Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
no journal, ,
Scintillators are generally used to detect various kinds of particles such as electrons, gammas, protons and heavy ions. Scintillators emit photons according to the energy deposited to the crystal. It is also known that light yield is suppressed for particles depositing energy densely owing to quenching. Moreover, it is suggested that quenching is attributed to transfer of energy from excited fluorescent molecules to damaged molecules (F rster mechanism). In this study, energy deposition in a scintillator crystal by radiation was calculated using radiation transport codes to finally obtain excitation and damage of fluorescent molecules. Based on the calculation, spatial configuration of exited and damaged molecules. Then the probability that F
rster mechanism). In this study, energy deposition in a scintillator crystal by radiation was calculated using radiation transport codes to finally obtain excitation and damage of fluorescent molecules. Based on the calculation, spatial configuration of exited and damaged molecules. Then the probability that F rster mechanism takes place in excited molecules were estimated to obtain the number of fluorescent molecules that emit photons. As a result, light yield is proportionally increased with increase in the incident energy in case of electron incidence. On the other hand, light yield is increased non-linearly in case of proton incidence. This trend is in a good agreement with the experimental results.
rster mechanism takes place in excited molecules were estimated to obtain the number of fluorescent molecules that emit photons. As a result, light yield is proportionally increased with increase in the incident energy in case of electron incidence. On the other hand, light yield is increased non-linearly in case of proton incidence. This trend is in a good agreement with the experimental results.
Kai, Takeshi; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Abe, Shinichiro; Sato, Tatsuhiko
no journal, ,
In study of radiation interaction induced in small spatial region of nanoscale, it is important to reveal electron behavior below 1 keV and its energy deposition. However, current radiation transport simulation code PHITS cannot simulate precisely the behavior in the materials. To clear the question, we have developed track structure code, also have an implementation plan of the code into PHITS. We calculated the microscopic behavior of the electron in water by using the developed code. As the results, we could predict theoretically that the electron thermalization progress contemporaneously with formation of prehydrated electron against previous prediction. In this presentation, we report our outcomes obtained from the developed track structure code, future plan for and implementation of the code into the PHITS as well as the functional extension.
Abe, Shinichiro; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Kato, Takashi*; Matsuyama, Hideya*
no journal, ,
Radiation-induced charges in semiconductor device cause temporary and non-destructive faults (the so-called soft errors) in microelectronic devices. The model which estimates charges collected in the storage node of a memory element quickly and accurately is necessary to evaluate soft error rate by simulation. It is predicted that charge collection process in FinFET is differs from that in planar process due to differences in their structures. In this study, we perform systematic investigation of charge collection caused by radiation using 3-D TCAD simulator HyENEXSS in order to construct the charge collection model for FinFET. As a result of that investigation, it is found that temporal conduction between source node and drain node arises at few psec. It is also clarified that the temporal conduction has a major impact on charge collection process when charges deposited only near fin. Meanwhile, it is found that diffusion process is the main cause of charge collection when charges deposited in the substrate.
Yano, Masahiro; Suzuki, Shota; Uozumi, Yuki; Asaoka, Hidehito
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Junichiro; Ogiwara, Norio; Kinsho, Michikazu; Yamamoto, Kazami
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Kenta*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Shih, H.*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Initial oxidation process of AlGaN surface during thermal oxidation was investigated by synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy. Thermal oxidation of AlGaN/GaN/Si(111) substrates was carried out for 30 min in the temperature range from 200 to 1000 degrees in O ambient. The obtained Ga 2p spectra exhibited peak shift toward the higher binding energy with increasing oxidation temperature, suggesting the growth of Ga oxides on AlGaN surface. The peak deconvolution of Ga 2p spectra into Ga-O and Ga-N components revealed that the formation of Ga oxides was formed on AlGaN surface at above 400 degrees while GaN surface was stable below 600 degrees. These results indicate that AlGaN surface is easy to be oxidized compared to GaN surface.
ambient. The obtained Ga 2p spectra exhibited peak shift toward the higher binding energy with increasing oxidation temperature, suggesting the growth of Ga oxides on AlGaN surface. The peak deconvolution of Ga 2p spectra into Ga-O and Ga-N components revealed that the formation of Ga oxides was formed on AlGaN surface at above 400 degrees while GaN surface was stable below 600 degrees. These results indicate that AlGaN surface is easy to be oxidized compared to GaN surface.
 Pt(111) surface with hyperthermal oxygen molecule
Pt(111) surface with hyperthermal oxygen moleculeTsuda, Yasutaka*; Makino, Takamasa*; Tsukada, Chie; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Fukuyama, Tetsuya*; Okada, Michio*
no journal, ,
Oxidation is a main reaction in corrosion processes and its understabding is important to develop anticorrosion materials. In this study, initial oxidation at Cu Pt(111) surface was investigated by using surface analysis apparatus at BL23SU of SPring-8. The surface oxidized by 2.3 eV molecular beams was analzyed by synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy. We confirmed that Cu L
Pt(111) surface was investigated by using surface analysis apparatus at BL23SU of SPring-8. The surface oxidized by 2.3 eV molecular beams was analzyed by synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy. We confirmed that Cu L M
M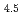 M
M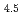 AES spectrum and Cu-2p XPS spectrum show the only growth of Cu oxide whereas Pt oxide was not formed from the results of Pt-4f XPS. It was also found that the reactivity of Cu
AES spectrum and Cu-2p XPS spectrum show the only growth of Cu oxide whereas Pt oxide was not formed from the results of Pt-4f XPS. It was also found that the reactivity of Cu Pd(111) surface is lower than that of Cu
Pd(111) surface is lower than that of Cu Au(111) surface.
Au(111) surface.
Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
In this invited talk, surface chemistry researches for various applications, which have been conducted by using surface reaction analysis apparatus constructed at JAEA soft X-ray beamline (BL23SU) of SPing-8 are presented. Several results on in situ synchrotron radiation photoemission analysis of surface reactions induced by supersonic molecular beams are mainly talked. Furthermore, the studies on surface reaction dynamics which is clarified by the experiments of incident energy dependence are also presented. The usefulness of our experimental approaches applying to various surface processes and future perspectives of theses research fields will be talked based on basic sciences and technologies viewpoints.