Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ozu, Akira; Maeda, Makoto; Komeda, Masao; Toh, Yosuke
Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2019), Vol.1, p.101 - 104, 2020/08
Tada, Kenichi; Kunieda, Satoshi; Nagaya, Yasunobu
Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2019), Vol.1, p.48 - 49, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nuclear data processing is an important interface between evaluated nuclear data library and neutronics transport codes. JAEA developed a new nuclear data processing code FRENDY in order to process the evaluated nuclear data library JEND. JAEA released FRENDY version 1 as an open source software under the 2-clause BSD license. The current version of FRENDY can generate ACE formatted files for continuous energy Monte Carlo calculation codes such as MCNP and PHITS. It uses the same processing method as NJOY because the implementation of the conventional method is an important step to develop the new code. For verification, we compared the processing results of FRENDY with those of NJOY and confirmed FRENDY provided us with almost the same outputs as NJOY. In this presentation, we explains the overview and a future plan of FRENDY.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru
Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2019), Vol.1, p.735 - 736, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)A large area, position-sensitive scintillation neutron detector was developed for upgrading the SENJU, time-of-flight Laue single crystal neutron diffractometer, in J-PARC MLF. The detector has a neutron-sensitive area of 512  512 mm with a pixel size of 4
512 mm with a pixel size of 4  4 mm. The detector was developed for upgrading of the SENJU instrument. The large area detector is to be installed below the vacuum tank to enlarge a covering solid angle. A
4 mm. The detector was developed for upgrading of the SENJU instrument. The large area detector is to be installed below the vacuum tank to enlarge a covering solid angle. A  Li:ZnS (Ag) scintillator and wavelength-shifting fiber technologies are employed. Each fiber channel is read out individually with photon counting mode. The electronics boards are implemented at the backside of the detector, enabling the detector depth as short as 20 cm. The detector exhibited a detection efficiency of 45% for thermal neutron. No degradation in fiber position and in neutron sensitivity has been observed over one year after production. In this paper, detector design and detector performances are presented.
Li:ZnS (Ag) scintillator and wavelength-shifting fiber technologies are employed. Each fiber channel is read out individually with photon counting mode. The electronics boards are implemented at the backside of the detector, enabling the detector depth as short as 20 cm. The detector exhibited a detection efficiency of 45% for thermal neutron. No degradation in fiber position and in neutron sensitivity has been observed over one year after production. In this paper, detector design and detector performances are presented.
To, Kentaro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Sakasai, Kaoru; Yamagishi, Hideshi*
Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2019), Vol.1, p.447 - 449, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)A real-time data display and storage device was developed for pulsed neutron scattering experiments using the time-of-flight method. The device contains two sets of field programmable gate arrays and on-board microcomputers for data display and storage. The developed device can determine the time-of-flight and time-resolved neutron position data with a time range from 0 to 40 ms using a beam of pulsed neutrons at 25 Hz from an experimental facility. Operation tests were performed using test signals that simulate the neutron detector output signals. It was found that the device could separate double pulses with a time interval of 1  s; furthermore, it could measure the continuous pulses with a frequency of 1 MHz. Consequently, it was confirmed that the developed device demonstrated a counting rate capability of beyond 1 Mcps.
s; furthermore, it could measure the continuous pulses with a frequency of 1 MHz. Consequently, it was confirmed that the developed device demonstrated a counting rate capability of beyond 1 Mcps.
Hara, Kaoru*; Asako, Minoru*; Kai, Tetsuya; Sato, Hiroaki*; Kamiyama, Takashi*
Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2019), Vol.2, p.1500 - 1501, 2020/08
Tada, Kenichi; Iwamoto, Osamu
Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2019), Vol.2, p.1622 - 1624, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)JAEA has published the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL to improve the prediction accuracy of nuclear calculations. JENDL is now one of the most famous evaluated nuclear data libraries in the world. This presentation explains the recent activity of the JENDL project and overview of the next version of general-purpose file JENDL-5. Nuclear calculation codes cannot treat the evaluated nuclear data library. This presentation also explains the nuclear data processing system FRENDY which is used to generate cross section library for a nuclear calculation code.
Morishita, Yuki; Ye, Y.*; Mata, L.*; Pozzi, S.*; Kearfott, K.*
no journal, ,
A compact organic scintillator-based 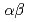 spectrometer was developed and tested for radon measurements. The spectrometer was composed of a Through Silicon Via (TSV) silicon photomultiplier or SiPM and a 6 mm
spectrometer was developed and tested for radon measurements. The spectrometer was composed of a Through Silicon Via (TSV) silicon photomultiplier or SiPM and a 6 mm  6 mm
6 mm  6 mm stilbene cube crystal. Analog signals from the SiPM were sent to a digitizer. The detector was placed in a light-tight box and a stacked air filter was embedded on the side surface of the light-tight box. A continuous radon monitor, the AlphaGUARD, and
6 mm stilbene cube crystal. Analog signals from the SiPM were sent to a digitizer. The detector was placed in a light-tight box and a stacked air filter was embedded on the side surface of the light-tight box. A continuous radon monitor, the AlphaGUARD, and  Ra sources were placed in a small radon chamber constructed using a cylindrical 0.57 m diameter, 0.88 m tall steel drum. By applying a pulse shape discrimination technique, alpha and beta spectra were simultaneously clearly separated and quantitatively measured. Two peaks were registered in the measured alpha spectrum:
Ra sources were placed in a small radon chamber constructed using a cylindrical 0.57 m diameter, 0.88 m tall steel drum. By applying a pulse shape discrimination technique, alpha and beta spectra were simultaneously clearly separated and quantitatively measured. Two peaks were registered in the measured alpha spectrum: 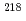 Po was registered in the lower peak and
Po was registered in the lower peak and  Po was registered in the higher peak. A linear relationship was observed between radon counts from the AlphaGUARD and count-rates from the stilbene-SiPM detector. The thickness of the stilbene-SiPM detector was less than 10 mm, thus easy increases insensitivity should be possible with future construction. Thus, the compact organic scintillator-based alpha/beta spectrometer shows promise for use in novel radon detection systems.
Po was registered in the higher peak. A linear relationship was observed between radon counts from the AlphaGUARD and count-rates from the stilbene-SiPM detector. The thickness of the stilbene-SiPM detector was less than 10 mm, thus easy increases insensitivity should be possible with future construction. Thus, the compact organic scintillator-based alpha/beta spectrometer shows promise for use in novel radon detection systems.
Rossi, F.; Rodriguez, D.; Seya, Michio; Takahashi, Tone; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Abbas, K.*; Crochemore, J.-M.*; Pedersen, B.*; Bogucarska, T.*; Varasano, G.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Morishita, Yuki; Torii, Tatsuo; Usami, Hiroshi; Kikuchi, Hiroyuki*; Utsugi, Wataru*; Takahira, Shiro*
no journal, ,
We measured alpha emitters obtained from a reactor building in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) by using an alpha particle imaging detector. For developing the detector, we used a very thin (0.05-mm-thick) a cerium-doped Gd (Ga,Al)
(Ga,Al)  O
O (Ce GAGG) scintillator and silicon photomultiplier (SiPM) arrays as the photodetector. The floor of the reactor building in FDNPP was wiped off by using smear papers, and the radioactivity of these papers was measured by the alpha particle imaging detector. In addition, we measured a Plutonium (Pu) sample (mainly 5.5 MeV alpha particles from
(Ce GAGG) scintillator and silicon photomultiplier (SiPM) arrays as the photodetector. The floor of the reactor building in FDNPP was wiped off by using smear papers, and the radioactivity of these papers was measured by the alpha particle imaging detector. In addition, we measured a Plutonium (Pu) sample (mainly 5.5 MeV alpha particles from  Pu) obtained from a nuclear fuel facility by using of the same detector for comparison with the smear papers. The alpha spectrum was in the energy range of 5-6 MeV, which corresponds to the alpha particle energy of
Pu) obtained from a nuclear fuel facility by using of the same detector for comparison with the smear papers. The alpha spectrum was in the energy range of 5-6 MeV, which corresponds to the alpha particle energy of  Pu (5.5 MeV). The correlation coefficient of the alpha spectra of the smear papers and the Pu sample had a strong positive linear relation. Moreover, the peak of
Pu (5.5 MeV). The correlation coefficient of the alpha spectra of the smear papers and the Pu sample had a strong positive linear relation. Moreover, the peak of  Am was identified by gamma spectrum measurement. Based on these results, it is highly likely that the alpha emitters in the reactor building of FDNPP are
Am was identified by gamma spectrum measurement. Based on these results, it is highly likely that the alpha emitters in the reactor building of FDNPP are  Pu and
Pu and  Am, which originated from the nuclear fuel. The surface contamination level of alpha emitters exceeded 4 Bq/cm
Am, which originated from the nuclear fuel. The surface contamination level of alpha emitters exceeded 4 Bq/cm .
.