Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sasaki, Akira; Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Sunahara, Atsushi*; Nishikawa, Takeshi*; Koike, Fumihiro*; Tanuma, Hajime*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tsuji, Toshiyuki*; Kobayashi, Akira*; Yoshida, Eiji*; Ichihara, Chikara*; Adachi, Shigeto*; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Haga, Junji
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamauchi, Toshihiko; Nakagaki, Keita; Kanno, Yoshinori*; Kobayashi, Seiji*; Takemoto, Ryo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Togashi, Hideaki*; Yamamoto, Yoshihisa*; Goto, Seiichi*; Takahashi, Yuya*; Nakano, Takuya*; Konno, Atsushi*; Suemitsu, Maki*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
no journal, ,
Oxygen-adsorbed Si(110)-16 2 surfaces at room temperature and their thermally-treated surfaces were analyzed by real-time photoemission spectroscopy with synchrotron radiation (SR-PES) and scanning tunneling microscopy (STM). Thermal stability of the oxygen-adsorbed Si(110) surfaces was clearified. By thermal annealing of Si(110) surface exposed to 10L oxygen gas at room temperature, photoemission peak positions of Si
2 surfaces at room temperature and their thermally-treated surfaces were analyzed by real-time photoemission spectroscopy with synchrotron radiation (SR-PES) and scanning tunneling microscopy (STM). Thermal stability of the oxygen-adsorbed Si(110) surfaces was clearified. By thermal annealing of Si(110) surface exposed to 10L oxygen gas at room temperature, photoemission peak positions of Si and Si
and Si components were shifted to higher energy side by 0.20eV and 0.12eV,respectively, and reached nearly to those of thermal oxide films. This behaviour is due to change of Si-O-Si bond angle and Si-O bond length. The STM observation for Si(110) surfaces revealed that the oxygen-adsorbed surface structure changed to the condensed oxide structure by thermal annealing. These SR-PES and STM results showed that the oxygen-adsorbed Si(110)-16
components were shifted to higher energy side by 0.20eV and 0.12eV,respectively, and reached nearly to those of thermal oxide films. This behaviour is due to change of Si-O-Si bond angle and Si-O bond length. The STM observation for Si(110) surfaces revealed that the oxygen-adsorbed surface structure changed to the condensed oxide structure by thermal annealing. These SR-PES and STM results showed that the oxygen-adsorbed Si(110)-16 2 structure was metastable and changed to more stable condensed oxide structure by thermal annealing.
2 structure was metastable and changed to more stable condensed oxide structure by thermal annealing.
Otobe, Tomohito
no journal, ,
The optical breakdown is the most important process to control and manipulate the dielectrics by the intense laser field. However, the first-principle simulation for this process has not been studied. In this study, we employ the time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT) to describe the electron dynamics of many electron system. Our computational results shows that the electron excitation occurs around the electric bond and the above threshold photo-absorption process which is similar to the atom or molecular case.
 oxidation of H-terminated Si(110) surface
oxidation of H-terminated Si(110) surfaceNakano, Takuya*; Togashi, Hideaki*; Matsumoto, Mitsutaka*; Yamamoto, Yoshihisa*; Suzuki, Yasushi*; Teraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Suemitsu, Maki*
no journal, ,
Time evolution of oxide layers in the H-terminated Si(110) surface by the UV/O treatment at room temperature was observed by photoemission spectroscopy with synchrotron radiation. Special oxidation mechanisms for the H-terminated Si(110) surface were found. Si(110) surfaces were hydrogenated by HF treatments. The surface was irradiated and oxidized by UV light (253.7, 184.9 nm) of a low pressure Hg lamp in the air. The UV/O
treatment at room temperature was observed by photoemission spectroscopy with synchrotron radiation. Special oxidation mechanisms for the H-terminated Si(110) surface were found. Si(110) surfaces were hydrogenated by HF treatments. The surface was irradiated and oxidized by UV light (253.7, 184.9 nm) of a low pressure Hg lamp in the air. The UV/O irradiation time dependence of oxide thickness showed a step-wise profile. The step width was about 0.2 nm. The value is close to one oxide layer thickness (0.19 nm) for the Si(110) surface. Si atoms at the Si(110) surface are categolized to A bonds which are chain-like dense bonds, and B bonds which connect up and down A bond chains. The step-wise oxidation behaviour is reasonable if oxidation at the B bonds, in which oxidation strain is smaller than that of A bonds, has larger reaction rate than at the A bonds.
irradiation time dependence of oxide thickness showed a step-wise profile. The step width was about 0.2 nm. The value is close to one oxide layer thickness (0.19 nm) for the Si(110) surface. Si atoms at the Si(110) surface are categolized to A bonds which are chain-like dense bonds, and B bonds which connect up and down A bond chains. The step-wise oxidation behaviour is reasonable if oxidation at the B bonds, in which oxidation strain is smaller than that of A bonds, has larger reaction rate than at the A bonds.
 molecular beam
molecular beamOkada, Michio*; Vattuone, L.*; Moritani, Kosuke*; Gerbi, A.*; Savio, L.*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Rocca, M.*; Kasai, Toshio*
no journal, ,
Initial oxidation processes at Cu(100) and Cu(410) surfaces by hyperthermal oxygen molecular beams (HOMB) have been investigated. In order to make clear effects of surface temperature, oxidation behaviour of steps at the Cu(410) surface, which had a moderate oxidation rate, was studied by high energy-resolution X-ray photoemission spectroscopy at the BL23SU in the SPring-8. Consequently, formation of Cu O was observed at room temperature by using HOMB of about 2 eV. And metastable CuO was formed at 100 K. These facts indicate that interest surface layers can be formed by controlling incident energy of oxygen molecular beams and surface temperature.
O was observed at room temperature by using HOMB of about 2 eV. And metastable CuO was formed at 100 K. These facts indicate that interest surface layers can be formed by controlling incident energy of oxygen molecular beams and surface temperature.
 -FeSi
-FeSi /Si(100) interface using ion irradiated Si substrate
/Si(100) interface using ion irradiated Si substrateSasase, Masato*; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Shamoto, Shinichi
no journal, ,
Beta iron disilicide thin film has been fabricated on Si substrate by means of ion beam sputter deposition method. By 1 keV irradiation at the fluence of 3 10
10 ions/m
ions/m , epitaxially grown
, epitaxially grown  -FeSi
-FeSi film has been obtained on Si(100) subatrate with atomically smooth interface.
film has been obtained on Si(100) subatrate with atomically smooth interface.
Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Hirade, Tetsuya; Miwa, Yukio
no journal, ,
We developed the scanning positron microscope. By scanning the positron microbeam which diameter is several micrometers, spatial distributions of annihilation  rays can be obtained. It becomes possible to acquire the two-dimensional distributions of vacancy-type defects, or to perform the defect observation in the selected area. A small sealed sodium-22 source (effective diameter of 2 mm, 55 MBq) developed by us is used as positron source. Using a objective lens, a positron microbeam of 1.9 micrometer is formed. When the stainless steel which has stress corrosion cracking is observed, we found defective areas far from the tip of crack. Those cannot be detected by conventional optical and electron microscope.
rays can be obtained. It becomes possible to acquire the two-dimensional distributions of vacancy-type defects, or to perform the defect observation in the selected area. A small sealed sodium-22 source (effective diameter of 2 mm, 55 MBq) developed by us is used as positron source. Using a objective lens, a positron microbeam of 1.9 micrometer is formed. When the stainless steel which has stress corrosion cracking is observed, we found defective areas far from the tip of crack. Those cannot be detected by conventional optical and electron microscope.
Abe, Hiroshi; Morimoto, Ryo*; Aone, Shigeo*; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Oshima, Takeshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Aone, Shigeo*; Abe, Hiroshi; Uchida, Hirohisa*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Umeda, Takahide*; Isoya, Junichi*; Morishita, Norio; Oshima, Takeshi; Ito, Hisayoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kamiura, Yoshitomo*; Umezawa, Kenji*; Teraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
Nitrogen ion beams (N , N
, N
 ) with kinetic energy of 2.5 keV were irradiated to poly W surfaces with thin oxide films at room temperature. The element ratio and depth profile of chemical bonding states for the modified-W surface were analyzed by photoemission spectroscopy with the surface reaction analysis apparatus at the BL23SU in the SPring-8. W4f photoemission spectra were observed using synchrotron radiation of 592 eV for the W surfaces which were irradiated by nitrogen ion beams with the dose of 2
) with kinetic energy of 2.5 keV were irradiated to poly W surfaces with thin oxide films at room temperature. The element ratio and depth profile of chemical bonding states for the modified-W surface were analyzed by photoemission spectroscopy with the surface reaction analysis apparatus at the BL23SU in the SPring-8. W4f photoemission spectra were observed using synchrotron radiation of 592 eV for the W surfaces which were irradiated by nitrogen ion beams with the dose of 2 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm . Nitridized W in addition to metal W4f
. Nitridized W in addition to metal W4f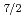 , W4f
, W4f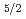 and their oxidized components were observed. N1s photoemission spectra, which were simultaneously measured, showed a chemical shift in the high energy side. This implies that nitrogen atoms were in the dpper positions.
and their oxidized components were observed. N1s photoemission spectra, which were simultaneously measured, showed a chemical shift in the high energy side. This implies that nitrogen atoms were in the dpper positions.
Yamamoto, Yoshihisa*; Togashi, Hideaki*; Kato, Atsushi*; Suemitsu, Maki*; Narita, Yuzuru*; Teraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
Formation processes of one atomic oxide layer and time evolution of chemical bonding states at the interface were investigated by using real-time photoemission spectroscopy with synchrotron radiation. Time evolutions for oxide components (Si :n=1-4) of Si2p photoemission spectra, observed in the conditions of 813K substrate temperature and 1.1
:n=1-4) of Si2p photoemission spectra, observed in the conditions of 813K substrate temperature and 1.1 10
10 Pa O
Pa O pressure, were analyzed. Rapid increase of Si
pressure, were analyzed. Rapid increase of Si component until oxygen dose of 10 L indicates existance of a reaction path through the Si
component until oxygen dose of 10 L indicates existance of a reaction path through the Si state. On the other hand, contrary to the Si(001) oxidation, the Si
state. On the other hand, contrary to the Si(001) oxidation, the Si component was larger than the Si
component was larger than the Si component during oxidation. Reaction mechanisms was considered from these facts. Oxygen insertion into chain-like Si-Si bonds densely existing on the (110) surface (A bond) and Si-Si bonds on the (-110) surface is an origin of the first layer oxidation at Si(110) surface. The A bonds may be oxidized partially due to storage of oxidation strains.
component during oxidation. Reaction mechanisms was considered from these facts. Oxygen insertion into chain-like Si-Si bonds densely existing on the (110) surface (A bond) and Si-Si bonds on the (-110) surface is an origin of the first layer oxidation at Si(110) surface. The A bonds may be oxidized partially due to storage of oxidation strains.
Akahane, Yutaka; Aoyama, Makoto; Sugiyama, Akira; Kubo, Ryoichi; Ogawa, Kanade; Tsuji, Koichi; Yamakawa, Koichi
no journal, ,
A diode-pumped, cryogenically-cooled Yb :LuLiF
:LuLiF regenerative amplifier has been developed for the first time to our knowledge, which generated 6-mJ, 13-ps pulses at 999 nm wavelength without a pulse compressor.
regenerative amplifier has been developed for the first time to our knowledge, which generated 6-mJ, 13-ps pulses at 999 nm wavelength without a pulse compressor.
Sagisaka, Akito; Daido, Hiroyuki; Ma, J.-L.; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 7 by O
7 by O
Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
no journal, ,
In order to clarify the O adsorption on Si(111)-7
adsorption on Si(111)-7 7, we investigated surface temperature dependence of initial sticking probability (S0) by synchrotron radiation real-time O1s XPS. All experiments were performed at SUREAC2000 of BL23SU in SPring-8. Translational energy (En) is controlled up to 2.3eV. The variable leak valve was used to perform the 0.03eV exposure condition. The S0 is evaluated to be the differential value at the zero dosage in the oxygen uptake curve. In the condition observed for negligibly small variation of S0 depending on En (0.15eV, 2.23eV), the Ts dependence is not observed within the margin of error. This result implys that the direct adsorption mechanism is dominant in this energy region. On the other hand, we found that the S0 decreases with increasing Ts and thus the trapping mediated adsorption mechanism is dominant in the energy condition of 0.03eV and 0.06eV. These results are consistent with the reaction dynamics observed in En dependence of S0.
7, we investigated surface temperature dependence of initial sticking probability (S0) by synchrotron radiation real-time O1s XPS. All experiments were performed at SUREAC2000 of BL23SU in SPring-8. Translational energy (En) is controlled up to 2.3eV. The variable leak valve was used to perform the 0.03eV exposure condition. The S0 is evaluated to be the differential value at the zero dosage in the oxygen uptake curve. In the condition observed for negligibly small variation of S0 depending on En (0.15eV, 2.23eV), the Ts dependence is not observed within the margin of error. This result implys that the direct adsorption mechanism is dominant in this energy region. On the other hand, we found that the S0 decreases with increasing Ts and thus the trapping mediated adsorption mechanism is dominant in the energy condition of 0.03eV and 0.06eV. These results are consistent with the reaction dynamics observed in En dependence of S0.
 7 in the oxidation at 300K by using synchrotron radiation XPS
7 in the oxidation at 300K by using synchrotron radiation XPSYoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
no journal, ,
Time evolution of rest atoms on Si(111)-7 7 at 300K was investigated by using synchrotron radiation real-time XPS. All experiments were performed at SUREAC2000 of BL23SU at SPring-8. The O
7 at 300K was investigated by using synchrotron radiation real-time XPS. All experiments were performed at SUREAC2000 of BL23SU at SPring-8. The O pressure was controlled to be 5.2
pressure was controlled to be 5.2 10
10 Pa by using variable leak valve. The simultaneous O1s and Si2p real-time XPS was measured by 670eV photon energy. The intensity of rest atoms decreases with increasing the oxygen coverage just after starting oxidation and it reached to become constant value at around 0.4
Pa by using variable leak valve. The simultaneous O1s and Si2p real-time XPS was measured by 670eV photon energy. The intensity of rest atoms decreases with increasing the oxygen coverage just after starting oxidation and it reached to become constant value at around 0.4 10
10 cm
cm (coverage:0.43ML) without vanishment. Since the binding energy of rest atoms is almost identical with that of alpha peak which is originated from Si-Si bond variations at the oxide/substrate interface and is normally observed in Si(001) oxidation, we find that the alpha component grows with decreasing the rest atoms according to the progress of oxidation.
(coverage:0.43ML) without vanishment. Since the binding energy of rest atoms is almost identical with that of alpha peak which is originated from Si-Si bond variations at the oxide/substrate interface and is normally observed in Si(001) oxidation, we find that the alpha component grows with decreasing the rest atoms according to the progress of oxidation.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Nakai, Yoshiki; Shimomura, Takuya*; Tanoue, Manabu*; Akutsu, Atsushi; Okada, Hajime; Motomura, Tomohiro*; Kondo, Shuji; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Daido, Hiroyuki; Yogo, Akifumi; Orimo, Satoshi; Ogura, Koichi; Ma, J.-L.; Sagisaka, Akito; Mori, Michiaki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; et al.
no journal, ,
The efficient proton beam whose maximum energy of up to 4 MeV was produced by the 50TW short pulse intensity Ti:Sap laser irradiated on the polyimide target [(C H
H O
O N
N )n] with the thicknesses of 7.5
)n] with the thicknesses of 7.5 m, 12.5
m, 12.5 m, 25
m, 25 m, which is transparent to the 800 nm laser. The laser parameters are energy of 1.7J, pulse width of 35fs and the intensity of 3
m, which is transparent to the 800 nm laser. The laser parameters are energy of 1.7J, pulse width of 35fs and the intensity of 3 10
10 Wcm
Wcm . The contrast of the ASE component is 4
. The contrast of the ASE component is 4 10
10 . The conversion efficiency from laser energy into the proton kinetic energy is up to
. The conversion efficiency from laser energy into the proton kinetic energy is up to  3%. This conversion efficiency is comparable or even higher than the results obtained with the same level laser (
3%. This conversion efficiency is comparable or even higher than the results obtained with the same level laser ( J energy) interacts with the nano-meter level ultra thin target. In this paper we discuss on the comparison between our results and other experimental results obtained in other facilities.
J energy) interacts with the nano-meter level ultra thin target. In this paper we discuss on the comparison between our results and other experimental results obtained in other facilities.