Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
光田 智昭*; 小林 一平*; 小杉 晋也*; 藤田 直樹*; 齋藤 勇一; 堀 史説*; 千星 聡*; 金野 泰幸*; 西田 憲二*; 曽根田 直樹*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 272, p.49 - 52, 2012/02
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:57.76(Instruments & Instrumentation)So far, we have found that the hardness of Al-Cu-Mg alloy (JIS2017, Duralumin) increases by energetic heavy ion irradiation at room temperature. Observations by using the three-dimensional atom probe (3DAP) have revealed that nano-meter sized precipitates are homogeneously distributed in the irradiated specimens, which are produced through the irradiation enhanced diffusion of solute atoms. The small precipitates contribute to the increase in hardness. In this report, we show the results for the hardness modification of Al-Cu-Mg alloy by the combination of energetic ion irradiation and thermal aging treatment. The hardness of the specimens pre-irradiated and thermally aged at 423 K is much larger than that without the pre-irradiation. The present result indicates that the combination of energetic ion irradiation and subsequent thermal aging can be used as an effective tool for the hardness modification of Al-Cu-Mg alloy.
笹瀬 雅人*; 山本 博之; 岡安 悟
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 272, p.318 - 321, 2012/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)イオンビームは薄膜作製において、基板処理,成膜,改質など種々の場面に広く利用される。これはそのエネルギーに応じて固体との相互作用が変化し、照射効果も大きく異なることによる。ここでは、環境に優しい将来の半導体材料として期待される鉄シリサイド薄膜に注目し、全く異なる二つのエネルギー領域で成膜・改質に応用した結果を紹介する。基板の表面処理に応用した例では、数keVのイオンビームを表面に照射することにより、化合物半導体薄膜の膜質向上につなげた。これは基板に適度な量の欠陥を生成することで相互拡散・反応を促進させるとともに、基板との結晶方位関係を一定に保つことに成功したものである。条件を最適化することにより、薄膜/基板界面を原子レベルで急峻なものとすることにもつなげた。また改質に応用した例では、100MeV程度の重イオンを照射して薄膜中にビームトラックを形成させ、半導体から金属への相転移により物性が変化することを見いだした。これらはいずれもイオンビームのエネルギーに応じた固体との相互作用を利用したものである。発表ではイオンビームの固体へのエネルギー付与量,阻止能,欠陥生成の深さ分布などと併せて議論を行う。
阿部 浩之; 大貫 駿*; 篠原 義明*; Sutrisna, F.*; 内海 倫明*; 松村 義人*; 大島 武
no journal, ,
La-Ni系水素吸蔵合金は、昨今のハイブリッドカーの電源に代表されるニッケル水素バッテリー(Ni-MH)の負極材として利用されている。これら材料の新規開発や電池としての能力向上の研究開発が急務となっており、本研究では既存材料について水素吸蔵能向上の研究を行っている。従来、吸蔵能向上はケミカルエッチングなどに頼ってきたが、LaNi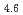 Al
Al 合金について水素吸蔵の初期反応速度(充電放電)に着目し、水素が材料表面に敏感なことから、イオン照射(Kイオン)による表面改質を試みた。Kイオン照射を350keV, 1
合金について水素吸蔵の初期反応速度(充電放電)に着目し、水素が材料表面に敏感なことから、イオン照射(Kイオン)による表面改質を試みた。Kイオン照射を350keV, 1 10
10
 1
1 10
10 cm
cm の照射量の範囲で行った結果、イオン照射を施していない未照射サンプルよりも初期水素吸蔵速度が速くなり(充電反応)、水素吸蔵能が向上することが判明した。
の照射量の範囲で行った結果、イオン照射を施していない未照射サンプルよりも初期水素吸蔵速度が速くなり(充電反応)、水素吸蔵能が向上することが判明した。