Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sekine, Yurina; Chi, S.*; Fernandez Baca, J.*; Fukazawa, Tomoko*; Fukazawa, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
Neutron diffraction profiles of high and low- D O-content poly-N,N,-dimethylacrylamide (PDMAA) hydrogels were measured from 100 to 300 K to investigate the structure and properties of water in hydrogels. For high D
O-content poly-N,N,-dimethylacrylamide (PDMAA) hydrogels were measured from 100 to 300 K to investigate the structure and properties of water in hydrogels. For high D O content hydrogel, strong sharp peaks are observed in 100 to 250 K. The feature of the peaks is similar to that of hexagonal ice (ice Ih). For low D
O content hydrogel, strong sharp peaks are observed in 100 to 250 K. The feature of the peaks is similar to that of hexagonal ice (ice Ih). For low D O-content hydrogel, a broad band is observed at temperatures less than 220 K. The result indicates the existence of amorphous ice in the hydrogel. During the heating process, diffraction peaks from ice crystals appear in the profiles. The peaks indicate that cubic ice and hexagonal ice exist at temperatures above 220 K. We first obtained structure parameters of these ices in the hydrogel, which indicate the existence of low-density ice in the hydrogel.
O-content hydrogel, a broad band is observed at temperatures less than 220 K. The result indicates the existence of amorphous ice in the hydrogel. During the heating process, diffraction peaks from ice crystals appear in the profiles. The peaks indicate that cubic ice and hexagonal ice exist at temperatures above 220 K. We first obtained structure parameters of these ices in the hydrogel, which indicate the existence of low-density ice in the hydrogel.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*; Horigane, Kazumasa*
no journal, ,
Carrier doping into transition metal oxides triggers various phenomena, which have been subjected to intensive investigations. Layered oxide La MO
MO (M: 3d metal) is one of the model systems for such studies. In cobalates, contribution of orbital moment and possible spin state of Co
(M: 3d metal) is one of the model systems for such studies. In cobalates, contribution of orbital moment and possible spin state of Co give further complexity. In La
give further complexity. In La Sr
Sr CoO
CoO , charges order in checker-board style and Co
, charges order in checker-board style and Co spin correlations are modulated in momentum space by the ordered charges. (1) Magnetic excitations in this system are reported to be accounted for spin-waves of Co
spin correlations are modulated in momentum space by the ordered charges. (1) Magnetic excitations in this system are reported to be accounted for spin-waves of Co spins taking into account the orbital moment. (2) In this study, we have investigated magnetic excitations in another almost half-doped system La
spins taking into account the orbital moment. (2) In this study, we have investigated magnetic excitations in another almost half-doped system La CoO
CoO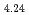 by inelastic neutron scattering. Clear spin-wave excitations consistent to previous report on La
by inelastic neutron scattering. Clear spin-wave excitations consistent to previous report on La Sr
Sr CoO
CoO were observed. However, we also observed an additional excitations with different zone center positions as well as excitation with higher spin-wave velocity. We expect detail analysis of present results can provide a key clue to understand the mechanism of complicated magnetic excitations caused by doped carrier, spin-orbital coupling and spins in transition metal oxides.
were observed. However, we also observed an additional excitations with different zone center positions as well as excitation with higher spin-wave velocity. We expect detail analysis of present results can provide a key clue to understand the mechanism of complicated magnetic excitations caused by doped carrier, spin-orbital coupling and spins in transition metal oxides.

Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Hasegawa, Yoshio*; Hishinuma, Yukio*; Suzuki, Masashi*; Kodama, Hiroto*; Koizumi, Satoshi*; Noda, Yohei; Oba, Yojiro*
no journal, ,
Anion, e.g., nitrogen (N) doped titanium dioxide (TiO ), being expected to exhibit an improved photo-catalytic property due to the effect of narrowing in the band gap, was investigated by small- (SANS) and wide-angle neutron scattering. Among wide variety of photo-catalytic products, TiO
), being expected to exhibit an improved photo-catalytic property due to the effect of narrowing in the band gap, was investigated by small- (SANS) and wide-angle neutron scattering. Among wide variety of photo-catalytic products, TiO is one of the most promising and various improvements have been done. However, the difference in structure between bare TiO
is one of the most promising and various improvements have been done. However, the difference in structure between bare TiO and N-doped TiO
and N-doped TiO has not yet definitively clarified despite the considerable structural analyses by X-ray diffraction or X-ray photoemission spectroscopy. With profiting from an enhanced scattering length of N atoms to the neutron beam, an attempt to capture the distribution of N atoms in N-doped TiO
has not yet definitively clarified despite the considerable structural analyses by X-ray diffraction or X-ray photoemission spectroscopy. With profiting from an enhanced scattering length of N atoms to the neutron beam, an attempt to capture the distribution of N atoms in N-doped TiO by SANS was conducted. Specimens prepared with and without N-doping were compared. The traces of doped N species on the scattering profiles might be brought out from invisible differences with contrast variation method employing the soakage in tuned H
by SANS was conducted. Specimens prepared with and without N-doping were compared. The traces of doped N species on the scattering profiles might be brought out from invisible differences with contrast variation method employing the soakage in tuned H O/D
O/D O mixture possessing nearly the same scattering length density as TiO
O mixture possessing nearly the same scattering length density as TiO component.
component.
 Sr
Sr CuO
CuO studied by complementary use of neutron and X-ray
studied by complementary use of neutron and X-rayWakimoto, Shuichi
no journal, ,
Fukazawa, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
Water and ice are the most common liquid and solid on Earth, and they constitute an important medium. Hydrogels are unique materials because large amounts of water can be contained among their 3D cross-linked polymer chains. Water content varies from a dry condition to nearly 98 wt %. The scanning electron microscope image shows that hydrogels have empty spaces that can accommodate water molecules. However, the structure and dynamics of water molecules in these spaces are not fully understood at the atomic level. Neutron is useful to investigate water and hydrogen bonding because of the large neutron scattering cross sections. Therefore, we have used neutron beam to study gels at the HANARO, KAERI. We here show neutron diffraction and scattering of hydrogels with acrylamide or polysaccharides, which contain weak hydrogen bond or low-density water. Furthermore, we report a new hydrogel developed by QuBS, JAEA. This hydrogel has been tested as a cesium capturing material and is important in the Fukushima recovery effort.