Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kisohara, Naoyuki; Ishikawa, Hiroyasu; Futagami, Satoshi; Xu, Y.*; Shimoji, Kuniyuki*; Kawamura, Masaya*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2011/10
The cooling system of the JSFR adopts an integrated primary sodium pump/intermediate heat exchanger (IHX), dual structure straight tube steam generator (SG) and short elbow sodium piping layout. Since, however, this is the first experience applying these technologies to SFRs in Japan, design approaches have been evaluated and R&D has been undertaken. This paper addresses the design study of the cooling system of the demonstration reactor JSFR in terms of thermal-hydraulic and structural integrity. Recent studies have shown that these new technologies have potential to be applied to the JSFR.
Obayashi, Hironari; Sugawara, Takanori; Nishihara, Kenji
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/10
Kurikami, Hiroshi; Niizato, Tadafumi; Yasue, Kenichi
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/10
Description of system evolution is an important task in safety and investigation strategies. This paper showed the method to describe system evolution based on safety functions and FEPs and its application to the Horonobe site. Based on the SDM and the Horonobe-specific FEPs, the important FEPs were put in a timeline with the main safety functions. According to the FEPs, we defined thermal and resaturation phase, steady geology phase and geologically evolution phase. In the steady geology phase, the functions of retardation and dilution in the deeper part of the Wakkanai Formation are important, therefore, advection, dispersion and sorption in the domain should be assessed based on the nuclide migration scenario. In the geologically evolution phase, the uplift and denudation are important. Thus, the uplift, denudation and the consequent THMC processes were involved in the reference evolution. Through the application and the discussion, the method was found to be applied to other sites.
Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Ueta, Shohei; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/10
The three gas circulators trip test and the vessel cooling system stop test as the safety demonstration test by using the High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) are under planning to demonstrate inherent safety features of High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR). All three gas circulators to circulate the helium gas as the coolant are stopped to simulate the loss of forced cooling in the three gas circulators trip test. The stop of the vessel cooling system located outside the Reactor Pressure Vessel (RPV) to remove the residual heat of the reactor core follows the stop of all three gas circulators in the vessel cooling system stop test. The analysis of the reactor transient for such tests and abnormal events postulated during the test is performed. From the result of analysis, it is confirmed that the three gas circulators trip test and the vessel cooling system stop test can be performed within the region of the normal operation in the HTTR.
Sato, Hiroyuki; Park, H.*; Knoll, D.*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/10
Multiphysics core simulations for a prismatic-type VHTR are performed in this study. Our solution scheme is based on the JFNK method. As a preliminary example, a thermal-fluid calculation is performed with an idealized two-dimensional symmetric representation of the GT-MHR and compared with the RELAP5-3D simulation results. Also, a neutronics calculation is conducted using the same geometry as the thermal-fluid calculation, and using cross section data obtained from an HTGR benchmark problem. In addition, a coupled steady-state thermal-fluids neutronics calculation is performed. The calculation results showed that the developed prismatic VHTR core simulator can perform tightly-coupled multiphysics simulations efficiently.
Yan, X.; Sato, Hiroyuki; Tachibana, Yukio
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2011/10
This paper describes the design of a modular HTGR system cogenerating electricity and process heat and discusses its operational feasibility of electric load follow using a new control scheme. The load follow operations are performed by controlling the reactor coolant inventory while keeping the primary system thermal conditions including reactor power, reactor temperature, and turbine temperatures unchanged. This control strategy is designed to achieve high thermal efficiency in a wide range of part electric load and, by minimizing thermal transient of the reactor, to enable response to rapid load follow demand. The newly proposed control strategy is evaluated by simulation of a bounding load-follow event.
Kurisaka, Kenichi; Okamura, Shigeki*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been developing the Japan Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor (JSFR) in the Fast Reactor Cycle Technology Development (FaCT) Project. Risk targets were set out as part of the safety-related design requirement: i.e., the quantitative safety design requirements on the core damage frequency (CDF) and the containment failure frequency (CFF). This paper describes a preliminary evaluation of achievement level of JSFR to the risk targets at the FaCT project phase-I: JFY2006 to JFY2010. A Level-1 PSA has been implemented preliminarily to evaluate the CDF related to internal initiators in power operation. The calculated CDF became lower than the both requirements on CDF and CFF. For seismic events, the seismic fragility of principal structures and components was evaluated in terms of core damage prevention. This evaluation was based on the seismic response analysis, which considered the seismic isolation effect and the hardening effect of the laminated rubber bearing in the isolation devices. As a result, we confirmed that the principal structures and components of JSFR have sufficient seismic margin. Based on this, we judged the risk target could be achieved against the seismic event.
Furukawa, Tomohiro; Kato, Shoichi; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Aritomi, Masanori*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2011/10
A key problem in the application of a supercritical carbon dioxide (CO ) turbine cycle to a fast breeder reactor is the corrosion of structural materials brought about by supercritical CO
) turbine cycle to a fast breeder reactor is the corrosion of structural materials brought about by supercritical CO at high temperatures. In this study, high-temperature oxidation tests on the structural materials were performed in carbon dioxide pressurized at 0.2 and 1 MPa, and in air, and the oxidation behavior were compared. Results of investigating the effect of CO
at high temperatures. In this study, high-temperature oxidation tests on the structural materials were performed in carbon dioxide pressurized at 0.2 and 1 MPa, and in air, and the oxidation behavior were compared. Results of investigating the effect of CO pressure including the previous reports tested at 10 MPa and at 20 MPa, the effect was hardly observed for all steels. In air environment, weight gain caused by high temperature oxidation was much lower than that in CO
pressure including the previous reports tested at 10 MPa and at 20 MPa, the effect was hardly observed for all steels. In air environment, weight gain caused by high temperature oxidation was much lower than that in CO .
.
Kosaka, Hiroshi; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Yasue, Kenichi; Kusano, Tomohiro; Onoe, Hironori
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2011/10
The methodology for estimation of the long-term evolution of groundwater flow conditions are being developed using approaches on the basis of deductive and inductive methods in the case of Tono area. Based on the studies using the approach on the basis of deductive method, it has been confirmed that the method combining physical modeling of topographic change and groundwater flow simulations is useful for estimating of changes in groundwater flow conditions in the future due to topographic and climatic perturbations. Existing information for estimation of surface hydrological conditions, which are to be used for assignment of boundary conditions for the groundwater flow simulation, has been gathered from many sources and reviewed based on modern-analogue methods. In the studies using the approach on the basis of inductive method, paleo-hydrogeological studies have been carried out on several spatial and time scales. Through the study on the largest spatial scale, a methodology needed to understand changes of groundwater flow conditions due to long-term topographic change is proposed to efficiently identify the area to be carried out site characterization involving field investigations. And then, information to estimate the paleo-topography and paleo-climate has been obtained from literature surveys and field investigations. Through these studies, it has been confirmed that these two approaches are useful for estimation of the long-term evolution of deep groundwater flow conditions.
Kondo, Hiroo; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Iuchi, Hiroshi; Ida, Mizuho; Watanabe, Kazuyoshi; Kanemura, Takuji; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Yamaoka, Nobuo*; Matsushita, Izuru*; et al.
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2011/10
Engineering Validation and Engineering Design Activities (EVEDA) for the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) were started from July 2007 under an international agreement called ITER Broader Approach. As a major Japanese activity, EVEDA Li test loop (ELTL) to simulate hydraulic and impurity conditions of IFMIF has already designed and is under construction, in which feasibility of hydraulic stability of the liquid Li target, the purification systems of hot traps are major key issues to be validated in this loop. This paper presents the engineering design of the main electro-magnetic pump of the ELTL including the pressure drop calculation and evaluation of the cavitation inception.
 O-I
O-I solution in the thermochemical hydrogen production iodine-sulfur (IS) process
solution in the thermochemical hydrogen production iodine-sulfur (IS) processKasahara, Seiji; Guo, H.*; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kubo, Shinji; Onuki, Kaoru
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/10
Flowsheet investigation of the subsection of HI separation from HI-H O-I
O-I solution in the thermochemical hydrogen production iodine-sulfur (IS) process was performed. Concentration of HI by electro-electrodialysis (EED) and distillation of HI were applied. Experimental data of the EED cell applying Nafion membrane was used to establish heat/mass balance equations for the cell. Heat/mass balance of HI distillation column was calculated using ESP, a process simulation software. HI molality at the cathode outlet of the cell, pressure in the HI distillation column, and flow rate ratio of the feed to the subsection to distillate of the column were focused as variable parameters for minimum heat demand. Parameters of the EED membrane, electric resistance and upper limit of HI molality between outlet streams, had a great effect on the heat demand; improvement of the membrane parameters is important to reduce the heat demand.
solution in the thermochemical hydrogen production iodine-sulfur (IS) process was performed. Concentration of HI by electro-electrodialysis (EED) and distillation of HI were applied. Experimental data of the EED cell applying Nafion membrane was used to establish heat/mass balance equations for the cell. Heat/mass balance of HI distillation column was calculated using ESP, a process simulation software. HI molality at the cathode outlet of the cell, pressure in the HI distillation column, and flow rate ratio of the feed to the subsection to distillate of the column were focused as variable parameters for minimum heat demand. Parameters of the EED membrane, electric resistance and upper limit of HI molality between outlet streams, had a great effect on the heat demand; improvement of the membrane parameters is important to reduce the heat demand.
Kobayashi, Jun; Kimura, Nobuyuki; Tobita, Akira; Kamide, Hideki; Watanabe, Osamu*; Oyama, Kazuhiro*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/10
Design study of an advanced loop-type sodium-cooled fast reactor, JSFR, has been carried out in a frame work of Fast Reactor Cycle Technology Development Project (FaCT) in Japan. As the temperature differences among the control rod channels, blanket assemblies and the core fuel assemblies are 100 C centigrade in the maximum, temperature fluctuation due to the fluid mixing at the core outlet may cause high cycle thermal fatigue at the bottom of Upper Internal Structure (UIS). In this investigation, a water experiment was conducted using a 1/3 scale 60
C centigrade in the maximum, temperature fluctuation due to the fluid mixing at the core outlet may cause high cycle thermal fatigue at the bottom of Upper Internal Structure (UIS). In this investigation, a water experiment was conducted using a 1/3 scale 60 sector model of the core and reactor upper plenum. Characteristics of temperature fluctuations near the cold fluid outlets were obtained and it was confirmed that several countermeasures can reduce temperature fluctuations at the bottom of UIS.
sector model of the core and reactor upper plenum. Characteristics of temperature fluctuations near the cold fluid outlets were obtained and it was confirmed that several countermeasures can reduce temperature fluctuations at the bottom of UIS.
Iwamoto, Yukiharu*; Kondo, Manabu*; Yasuda, Kazunori*; Sogo, Motosuke*; Tanaka, Masaaki; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/10
Tani, Akihiro*; Shimakawa, Yoshio*; Kubo, Shigenobu*; Fujimura, Ken; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/10
Baba, Takeo*; Hirota, Kazuo*; Sago, Hiromi*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Aizawa, Kosuke; Xu, Y.*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2011/10
Sago, Hiromi*; Shiraishi, Tadashi*; Watakabe, Hisato*; Xu, Y.*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/10
Goto, Minoru; Shimakawa, Satoshi; Tachibana, Yukio
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2011/10
In the past, benchmark calculations of criticality approach for the HTTR, which is a Japanese HTGR, were performed by research institutes in several countries, and almost all of the calculations overestimated the excess reactivity. In Japan, the benchmark calculations were performed by JAEA, and were also resulted in overestimation. JAEA improved the calculations by revising the geometric model and replacing the nuclear data library with JENDL-3.3, which was the latest JENDL at that time. However, the overestimation remained and this problem has not been resolved until today. We performed calculations of the HTTR criticality approach with several nuclear data libraries, and found that slight difference in the neutron capture cross section of carbon at thermal energy among the libraries causes significant difference in the 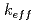 values. The cross section value of carbon was not concerned in reactor neutronics calculation because of its small value of the order of 1E-3 burn, and consequently the cross section value had not been revised for a long time even in the major nuclear data libraries: JENDL, ENDF/B and JEFF. We thought that the cross section should be revised based on the latest measurement data to improve the accuracy of the HTGR criticality analysis. In May 2010, the latest JENDL (JENDL-4.0) was released by JAEA, and the capture cross section of carbon was revised. JENDL-4.0 yielded 0.4-0.9%
values. The cross section value of carbon was not concerned in reactor neutronics calculation because of its small value of the order of 1E-3 burn, and consequently the cross section value had not been revised for a long time even in the major nuclear data libraries: JENDL, ENDF/B and JEFF. We thought that the cross section should be revised based on the latest measurement data to improve the accuracy of the HTGR criticality analysis. In May 2010, the latest JENDL (JENDL-4.0) was released by JAEA, and the capture cross section of carbon was revised. JENDL-4.0 yielded 0.4-0.9% k/k smaller
k/k smaller 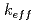 values than JENDL-3.3 in the criticality calculations for the HTTR critical approach, and consequently the problem of the overestimation of the excess reactivity in the HTTR benchmark calculation was resolved by replacing the nuclear data libraries with JENDL-4.0.
values than JENDL-3.3 in the criticality calculations for the HTTR critical approach, and consequently the problem of the overestimation of the excess reactivity in the HTTR benchmark calculation was resolved by replacing the nuclear data libraries with JENDL-4.0.
Takeda, Takeshi; Maruyama, Yu; Watanabe, Tadashi; Nakamura, Hideo
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2011/10
Experiments simulating PWR intermediate-break loss-of-coolant accidents (IBLOCAs) with 17% break at hot leg or cold leg were conducted in OECD/NEA ROSA-2 project using LSTF. In the hot leg IBLOCA test, core uncovery appeared simultaneously with loop seal clearing (LSC). Water remained on upper core plate in upper plenum due to CCFL. In the cold leg IBLOCA test, core dryout took place before LSC. Liquid was accumulated in upper plenum, SG U-tube upflow-side and SG inlet plenum before the LSC due to CCFL. The RELAP5/MOD3.2.1.2 post-test analyses were performed. In the hot leg IBLOCA case, cladding surface temperature was underpredicted due to overprediction of core liquid level after the core uncovery. In the cold leg IBLOCA case, the cladding surface temperature was underpredicted too due to later core uncovery than in the experiment. These may suggest that the code has remaining problems in proper prediction of primary coolant distribution.
Ohno, Shuji; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Tajima, Yuji*; Oki, Hiroshi*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/10
Conceptual design study of the JSFR needs the evaluation of thermodynamic consequences in hypothetical sodium fire accident. The authors are therefore initiating systematic V&V activity for sodium fire evaluation tools. The activity is in progress with the main focuses on already developed sodium fire analysis codes SPHINCS and AQUA-SF. The present paper describes that a preliminary "PIRT" is developed at first, and an "assessment matrix" is proposed which summarizes both separate effect tests (SET) and integral effect tests (IET) for validating the computational models or whole code for important phenomena. Furthermore, the paper shows an individual validation with SET in which the spray droplet combustion model of SPHINCS and AQUA-SF predicts the burned amount of a falling sodium droplet with the error mostly less than 30%.
Onoe, Hironori; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Daimaru, Shuji; Karino, Tomoyuki
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2011/10