Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kubo, Shinji; Kasahara, Seiji; Sato, Hiroyuki; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Iwatsuki, Jin; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Miyashita, Reiko*; Tago, Yasuhiro*; Onuki, Kaoru
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/12
A stable hydrogen production via the IS process is relatively difficult because of the unique characteristics of the closed-cycle condition involved. This issue is therefore a high targeted priority when industrializing the process as feasible in a chemical plant. In system of IS process coupled with helium gas heat source, a process control method to maintain mass balance of the process was devised. The method is equipped with measurements of Bunsen reaction composition and allocation of heat for the O and H
and H production sections in strict proportion. Via computer simulation for closed-cycle and fully multi-section driven by high-temperature helium gas, the system worked automatically to maintain stoichiometric production ratio in response to shifts of helium gas conditions.
production sections in strict proportion. Via computer simulation for closed-cycle and fully multi-section driven by high-temperature helium gas, the system worked automatically to maintain stoichiometric production ratio in response to shifts of helium gas conditions.
Sakaba, Nariaki; Sato, Hiroyuki; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Tachibana, Yukio; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency launched the HTTR-IS program which is a nuclear hydrogen production demonstration program using the Japan's first high-temperature gas-cooled reactor HTTR in 2005. It is expected to be the world's first demonstration of nuclear hydrogen. The candidate system of the hydrogen production is a thermochemical water splitting iodine sulphur process (IS process). The thermochemical water splitting process can produce massive quantity of hydrogen without carbon dioxide greenhouse gas emission. This paper focused on the key issues to be developed for the IS process to couple with the HTTR (HTTR-IS system). The key issues to be established are the safety philosophy for non-nuclear grade system as a conventional chemical system and simplification of the plant for an economic competitiveness. The conceptual safety study for non-nuclear system was carried out. The key elements were proposed which can exempt the IS process from "Prevention System 3" and identify abnormal events initiated from the IS process as external events. Also, the conceptual design study for integration of the components such as a Bunsen reactor and a sulphuric acid decomposer was carried out. Reduction of number of components was proposed by coupling with some of equipment. The proposed philosophy and its supporting technologies are expected to contribute economically for the commercialization of nuclear hydrogen.
Takamine, Jun; Haruyama, Mitsuo; Takase, Misao; Yamaguchi, Satoshi
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
When an object including a lot of hydrogen atoms such as the cemented waste is measured by using the conventional active neutron method, radial sensitivity distribution in the region of surface and center is different more than 100 times. Then we developed the method to detect a nuclear fission neutron induced by the neutron which slowed down in the matrix itself, and so performed a position sensitivity difference of 10%. Furthermore, we understood that the background neutron in nuclear fission neutron counting area is great decrease by using SUS-304 instead of graphite as a moderator of conventional detection system. And then, this new system enabled to measure clearance level activity included in cemented waste. Besides, we modified the optimum structure of the detector bank, which enabled to measure precisely even metal compaction waste (the density is 3 4 g/cm
4 g/cm ). In this session, we introduce the process of the past research, applied examples, recent results of the research.
). In this session, we introduce the process of the past research, applied examples, recent results of the research.
Shibata, Keiichi; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ichihara, Akira; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kunieda, Satoshi; Otsuka, Naohiko*; Fukahori, Tokio; Nakagawa, Tsuneo; Katakura, Junichi
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
Evaluated nuclear data play an important role in nuclear engineering. After we released the first version of Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library JENDL-1 about 30 years ago, JENDL has been revised several times by considering the feedback from users and recent experimental data. JENDL-3.3, which was released in 2002, is being used in various fields, and its reliability has been confirmed. We are developing JENDL-4 for innovative reactors with much emphasis on the improvements of FP and MA data. Nuclear model codes were developed. The actinide data were already released as JENDL Actinoid File 2008. The complete library JENDL-4 will be made available in FY2009.
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Morita, Koji*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Zhang, S.*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Naito, Masanori*; Okada, Hidetoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
A computer code, named COMPASS, is being developed for various complex phenomena of core disruptive accidents (CDAs) in sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). The COMPASS is designed to analyze multi-physics problems involving thermal hydraulics, structure and phase change, in a unified framework of the MPS (Moving Particle Semi-implicit) method. The project has been carried out by six organizations for five years from FY2005 to FY2009. In this paper, the outcomes of the project in FY2007 are presented. Three validation calculations were completed by following the validation plan: melt freezing and blockage formation, molten pool boiling, and duct wall failure. The COMPASS code development was supported by basic studies of the numerical method, material science for eutectic reaction of the metal fuel, and SIMMER-III analyses.
Ishibashi, Makoto*; Sato, Kazuhiko; Kawatsuma, Shinji
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
no abstracts in English
Yamamura, Osamu
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
Tokai reprocessing plant (TRP) has been processing over 1,123 tons of spent fuels from the beginning of its active operation in Sept. 1977. For 30 years operation of TRP, many technological problems have been overcome to obtain the stable and reliable operation. The process for establishments of maintenance technology in TRP was evaluated through the analysis of significant plant equipment failures reported to the authorities concerned. Through these troubles and its solution, following knowledge could be obtained.
Tamaki, Hitoshi; Yoshida, Kazuo; Hamaguchi, Yoshikane*
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
A PSA is a comprehensive and structured method for assessing the safety of a nuclear facility. This method also provides risk information that could be applied to effective regulatory activities for nuclear facilities and so on. A PSA procedure for MOX fuel fabrication facility has been developed at JAEA. This procedure consists of two steps. One is called as preliminary PSA using simple methods for likelihood and consequence evaluation through whole processes in the facility. The other step is called as detailed PSA and is carried out to evaluate risk of the significant events using methods corresponding to level 1 PSA and level 2 PSA for nuclear power plants. The procedure was applied to a practical model facility based on process information and handling quantities of materials from the planned MOX fabrication plant to understand risks at whole processes in the model facility. A risk-profile, which consisted of dominant accident sequences, was also obtained through this analysis.
Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Namekawa, Takashi; Asano, Takashi; Niita, Koji*
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
The advanced MOX fabrication process in FaCT project has been studies to investigate an overall characteristic of nuclear material accounting of Pu in the proposed confinement box. Flow field induced by a forced convection inside the box is numerically simulated to evaluate the MOX particle behavior and a radiation field due to the spontaneous and induced neutrons emitted from Cm and Pu is calculated using PHITS code. The possibility of remote-monitoring techniques using non-destructive assay to apply to a future safegurads measure is invetigated.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Numata, Kazuyuki*; Hazama, Taira; Ishikawa, Makoto
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
The new solver for cross section adjustment and design accuracy evaluation has been developed for the new reactor physics analysis code system, MARBLE. In this development, object-oriented design was applied for achieving software extendibility. The new solver was successfully designed to easily add a uncertainty prediction method. This extendibility was confirmed by implementing the extended bias method. The new solver reproduces all functions of the conventional code system and can be used as standard solver for cross section adjustment and design accuracy evaluation in MARBLE.
Morizono, Koji; Takeuchi, Norihiko; Takayama, Koichi; Deshimaru, Takehide; Mukai, Kazuo
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2008/10
Prototype fast breeder reactor Monju is the first power generating FBR in Japan which is a plant for research & development to demonstrate reliability of fast breeder reactor as a power plant and establish sodium handling technology etc. Monju started construction in 1985, achieved initial criticality in 1994 and attained 40% output in 1995, however the sodium leak accident occurred during the test operation at the end of that year. Since then, the plant remained shut down for 12 years. In this subject, our efforts for the restart of this long term shut down plant will be presented.
Kobayashi, Tsuguyuki*; Namba, Takashi*; Kawabe, Yukinari*; Washiya, Tadahiro
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
Japan Atomic Power Company (JAPC) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have been developing fuel disassembly and fuel pin chopping systems for a future Japanese commercial FBR. At first, the wrapper tube is cut by the slit-cut to pull it out, then the fuel pins are cut by the crop-cut at their end-plugs to separate them from the entrance nozzle. The pins are transferred to the magazine of the chopping machine. A series of tests were performed to develop this procedure. As the result of mechanical cutting tests, the CBN wheel was selected. The slit-cut tests were carried out to evaluated the cutting performance of the wheel. Fuel pin handling tests were performed to transfer them from the disassembly machine to the chopping machine. The Saucer tray was selected to receive the disassembled pins. All the pins were transferred and loaded into a magazine of the chopping machine.
Nagaoki, Yoshihiro; Kikuchi, Shin; Ichimiya, Masakazu
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
"Fast Reactor Cycle Technology Development (FaCT)" project has been conducted since 2006. In this project, design study and research and development (R&D) on innovative technologies for fast reactor (FR) cycle system are implemented in order to present the conceptual designs of commercial and demonstration facilities by 2015 and start operating demonstration fast reactor in 2025. The R&Ds has been stepped forward into the development stage to establish the realization of innovative technologies which bring excellent performance to fast reactor cycle system. The purpose of R&D by 2010 is to decide weather innovative technologies shall be adopted. So promoting R&D of FR, the project governance was organized. Furthermore, several possible R&D have been effectively carried out within the frameworks of international cooperation, such as GNEP, GIF, and INPRO.
Enoeda, Mikio; Tanigawa, Hisashi; Tsuru, Daigo; Hirose, Takanori; Ezato, Koichiro; Yokoyama, Kenji; Dairaku, Masayuki; Seki, Yohji; Suzuki, Satoshi; Mori, Kensuke*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
Uchikawa, Sadao; Okubo, Tsutomu; Nakano, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Noboru
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
An advanced LWR concept with hard neutron spectrum (FLWR) has been proposed in order to ensure sustainable energy supply in the future based on the well-experienced LWR technologies. The FLWR is essentially a BWR-type reactor, in which the moderation of neutron in the core is reduced by use of the hexagonal-shaped fuel assemblies with the triangular-tight-lattice fuel rod configuration. The core design concept of FLWR is to realize effective and flexible utilization of uranium and plutonium resources by two stages, corresponding to the advancement of the fuel cycle technologies and related infrastructures. The core in the first stage of FLWR aims at intensive utilization and preservation of plutonium based on the experiences of the current LWR and MOX utilization, and the one in the second stage realizes sustainable multiple plutonium recycling with a high conversion ratio over 1.0. The present paper summarizes the recent core design studies of FLWR.
Fukasawa, Tetsuo*; Yamashita, Junichi*; Hoshino, Kuniyoshi*; Sasahira, Akira*; Inoue, Tadashi*; Minato, Kazuo; Sato, Seichi*
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
Transition period from light water reactors (LWR) to fast breeder reactors (FBR) is quite important to achieve the future FBR cycle system. The transition scenarios were carefully studied and the Flexible Fuel Cycle Initiative (FFCI) was proposed in this study. FFCI carries out about 90% uranium (U) removal from LWR spent fuels (SF) at first and then recovers plutonium/uranium (Pu/U) from the remaining SF named "recycle material"(RM) (about 40% U, 15% Pu and 45% other nuclides) for FBR fresh fuel fabrication according to the FBR deployment status. The FFCI has some merits compared with ordinary system that carries out full reprocessing of LWR SF, that is volume reduction of LWR SF by its conversion to RM (proliferation resistant material), and storage and supply of high Pu density RM according to FBR deployment rate changes.
Sato, Tomonori; Ugachi, Hirokazu; Tsukada, Takashi; Uchida, Shunsuke
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
The major mechanism of Flow accelerated corrosion (FAC) is the dissolution of the protective oxide on carbon steel, which is enhanced by mass transfer and erosion under high flow velocity conditions. In this study, the effects of alloy composition and flow velocity on FAC of carbon steel were evaluated by measuring FAC rate of tube type carbon steel specimens in the neutral water condition at 150 C. Obtained results are summarized in follows. (1) High FAC rate was depended upon the v
C. Obtained results are summarized in follows. (1) High FAC rate was depended upon the v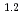 in the tube type specimen made of the standard alloy. (2) FAC was mitigated for the carbon steel with more than 0.03% of Cr content. (3) FAC rate decreased as Ni content increased in more than 0.1% of Ni content. (4) The difference in chemical composition of oxide film between Ni added carbon steel and Cr added one was confirmed. The hematite rich oxide was observed for Ni added carbon steel. (5) The effects of Cu on FAC rate was not observed up to 0.1% of Cu content.
in the tube type specimen made of the standard alloy. (2) FAC was mitigated for the carbon steel with more than 0.03% of Cr content. (3) FAC rate decreased as Ni content increased in more than 0.1% of Ni content. (4) The difference in chemical composition of oxide film between Ni added carbon steel and Cr added one was confirmed. The hematite rich oxide was observed for Ni added carbon steel. (5) The effects of Cu on FAC rate was not observed up to 0.1% of Cu content.
Wei, Y.*; Hoshi, Harutaka; Kumagai, Mikio*
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
To separate the long-lived minor actinides (MA=Am, Cm) from high level liquid waste, we have been studying an advanced separation process by extraction chromatography. The process consists of two separation columns packed with CMPO (octyl(phenyl)-N,N-diisobutylcarbamoyl-methyl phosphine oxide) extraction resin for elemental group separation and a soft-donor named R-BTP (2,6-bis-(5,6-dialkyl-1,2,4-triazine-3-yl)pyridine) extraction resin for the isolation of MA from lanthanides (Ln), respectively. In this work, a hot test for the separation of MA from MA containing effluent from the irradiated MOX-fuel treatment process was carried out using a column packed with R-BTP extraction resin. It was found that a complete separation between MA and Ln was achieved. In addition, small amounts of U and Pu remained in the MA-Ln effluent could be effectively recovered together with the MA. The test results indicate that the proposed MA separation process is essentially feasible.
Nishiyama, Yutaka; Onizawa, Kunio; Matsuzawa, Hiroshi*
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
The effects of grain-boundary P segregation and hardening on the embrittlement in terms of Charpy ductile-to-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) in several neutron-irradiated reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steels with different bulk contents of P have been investigated using a scanning Auger microbe, a local electrode atom probe and positron annihilation spectroscopy. Increasing the neutron fluence promotes intergranular P segregation, particularly in steels with high levels of P. The content of P significantly also affects irradiation hardening due to distinct formation of P-rich precipitates arising from the stabilization of vacancies. It was found that neutron irradiation mitigates an embrittling effect of segregated P, therefore the hardening more strongly affects the DBTT shift than the P segregation. The likelihood of intergranular embrittlement of RPV steels is discussed by these results.
Hayashi, Naoki
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
The J-PARC is a multi purpose research center using neutron/muon sources for research in material and life science, and using hadron or neutrino beams for nuclear and particle physics. Its proton accelerators have been beam commissioned since 2006. The second accelerator RCS (3GeV Rapid-Cycling Synchrotron) was commissioned in early 2008 and the third accelerator MR (Main Ring; 50GeV proton synchrotron) and experimental facilities will follow. This paper describes the beam commissioning of the accelerators, highlighting the RCS, and discusses the outlook of the RCS power up strategy and future plans for the accelerator complex.