanket and Divertor in a fusion reactor have a function of exhausting high heat and particle loads in order to maintain the structural soundness of the reactor. In the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor called ITER, build by ITER Organization under the framework of collaboration of seven parties including Japan, there are two kinds of blanket systems will be install. One is a shield blanket, which consists of a first wall (FW) and a block module shielding against neutron flux to a vacuum chamber and a superconducting magnet system. The other blanket system is called as a Test Blanket Module (TBM). TBM is a kind of prototype blanket for a fusion power plant and has functions of breeding of tritium (T) and extraction of energy from fusion plasma. TBM consists of FW and T-breeding/neutron (n)-multiplier zone. A concept of TBM developed by JAEA is water-cooled pebble-bed type, which means that FW and other structures are cooled by pressurized high temperature water and T-breeding/n-multiplier zone consists of multiple layers of pebble bed made of T-breeding and n-multiplier material. This paper describes the status of R&Ds on FW and pebble beds from the view of thermo-hydraulics and mechanics.
Akimoto, Hajime; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Kamide, Hideki; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Ezato, Koichiro; Takase, Kazuyuki; Nakamura, Hideo
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2009/09
Thermal-hydraulics researches at JAEA are performed in many nuclear R&D areas that investigate fusion reactor, fast reactors (FR), high temperature gas cooled reactors (HTGR), and light water reactors (LWRs). These researches are composed of both experimental and analytical efforts. Experimental efforts cover from small-scale fundamental works to large-scale system-integrated tests. Analytical efforts cover both so-called one-dimensional system analysis codes and detailed three-dimensional CFD codes. The thermal-hydraulic phenomena dealt at JAEA cover both normal operation conditions and accident conditions including severe accidents in LWR and FR. The phenomena include single phase flow of water, supercritical water, helium and sodium, two-phase flow of steam-water or sodium-argon, and multi-phase flows encountered in severe accidents. In this paper, we will summarize current status and future directions of thermal-hydraulic researches at JAEA.
Tanaka, Masaaki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Murakami, Satoshi*
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2009/09
This paper deals with numerical simulations focusing on several areas around typical CR channels in order to reveal thermal mixing phenomena and to confirm effect of mitigation measures to the thermal striping phenomena around the CR channel. By the numerical simulation, generation mechanism of influential temperature fluctuation on the CIP integrity is revealed and effect of mitigation measure based on the mixing mechanism is confirmed.
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Morita, Koji*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Zhang, S.*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Naito, Masanori*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Okada, Hidetoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2009/09
Dispersion and freezing of molten core material was calculated by the COMPASS code to compare with the experimental data of GEYSER. Molten core material flowed up with freezing on the pipe inner surface. As a molten pool behavior, CABRI-TPA2 experiment was analyzed, where a sphere of solid steel was surrounded by solid fuel. Power was injected to cause melting and boiling of the steel sphere. SCARABEE-BE+3 test was analyzed by COMPASS as a validation of failure of duct walls.
Zhang, B.*; Harada, Tetsushi*; Hirahara, Daisuke*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Morita, Koji*; Fukuda, Kenji*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Suzuki, Toru; Tobita, Yoshiharu
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 15 Pages, 2009/09
Although the decay heat from fuel debris drives the coolant boiling in fast reactor accident conditions, the present experiments were conducted by employing depressurization boiling of water to simulate axially increasing void distribution in a debris bed instead of conventional heating or gas injection from the debris bottom. Good agreements on self-leveling occurrence were obtained between model predictions and experimental results. Extrapolation of the present model was also discussed against reactor conditions.
Uchida, Mitsunori*; Someya, Satoshi*; Okamoto, Koji*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 13 Pages, 2009/09
When a heat exchanger in fast breeder reactor cracks, a sodium-water reaction occurs. Highly pressurized water or steam escapes into the surrounding liquid sodium. The release of steam into the liquid sodium media is a two-phase flow with an underexpansion. Several studies have examined only the underexpansion of the gas-gas phase. However, there are few reports on the underexpansion of the gas-liquid phase. In this study quantitative measurement was carried out for the purpose of revealing the flow with the underexpanded gas jet injected into water. The gas jet distance and the expansion angle were then obtained from the averaged images of a high-speed camera. The gas jet distance and the expansion angle increased approximately linearly with increasing pressure. The entrainment velocity and the velocity of entrained water droplets into the gas jet were obtained by PIV.
Suzuki, Hideaki; Nakama, Shigeo; Kimura, Makoto; Fujita, Tomoo
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 13 Pages, 2009/09
Ohno, Shuji; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Sugahara, Akihiro*; Oki, Hiroshi*
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2009/09
Multi-dimensional transient thermal hydraulic analyses for a sodium experiment are carried out in order to validate the applicability of basic simulation methods to a typical thermal stratification behavior in a reactor upper plenum region. Simulation predictability of the behavior is evaluated after the results of an existing experiment are reviewed and important fundamental characteristics of the behavior are quantified. The investigated results clarify that CFD codes provide good prediction for fundamental phenomena of steep temperature gradient and gradual rising behavior of the stratification interface under the condition of adopting appropriate mesh size, higher-order discretization scheme, and the RANS turbulence model.
Ezure, Toshiki; Kimura, Nobuyuki; Miyakoshi, Hiroyuki; Kamide, Hideki
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 16 Pages, 2009/09
According to the compact sizing of reactor vessel, gas entrainment at the free surface of sodium coolant becomes one of the significant issues in the latest sodium-cooled fast reactor design. In the present study, some basic experiments for gas entrainment due to surface vortices were performed in order to obtain the fundamental knowledge about entrained bubbles. The distribution of bubble diameters was obtained from an image processing technique from the images. In addition to that, velocity field and surface shape of gas core were measured to grasp the influences of the local velocity field on the gas core shape and detached bubbles. The results showed that the mean equivalent diameters of bubbles were varied from 1.34 to 2.06 mm in the range of present experimental conditions.