Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwata, Hajime; Kitamura, Akira
no journal, ,
The solubility of Nb was measured using oversaturation and undersaturation method. Compared with the values evaluated using JAEA-TDB, in the OS method a similar solubility was observed, and the measured values in the US method were around three orders magnitude below the evaluated values. It suggests that the solubility limiting solid differ between OS and US method.
Idesaki, Akira; Sugimoto, Masaki; Shimada, Akihiko; Yamamoto, Shunya; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Yamaki, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
Recently, development of platinum-substitute catalysts has been studied extensively; it has been found that a nitrogen-containing carbon material shows oxygen reduction activity almost same as platinum metal. We have been studying about synthesis process of a nitrogen-containing carbon material by pyrolysis of polymer precursors which are easy to be shaped as fiber, film, and so on. In this work, some materials were selected as polymer precursors and their organic-inorganic conversion process were investigated. It was found that polyimide and phenol resin show high carbon yield of 50-60% and graphite structure is formed above 800 C.
C.
Seko, Noriaki; Amada, Haruyo; Hoshina, Hiroyuki; Ikegawa, Atsushi*; Hatanaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
Okumura, Masahiko; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Sassi, M.*; Rosso, K.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Miyahara, Kaname; Iijima, Kazuki
no journal, ,
This presentation provides a concise overview of knowledge and experience gained from the activities for environmental remediation after the Fukushima Dai-ichi accident to establish the technical basis for strategic, off-site response to nuclear incidents. It is produced by JAEA, reflecting JAEA's key role in the research associated with both remediation of contaminated areas and the natural processes influencing contamination migration in non-remediated areas. This presentation also provides a perspective on the future actions to facilitate return of residents to the most contaminated zones from the standpoint of environmental chemistry and radiochemistry with special emphasis on associated waste management.
Baba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Izumi, Toshinori
no journal, ,
In order to clarify the chemical states of radioactive cesium in clay minerals, the X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS) have been measured for cesium and the other alkali metals on oxides and micaceous oxides. Since the number of atoms in radioactive Cs-137 is extremely small, we focused on the adsorption of trace amount of cesium. For this purpose, we applied total reflection XPS (TR-XPS) using synchrotron radiation. For micaceous oxide, the TR-XPS spectra show that the cesium is more positively charged compared with that for thicker layer. It was shown that trace-level cesium in micaceous oxides is ionically bonded at the interlayer due to the negative charge of the micaceous oxide. We consider that the observed unique adsorption-desorption behavior is specific to only trace-level cesium.
 isotopologues using femtosecond laser-induced molecular alignment
isotopologues using femtosecond laser-induced molecular alignmentAkagi, Hiroshi; Kasajima, Tatsuya*; Kumada, Takayuki; Itakura, Ryuji; Yokoyama, Atsushi; Hasegawa, Hirokazu*; Oshima, Yasuhiro*
no journal, ,
We propose a laser isotope separation method without tunable lasers, and demonstrate isotope selective ionization of nitrogen isotopologues. This method is based on molecular alignment and angular dependent ionization. A non-resonant femtosecond (fs) laser pulse with a linear polarization creates rotational wave packets in the isotopologues. These wave packets periodically exhibit aligned and antialigned distributions at specific time delays. At a specific time delay when one isotopologue is aligned and the other one is anti-aligned, another non-resonant linearly-polarized fs laser pulse (ionization pulse) ionizes the aligned isotopologue preferentially via the non-resonant multiphoton ionization, because of angular dependence of the N ionization probability. The ion yield ratio R [= I(
ionization probability. The ion yield ratio R [= I( N
N ) / I(
) / I( N
N )] depends on the time delay, ranging from 0.68 to 1.41.
)] depends on the time delay, ranging from 0.68 to 1.41.
Meguro, Yoshihiro; Sato, Junya; Kato, Jun; Nakagawa, Akinori; Koma, Yoshikazu; Ashida, Takashi
no journal, ,
A large quantity of contaminated water is accumulated in nuclear reactor buildings in Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. Because various radionuclides are dissolved in the accumulated water, several decontamination devices based on deposition and adsorption are used for the decontamination. Therefore, several sludge and used adsorption materials are generated. These most are different from wastes caused by the operation of commercial nuclear power stations so far in properties, and these have not been disposed of commercially. As then feasibility of conventional solidification techniques to the wastes should be investigated prior to selection of solidification technique of the wastes. In this study as a first step of feasibility study, three types of sludge and three absorbents were solidified using cement materials and solidification behavior and properties of solidified material were investigated, and then feasibility of cementation to these wastes was evaluated.
Hoshina, Hiroyuki; Seko, Noriaki; Ikegawa, Atsushi*; Hatanaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
Nagaishi, Ryuji; Inoue, Masao; Matsumura, Taichi; Yamagishi, Isao; Hino, Ryutaro; Ogawa, Toru
no journal, ,
Hydrogen gas generation in radiolysis of pure water or seawater coexisting with zeolite adsorbents has been investigated by using Co-60  -ray for hydrogen safety in decontamination of radioactive water after Fukushima Daiichi NPS accident. In this work, two types of void volumes present in the zeolite bed were paid attention microscopically, and the difference in water radiolysis between the volumes was considered. The oxygen generated by decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, as the counterpart of hydrogen molecule, contacting with the zeolites were also discussed.
-ray for hydrogen safety in decontamination of radioactive water after Fukushima Daiichi NPS accident. In this work, two types of void volumes present in the zeolite bed were paid attention microscopically, and the difference in water radiolysis between the volumes was considered. The oxygen generated by decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, as the counterpart of hydrogen molecule, contacting with the zeolites were also discussed.
Toyoshima, Atsushi
no journal, ,
Electrochemical studies of the heaviest elements carried out at JAEA will be presented. We have so far studied the oxidation of nobelium (No) and the reduction of mendelevium (Md) using a flow electrolytic column (FEC) apparatus. In these experiments, thin glassy carbon fibers modified with ion-exchange resin were employed as a working electrode as well as a cation-exchanger to identify oxidation states of single atoms. Chromatograms of  No and
No and  Md produced in the
Md produced in the  Cm(
Cm( C, 5n) and
C, 5n) and  Cm(
Cm( B, 4n) reactions, respectively, at the JAEA tandem accelerator were varied with increasing the applied potential on the working electrode. This proved that redox reactions of No and Md occur in the studied potential ranges. Recently, we newly started exploring electrochemical reduction of Sg using a new chemistry assembly consisting of a membrane degasser, a FEC, the continuous liquid-liquid extraction apparatus. In the congress, results on these electrochemistry experiments will be presented.
B, 4n) reactions, respectively, at the JAEA tandem accelerator were varied with increasing the applied potential on the working electrode. This proved that redox reactions of No and Md occur in the studied potential ranges. Recently, we newly started exploring electrochemical reduction of Sg using a new chemistry assembly consisting of a membrane degasser, a FEC, the continuous liquid-liquid extraction apparatus. In the congress, results on these electrochemistry experiments will be presented.
 Tc for Compton camera imaging
Tc for Compton camera imagingHatsukawa, Yuichi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Nagai, Yasuki; Tanimori, Toru*; Sonoda, Shinya*; Kabuki, Shigeto*; et al.
no journal, ,
In recent years, the Compton camera which is originally developed for the astrophysical studies was applied for medical diagnostic usage. For the Compton camera imaging require technetium isotopes emitting higher energy  -rays. Two Tc isotopes,
-rays. Two Tc isotopes,  Tc (T
Tc (T = 60 d; E
= 60 d; E = 204, 582 and 835 keV) and
= 204, 582 and 835 keV) and 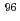 Tc(T
Tc(T = 4.28 d, E
= 4.28 d, E = 778 and 812 keV) are candidates for Compton camera imaging. Compton camera imaging can realize high position resolution without collimator. Because of no collimator using, the Compton camera makes higher
= 778 and 812 keV) are candidates for Compton camera imaging. Compton camera imaging can realize high position resolution without collimator. Because of no collimator using, the Compton camera makes higher  -ray detection efficiency. Compared with SPECT with
-ray detection efficiency. Compared with SPECT with  Tc, the Compton camera imaging technique can be expected that radiation exposure deduce to 1/5-1/10. In this study, technetium-95m was produced by the
Tc, the Compton camera imaging technique can be expected that radiation exposure deduce to 1/5-1/10. In this study, technetium-95m was produced by the  Mo(p,n)
Mo(p,n) Tc reaction.
Tc reaction.
Sekine, Yurina; Ishikawa, Nozomi*; Fukazawa, Tomoko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Wakaida, Ikuo; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Ito, Chikara; Oba, Masaki; Kato, Masaaki
no journal, ,
For the decommissioning of "Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant", development of onsite and in-situ remote diagnostic/analysis techniques under high radioactive environments will be strongly required. For the basic R&D on the decommissioning, Japan Atomic Energy Agency has opened the new research center "Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science". The concept of probing by light and diagnostic by light will be one of the powerful choices to accomplish these requirements. So, we are now developing the remote diagnostic technique for onsite, in-situ monitoring of nuclear debris. Optical Fiber based LIBS probe made by radiation resistant optical fiber was constructed, and we have successfully observed some specific spectra from the simulated sample of molten debris made by sintered oxide of Zr and U under the severe environment such as radioactive condition of 10 kGy/h and after total dose of 2 MGy.
Haga, Yoshinori
no journal, ,
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Kato, Masaaki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,
Development of remote analysis for nuclear fuel materials is of great importance to accelerate the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants. For instance, uranium and plutonium analyses are needed to detect fuel debris in pressure vessel. Also isotope analysis of the fuel debris will be needed for estimating the amounts of fissile materials in the debris for the purpose of safeguard verification. Presently, the laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) is thought to be one of the most promising techniques for this purpose. However, considering the relatively higher detection limit and lower spectral resolution of LIBS, an alternative analytical technique capable of compensating these drawbacks is desirable. In this presentation, we will discuss the applicability of laser ablation absorption spectroscopy. We will show a study for optimizing experimental conditions based on plume expansion dynamics as well as a study for evaluating analytical performances for U-Pu MOX samples.
Sato, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
We measured the first ionization energy (IE ) of nobelium (No, Z = 102) and lawrencium (Lr, Z =103) by exploiting the dependence of the ionization efficiency (
) of nobelium (No, Z = 102) and lawrencium (Lr, Z =103) by exploiting the dependence of the ionization efficiency (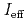 ) on the IE
) on the IE in a surface ionization process. The isotopes
in a surface ionization process. The isotopes  No (
No (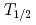 = 24.5s) and
= 24.5s) and  Lr (
Lr (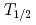 = 27 s), produced in the reaction
= 27 s), produced in the reaction  Cm (
Cm ( C, 4n) and
C, 4n) and  Cf (
Cf ( B, 4n), respectively, were used for studying their ionization. The reaction products recoiling from the targets were transported to a surface ion-source by a He/CdI
B, 4n), respectively, were used for studying their ionization. The reaction products recoiling from the targets were transported to a surface ion-source by a He/CdI gas-jet transport system. The products ionized in the ion-source were mass-separated with JAEA-ISOL. The number of ions collected at the end of the ISOL was determined by
gas-jet transport system. The products ionized in the ion-source were mass-separated with JAEA-ISOL. The number of ions collected at the end of the ISOL was determined by  -particle measurements and was used to evaluate
-particle measurements and was used to evaluate 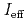 values. With the present system, we successfully ionized and mass-separated
values. With the present system, we successfully ionized and mass-separated  No and
No and  Lr with efficiencies of (0.5
Lr with efficiencies of (0.5  0.1)% and (36
0.1)% and (36  7)% at 2800 K, respectively. From these
7)% at 2800 K, respectively. From these 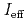 values, IE
values, IE values of No and Lr were determined based on the relationship between
values of No and Lr were determined based on the relationship between 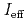 and IE
and IE . Our values are in good agreement with the predicted ones by theoretical calculations.
. Our values are in good agreement with the predicted ones by theoretical calculations.
 At]astato-
At]astato- -methyl-L-phenylalanine (2-AAMP) as a novel radiopharmaceutical for internal radiotherapy
-methyl-L-phenylalanine (2-AAMP) as a novel radiopharmaceutical for internal radiotherapyOhshima, Yasuhiro; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Hanaoka, Hirofumi*; Watanabe, Shigeki; Watanabe, Satoshi; Watanabe, Naoyuki*; Tsushima, Yoshito*; Endo, Keigo*; Arano, Yasushi*; Ishioka, Noriko
no journal, ,
Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Nozomi*; Watanabe, Satoshi; Ishioka, Noriko; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Kin, Tadahiro*; Takeda, Shinsaku*; Kawabata, Masako; Saeki, Hideya; et al.
no journal, ,
A new system has been proposed for the generation of radioisotopes with accelerator neutrons by deuterons, especially the production of Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64. Enriched Mo-100, Zr-90, Zn-68 and Zn-64 oxide samples were irradiated with neutrons, which were obtained by the  C(d,n) and Be(d,n) using 40 MeV deuterons provided from the TIARA cyclotron. Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64 were successfully produced via the (n, x) reactions, and we clearly observed the
C(d,n) and Be(d,n) using 40 MeV deuterons provided from the TIARA cyclotron. Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64 were successfully produced via the (n, x) reactions, and we clearly observed the  -rays. Particularly, yields of impurity radionuclides were much smaller than that of Mo-99 and Cu-67, and therefore radioactive waste produced during chemical processing would be reduced compared with other proposed reaction systems. The present results demonstrate that the radioisotopes, Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64, can be produced by using fast neutrons, and strongly suggest that the reaction system is one of the most promising routes to produce high quality medical radioisotope.
-rays. Particularly, yields of impurity radionuclides were much smaller than that of Mo-99 and Cu-67, and therefore radioactive waste produced during chemical processing would be reduced compared with other proposed reaction systems. The present results demonstrate that the radioisotopes, Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64, can be produced by using fast neutrons, and strongly suggest that the reaction system is one of the most promising routes to produce high quality medical radioisotope.
Hirota, Koichi; Sawahata, Hiroyuki*
no journal, ,
Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute has three irradiation facilities of ion-beam,  -ray, and electron-beam aimed at developing cutting-edge technologies for advanced materials, environmental conservation, biotechnology, and medical application. These facilities are available for basic and applied researches by academics, national and local government institutes, and private companies under the cooperation program. For example, the cyclotron is used for researches on radiation-degradation phenomena of semiconductors for space use, controlled polymerization of nanowire, breed improvement etc. The
-ray, and electron-beam aimed at developing cutting-edge technologies for advanced materials, environmental conservation, biotechnology, and medical application. These facilities are available for basic and applied researches by academics, national and local government institutes, and private companies under the cooperation program. For example, the cyclotron is used for researches on radiation-degradation phenomena of semiconductors for space use, controlled polymerization of nanowire, breed improvement etc. The  -ray facilities contribute to diverse research themes and recent noteworthy work is development of radiation-resistant materials for the decommissioning of damaged Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. Users under this cooperation program have advantages of preferential utilization of machine time and utilization fee subsidization. This presentation focuses on the detail of this program with the examples of actual research results.
-ray facilities contribute to diverse research themes and recent noteworthy work is development of radiation-resistant materials for the decommissioning of damaged Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. Users under this cooperation program have advantages of preferential utilization of machine time and utilization fee subsidization. This presentation focuses on the detail of this program with the examples of actual research results.