Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kobayashi, Taishi*; Teshima, Takeshi*; Wang, P.*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kitamura, Akira
no journal, ,
We focused on the complexation of U(IV) and U(VI) with isosaccharinic acid (ISA) and measured U(IV) and U(VI) solubility in the presence of ISA. The solubility dependences on hydrogen ion concentration (pHc) and ISA concentration revealed the dominant U(IV) and U(VI) ISA complexes and determined their formation constants. Furthermore, the solubility of Zr(IV), as an analogous of An(IV), in the presence of organic acids with different number of hydroxyl groups were investigated to elucidate the strong complexation ability of ISA.
Niizato, Tadafumi; Sasaki, Yoshito; Ito, Satomi; Mitachi, Katsuaki*; Watanabe, Takayoshi
no journal, ,
Kurikami, Hiroshi; Malins, A.; Niizato, Tadafumi; Iijima, Kazuki; Tsukada, Hirofumi*
no journal, ,
This study examined the evolution of reversibly sorbed  Cs in forest soil using a vertical transport model considering kinetic sorption. The simulated distributions and physicochemical forms of
Cs in forest soil using a vertical transport model considering kinetic sorption. The simulated distributions and physicochemical forms of  Cs were consistent with measurements, indicating the modelling approach was reasonable. The results suggest that
Cs were consistent with measurements, indicating the modelling approach was reasonable. The results suggest that  Cs concentrations in wild animals are somewhat linked with the concentration of reversibly sorbed
Cs concentrations in wild animals are somewhat linked with the concentration of reversibly sorbed  Cs in forest soil.
Cs in forest soil.
Liu, J.; Dotsuta, Yuma; Kitagaki, Toru; Kozai, Naofumi; Yamaji, Keiko*; Onuki, Toshihiko
no journal, ,
Fuel debris was formed in severe accident in nuclear power plant. After the confirmation of microorganisms in water in damaged plant, it is necessary to consider the element migration of fuel debris. Here, some widespread bacteria were applied. By cultivation with simulant fuel debris, the migration mechanism was estimated.
Havlov , V.*; Zuna, M.*; Br
, V.*; Zuna, M.*; Br zda, L.*; Rosendorf, T.*; Sammalj
zda, L.*; Rosendorf, T.*; Sammalj rvi, J.*; Nenonen, V.*; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Sasao, Eiji; Gvo
rvi, J.*; Nenonen, V.*; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Sasao, Eiji; Gvo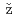 d
d k, L.*
k, L.*
no journal, ,
Anion exclusion is a process that has been widely observed mainly with concern to clay materials. However, this process has also been observed in some types of crystalline rock. Because anion exclusion exerts the impact on migration in the most constricted parts of nanometre-scale pores, this study focused on  H,
H,  Cl and
Cl and  I diffusion together with the characterisation of the rock pore structure of magmatic and metamorphic rocks. Both the anionic species exhibited lower diffusion coefficients than that of
I diffusion together with the characterisation of the rock pore structure of magmatic and metamorphic rocks. Both the anionic species exhibited lower diffusion coefficients than that of  H, thus indicating anionic exclusion mainly in the metamorphic rocks studied. The De values for the anions in the metamorphic rocks differed from those in the magmatic rocks by around one order of magnitude. The difference between the De values for magmatic and metamorphic rocks is clearly supported by pore structure visualisation by autoradiography. Preliminary results showed decreasing accessible porosity for anionic species rather than decreasing pore diffusion coefficients.
H, thus indicating anionic exclusion mainly in the metamorphic rocks studied. The De values for the anions in the metamorphic rocks differed from those in the magmatic rocks by around one order of magnitude. The difference between the De values for magmatic and metamorphic rocks is clearly supported by pore structure visualisation by autoradiography. Preliminary results showed decreasing accessible porosity for anionic species rather than decreasing pore diffusion coefficients.
Yamaguchi, Akiko; Kuribara, Yuichi; Okumura, Masahiko; Takahashi, Yoshio*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Okumura, Masahiko; Kerisit, S.*; Bourg, I.*; Lammers, L.*; Ikeda, Takashi*; Sassi, M.*; Rosso, K.*; Machida, Masahiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sakamoto, Fuminori; Kozai, Naofumi; Guido-Garcia, F.; Kimura, Tatsuki; Grambow, B.
no journal, ,
Soil microorganisms are known to remove a fraction of tightly fixed radiocesium and make it bioavailable. In this study, we attempted to nondestructively recover available radiocesium from soil using microorganisms instead of plants. Microbial activity was tested to form bioavailable radiocesium by the comparing the addition of nutrients and microbicide. Powdered minerals, a water absorbent material, and paper towels were packed in a fine mesh cloth bag (mineral bag) with a size of 50 cm  50 cm. The radiocesium concentration analysis revealed that the surface soil contained approximately 0.3-1.2 Bq/g. The mineral mat was replaced with a new one every two weeks. Two control experiments were established: one with 1 L of nutrient solution to activate microorganisms, and another with sodium hypochlorite aqueous solution to suppress microbial activity. These solutions were added every week. After eight weeks, radiocesium concentrations of the top soil and in the soil core were measured. The accumulative radiocesium concentration in the four mats after eight weeks was within 4.2
50 cm. The radiocesium concentration analysis revealed that the surface soil contained approximately 0.3-1.2 Bq/g. The mineral mat was replaced with a new one every two weeks. Two control experiments were established: one with 1 L of nutrient solution to activate microorganisms, and another with sodium hypochlorite aqueous solution to suppress microbial activity. These solutions were added every week. After eight weeks, radiocesium concentrations of the top soil and in the soil core were measured. The accumulative radiocesium concentration in the four mats after eight weeks was within 4.2 10
10 and 9.0
and 9.0 10
10 Bq, indicating that the mats indeed absorbed radiocesium from soil. The driving force of upward migration of radiocesium is thought to be soil water flow due to continuous water absorption from soil by the mat and evaporation from itself. These results suggest that cesium upward migration flow along with water is a behavior expected to happen in the environment.
Bq, indicating that the mats indeed absorbed radiocesium from soil. The driving force of upward migration of radiocesium is thought to be soil water flow due to continuous water absorption from soil by the mat and evaporation from itself. These results suggest that cesium upward migration flow along with water is a behavior expected to happen in the environment.
Kimura, Tatsuki; Guido-Garcia, F.; Kozai, Naofumi; Zhang, S.*; Yamaji, Keiko*; Yu, Q.*; Grambow, B.
no journal, ,
To understand bacterial ability to dissolve clay minerals, we isolated siderophore-producing bacteria from white clover roots grown in south Osaka, Japan. The ability to produce siderophores was evaluated by CAS plate method. llite, biotite, vermiculite and nontronite were used for testing as clay minerals. Three different bacteria strains were cultivated. Bacteria cells were centrifuged and washed before inoculation tests. Fifty mg dry weight of bacteria were inoculated into 100 mL modified Balland media and 100 mg of each clay mineral added. The suspension was sampled and new media was added. The concentrations of iron, aluminium and silicon were determined by ICP-OES. The presence of organic molecules was determined by SEC-ICP-OES. The peaks of siderophores were determined using the 405 nm absorbance. As a result, siderophore producing bacteria are able to dissolve clay. This suggests that the effect of siderophore on cesium dissolution is an indirectly process.
 Cs uptake by lentinula edodes (shiitake) mushrooms
Cs uptake by lentinula edodes (shiitake) mushroomsGuido-Garcia, F.; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Kozai, Naofumi; Grambow, B.; Devid, K.*
no journal, ,
The uptake of Cs by fungi has been thought to be similar to the uptake of K due to their chemical similarities. In this research we aimed to evaluate the impact of different concentrations of K in Cs uptake during mushrooms growth, as well as determine the spatial distribution of both within fruit bodies. Lentinula edodes (shiitake) was used as a model organism due to their capacity to produce fruit body. Preliminary results have shown that the concentrations of  Cs in the obtained mushroom samples from mushroom bed did not show any clear relationship to the different concentrations of added K. Higher concentrations of
Cs in the obtained mushroom samples from mushroom bed did not show any clear relationship to the different concentrations of added K. Higher concentrations of  Cs were observed in pileus than in stem, consistently. The results of Cs and K mapping did not show a significant spatial variation. This result suggest that Cs and K are distributed evenly, and that there is no specific or selective binding site for cesium.
Cs were observed in pileus than in stem, consistently. The results of Cs and K mapping did not show a significant spatial variation. This result suggest that Cs and K are distributed evenly, and that there is no specific or selective binding site for cesium.
Fujiwara, Kenso; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Matoba, Daisuke*; Iijima, Kazuki
no journal, ,
Depth profiles of radionuclides atmospheric discharged to the environment of Fukushima was obtained nearby the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS). According to the profiles, it was suggested that deposition of Pu-238 and Cs-137 was mostly caused by atmospheric discharge by the FDNPS accident, however, in the case of Pu-239+240, it is necessary to consider the effect of global fallout. For understanding on the migration behaviour of radionuclide, it is necessary to obtain the profiles attributed by the accident and global fallout. In this study, in order to clarify the profile of soil, time dependence of depth profile of Cs and Pu in the soil outside of FDNPS site was measured. Based on the results of this study, it was confirmed that Pu and Cs will not be transferred significantly in the soil over several years. In the case of Pu, concentration of fallout and discharge was calculated. This data is considered to be useful for the safety assessment of waste in FDNPS, especially, measurement of other nuclides can also show the utility of transport ratio based on Cs concentration.
Shimoyama, Iwao; Baba, Yuji*
no journal, ,
Management of radioactive contaminated soil is an unsolved problem after the nuclear incident in Fukushima, but soil decontamination is generally difficult due to the existence of micaseous clay minerals in which radiocesium is strongly fixed. Cesium-free mineralization (CFM) can remove Cs from the soil through the conversion process from clay minerals to other minerals and the choice of reactant is critically important for this method. Because CaCl has higher decontamination efficiency than CaCO
has higher decontamination efficiency than CaCO and Ca(OH)
and Ca(OH) and facilitates phase transformation of clay minerals around 700
and facilitates phase transformation of clay minerals around 700 C, it is deduced that Cl has a catalytic effect on phase transformation, however, the detail is not clear. In this work, Cs-sorbed weathered biotite (WB) was used as a model soil and chemical bonding states of Cl was studied using X-ray absorption spectroscopy and molecular orbital calculations. We clarified that Cl interacted with WB at 400
C, it is deduced that Cl has a catalytic effect on phase transformation, however, the detail is not clear. In this work, Cs-sorbed weathered biotite (WB) was used as a model soil and chemical bonding states of Cl was studied using X-ray absorption spectroscopy and molecular orbital calculations. We clarified that Cl interacted with WB at 400 C and Cl
C and Cl and higher valent Cl sites were formed by bonding with O in WB besides Cl
and higher valent Cl sites were formed by bonding with O in WB besides Cl sites in the early stage of the reaction. Because formation of Cl-O bonds can destabilize the silica network, Cl can facililate decomposition and phase transformation of WB at moderate temperatures.
sites in the early stage of the reaction. Because formation of Cl-O bonds can destabilize the silica network, Cl can facililate decomposition and phase transformation of WB at moderate temperatures.
Sugiura, Yuki; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Okazaki, Mitsuhiro*; Hamamoto, Takafumi*; Ishida, Keisuke*; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
Iwatsuki, Teruki; Ishii, Eiichi
no journal, ,
The paper reviews the applicable knowledge of the migration properties in deep underground gained by R&D in Mizunami and Horonobe URL. Summing up the major migration path, it is necessary to consider the fracture continuity / connectivity of hundreds of meters in granite of Mizunami area, while several hundred meters in the shallow part of sedimentary rock and of tens m scale in the deep part of Horonobe. On the other hand, it was also demonstrated that analogue elements are practically immobile in rock masses and closed galleries.
Ozaki, Yusuke; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Onoe, Hironori
no journal, ,
In this study, we evaluate the effect of shotcrete on the geo-environment after closure of drift. The shotcrete is known to be dissolved into water and change the groundwater chemistry. The detail of chemical process of dissolution of shotcrete is analyzed with the in-situ groundwater collected during GREET experiment in MIU. In addition, reactive transportation simulation is performed to predict the movement of high pH groundwater affected by dissolution of shotcrete. Our simulation results show that the movement of high pH water is slow owing to the diffusive condition after closure of drift under our simulation condition.
Kimuro, Shingo; Terashima, Motoki; Tachi, Yukio; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*
no journal, ,
Humic acid is confirmed to be present even in deep underground where radioactive wastes are planned to be disposed. Although the characteristic properties and reaction mechanism of humic acid are strongly affected by its origin, the reaction enthalpy and entropy for groundwater humic acid complexation are only estimated values obtained from the equilibrium constants at different temperature despite these thermodynamic quantities is necessary for the discussion of reaction thermodynamics. In this study, the thermodynamic quantities of the complexation of deep groundwater humic acid at Horonobe, Hokkaido, Japan with copper (II) and uranyl (VI) ion were determined by the combination of the potentiometry and calorimetry to cultivate a better understanding of the reaction mechanism. By the comparison of thermodynamic quantities with typical humic acid and simple organic acid, the characteristic reaction mechanism of Horonobe humic acid was revealed. In addition, thermodynamic equilibrium calculations based on the determined thermodynamic quantities were performed for the discussion of the impact of humic acid complexation and the origin of humic acid in the migration of radionuclide.
 pellet
pelletMoroi, Yuriko*; Kirishima, Akira*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kitamura, Akira; Kimuro, Shingo
no journal, ,
Development of spent nuclear fuel direct disposal system is one of important options in Japan to maintain flexibility of the back-end strategy of nuclear fuel cycle. Other countries like Sweden and Finland advance in research and development of the direct disposal system. However, it is known that some groundwater in Japan contains higher concentration of carbonate ion than that in Sweden or Finland. Therefore, the effect of carbonate ion on the dissolution rate of UO has to be discussed to evaluate feasibility of the direct disposal system in Japan.
has to be discussed to evaluate feasibility of the direct disposal system in Japan.
Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Arthur, R. C.*; Alt-Epping, P.*; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
The present study performed an interpretation of natural tracers (non or weakly sorption elements) profiles of groundwater observed in the boreholes drilled from the surface around the Horonobe Underground Laboratory based on the transport processes of advection and diffusion. In the interpretation, due to several uncertainty ranges for transport parameters in initial and boundary conditions, sensitivity analyses considering the relevant model parameters defined uncertainty limits were also conducted to evaluate the plausible parameter sets and conditions to be compatible with observations.
Fukatsu, Yuta; Ito, Tsuyoshi*; Tachi, Yukio; Ishida, Keisuke*; Martin, A.*
no journal, ,
Suno, Hiroya; Machida, Masahiko; Dohi, Terumi; Omura, Yoshihito*; Sasaki, Yoshito
no journal, ,
Complexation of biomolecules with radiocesium is known to play an important role in the accumulation and migration of radioactivity on the organic matter in forests. In this work, we identify typical molecules forming a metal complex in the forest organic matter and carry out atomistic analyses by performing quantum mechanical calculations in order to understand the alkali metal cation complexation selectivity of these organic molecules. Among these molecules, of particular interest are norbadione A (C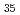 H
H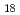 O
O ), a primary pigment molecule present in mushrooms, oxalic acid (C
), a primary pigment molecule present in mushrooms, oxalic acid (C H
H O
O ), atranorin (C
), atranorin (C H
H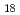 O
O ), lecanoric acid (C
), lecanoric acid (C H
H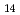 O
O ), and usnic acid (C
), and usnic acid (C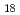 H
H O
O ), main secondary metabolites in lichens.
), main secondary metabolites in lichens.