Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Segawa, Tomoomi; Kawaguchi, Koichi; Ishii, Katsunori; Suzuki, Masahiro; Tachihara, Joji; Takato, Kiyoto; Okita, Takatoshi; Satone, Hiroshi*; Suzuki, Michitaka*
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2020/08
To reduce the hold-up of the nuclear fuel materials in the glove box and the external exposure dose, the technology of the MOX powder adhesion prevention by the nanoparticle coating to the acrylic panels of the glove box has been developed. Due to the formation of nano-sized tiny rugged surface, the nanoparticle coating reduced the minimum adhesion force between the UO particles and the acrylic test piece surface with the smallest particle size of about 5
particles and the acrylic test piece surface with the smallest particle size of about 5  m where desorption was observed, by about one-tenth. Moreover, the nanoparticle coating reduced the amount of the MOX powder adhering to the acrylic test piece to about one-tenth. In this study, it was found that applying the nanoparticle coating to the acrylic panels of glove box can prevent the adhesion of nuclear fuel materials. This method is effective for reducing the hold-up of the nuclear fuel materials in the glove box, the external exposure dose and improving the visibility of the acrylic panels.
m where desorption was observed, by about one-tenth. Moreover, the nanoparticle coating reduced the amount of the MOX powder adhering to the acrylic test piece to about one-tenth. In this study, it was found that applying the nanoparticle coating to the acrylic panels of glove box can prevent the adhesion of nuclear fuel materials. This method is effective for reducing the hold-up of the nuclear fuel materials in the glove box, the external exposure dose and improving the visibility of the acrylic panels.
Okuda, Yukihiko; Kang, Z.; Nishida, Akemi; Tsubota, Haruji; Li, Y.
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2020/08
In case of projectile impact to reactor building of nuclear power plants, stress waves due to the projectile impact propagate from the impacted wall to the interior of the structure. It is an important issue to assess the dynamic response generated with projectile impact for safety related internal equipment because stress waves are likely to excite high-frequency vibrations of internal equipment in the reactor building. The OECD (Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development) / NEA (Nuclear Energy Agency) launched the IRIS (Improving Robustness Assessment Methodologies for Structures Impacted by Projectiles) benchmark project in order to assess the dynamic response for nuclear facility by projectile impact and the third phase of IRIS (IRIS 3) contributes to the investigation on the dynamic response of reinforced concrete (RC) structure with internal equipment. We have participated in the IRIS 3 and have performed the calibration analysis for projectile impact test on the structure which models a reactor building and internal equipment. Specially, we have developed and validated a numerical approach to investigate impact response of the RC structure with internal equipment through the calibration correction. This paper presents partial simulation results from dynamic response of the RC structure with internal equipment and discusses the effect of supporting condition of the internal equipment and stress wave propagation.
Nishida, Akemi; Kang, Z.; Okuda, Yukihiko; Tsubota, Haruji; Li, Y.
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2020/08
Studies on the local damage to reinforced concrete (RC) panels subjected to projectile impact have mainly focused on collisions that occur at an angle normal to the structure; thus, research on oblique impact is scarce. Therefore, we conducted research focusing on oblique impact to enable more realistic impact assessment of projectile collisions. To date, the validity of the analytical method has been confirmed by comparing the results with those of previous tests, and the local damage of RC panels that have collided with projectiles has been analytically investigated focusing on the impact angle. Therefore, this study aims to confirm the validity of the analysis method by conducting impact tests under various conditions including the impact angle, and obtaining data for validation. This paper outlines the test for the local damage of RC panels subjected to normal and oblique impact.
Igarashi, Kai*; Onuki, Ryoji*; Sakai, Takaaki*; Kato, Shinya; Matsuba, Kenichi; Kamiyama, Kenji
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2020/08
Aoki, Takeshi; Sato, Hiroyuki; Ohashi, Hirofumi
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2020/08
The flow distribution analysis, which is a part of thermal hydraulic design of the prismatic-type of the high temperature gas cooled reactor (HTGR) considering unintended flows between graphite blocks, has been performed for steady and conservative conditions. On the other hand, the transient analysis for satisfactorily realistic conditions will be helpful for the design improvement of prismatic-type HTGR. The present study aims to develop the transient flow distribution analysis code and confirm its applicability for the transient flow distribution analysis for prismatic-type HTGRs during anticipated operational occurrences and accidents utilizing experiences on high temperature engineering test reactor (HTTR) design. The calculation model and code were developed and validated for analysis of the unintended flows in the core and the molecular diffusion dominant in beginning air ingress behavior in an air ingress accident.
Kawaguchi, Munemichi
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2020/08
In decommissioning sodium-cooled fast reactors, the operators can be exposed to radiation during dismantling of the cold trap equipment (C/T). The C/T has higher dose equipment because the C/T trapped the tritium of the fission product during the operation to purify the sodium coolant. In this research, the thermal decomposition temperature and rate of sodium hydride were measured as the fundamental research for improvement of the thermorlysis method prior to the dismantling. We measured the thermal decomposition temperature and rate using sodium hydride powder (95.3%, Sigma-Aldrich) in Al O
O crucible with TG-DTA (STA2500, NETASCH Japan). The heating rates were set to
crucible with TG-DTA (STA2500, NETASCH Japan). The heating rates were set to  = 2.0, 5.0, 10.0, 20.0 K/min, and the weight decrease was measured. The thermal decomposition temperature and rate were obtained from the temperature of the onset of the weigh decrease and the Kissinger plot, respectively. Furthermore, we set to the thermal decomposition temperature of around 600 K, and the weight decreasing rates were measured. The change of the chemical composition of the sodium hydride with heating (from NaH to Na) was measured with X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) analysis. As a result, the thermal decomposition occurred at around 600 K, and the almost all hydrogen in the sodium hydride released within 1 h. The thermal decomposition rate strongly depended on the heating temperature.
= 2.0, 5.0, 10.0, 20.0 K/min, and the weight decrease was measured. The thermal decomposition temperature and rate were obtained from the temperature of the onset of the weigh decrease and the Kissinger plot, respectively. Furthermore, we set to the thermal decomposition temperature of around 600 K, and the weight decreasing rates were measured. The change of the chemical composition of the sodium hydride with heating (from NaH to Na) was measured with X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) analysis. As a result, the thermal decomposition occurred at around 600 K, and the almost all hydrogen in the sodium hydride released within 1 h. The thermal decomposition rate strongly depended on the heating temperature.
Shimada, Asako; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takeda, Seiji
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2020/08
no abstracts in English
Taruta, Yasuyoshi; Yanagihara, Satoshi*; Hashimoto, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Shigeto*; Iguchi, Yukihiro; Kitamura, Koichi; Koda, Yuya; Tomoda, Koichi
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2020/08
Decommissioning is a long-term project during which generations are expected to change. Therefore, it is necessary to appropriately transfer knowledge and technology to the next generation. In recent years, in the world of decommissioning, attempts have been made to apply advanced technologies such as utilization of knowledge management and virtual reality. This study describes adaptation in decommissioning from the viewpoint of utilizing IT technology called digital twin from the viewpoint of knowledge management.
Yamashita, Susumu; Kino, Chiaki*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2020/08
In order to contribute the improvement of estimation accuracy for severe accident code such as SAMPSON, we have developed the chemical reaction model such as eutectic reaction and oxidation in micro scale, e.g., B C-SUS in the control rod blade and UO
C-SUS in the control rod blade and UO -Zry in fuel rods, and implemented them to the computational fluid dynamics code named JUPITER. And we try to develop the coupled analysis frame work using SAMPSON and JUPITER to decrease uncertainty due to micro scale phenomena which cannot be calculate by severe accident analysis codes. From the preliminary analysis in fuel rod heating analysis by JUPITER using SAMPSON output data, it was revealed that the implemented chemical reaction models work stably and obtain reasonable results.
-Zry in fuel rods, and implemented them to the computational fluid dynamics code named JUPITER. And we try to develop the coupled analysis frame work using SAMPSON and JUPITER to decrease uncertainty due to micro scale phenomena which cannot be calculate by severe accident analysis codes. From the preliminary analysis in fuel rod heating analysis by JUPITER using SAMPSON output data, it was revealed that the implemented chemical reaction models work stably and obtain reasonable results.
Trianti, N.; Motegi, Kosuke; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2020/08
Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Kikuchi, Shin; Emura, Yuki; Kamiyama, Kenji; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2020/08
One of the key issues in a core disruptive accident (CDA) evaluation in sodium-cooled fast reactors is eutectic reactions between boron carbide (B C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation. Such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses in the past, therefore it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study focuses on B
C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation. Such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses in the past, therefore it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study focuses on B C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in a range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a severe accident computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies conducted until 2018. Specific results in this paper are boron concentration distributions of solidified B
C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in a range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a severe accident computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies conducted until 2018. Specific results in this paper are boron concentration distributions of solidified B C-SS eutectic sample in the eutectic melting experiments, which would be used for the validation of the eutectic physical model implemented into the computer code.
C-SS eutectic sample in the eutectic melting experiments, which would be used for the validation of the eutectic physical model implemented into the computer code.
Sato, Hiroyuki; Aoki, Takeshi; Ohashi, Hirofumi
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2020/08
The present study aims to propose a guidance that facilitates to determine fuel design limits of commercial HTGR on the basis of licensing experience through the HTTR construction. The guidance consists of a set of FOMs and a process to determine their evaluation criteria. The FOMs are firstly identified to satisfy safety requirements and a basic concept of safety guides established in a special committee under the AESJ with the support of the Research Association of High Temperature Gas Cooled Reactor Plant. The development process for the evaluation criteria takes into account not only the top-level regulatory criteria but also design dependent constraints including the performance of fission product containment in physical barriers other than fuel, fuel qualification criteria, design specifications of an instrumentation and control system. As a result, a comprehensive and transparent procedure for designers of prismatic-type commercial HTGR has been developed.
Yada, Hiroki; Takaya, Shigeru; Enuma, Yasuhiro
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2020/08
Aizawa, Kosuke; Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Nishimura, Masahiro; Kurihara, Akikazu; Ishida, Katsuji*
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2020/08
A sodium-cooled fast reactor is designed to attain a high burn-up core in commercialized fast reactor cycle systems. In high burn-up fuel subassemblies, the deformation of fuel pin due to the swelling and thermal bowing may decrease local flow velocity in the subassembly and influence the heat removal capability. Therefore, it is important to obtain the flow velocity distribution in a wire wrapped pin bundle. In this study, the detailed flow velocity distribution in the subchannel has been obtained by PIV (Particle Image Velocimetry) measurement using a wire-wrapped 3-pin bundle water model. Flow velocity conditions in the pin bundle were set from 0.036 m/s (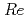 = 270) to 1.6m/s (
= 270) to 1.6m/s (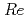 = 13,500). From the PIV results, the maximum flow velocity was increased by decreasing the
= 13,500). From the PIV results, the maximum flow velocity was increased by decreasing the 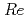 number in the region away from the wrapping wire. Moreover, the PIV measurements by using the 3-pin bundle geometry without the wrapping wire were conducted. From the results, the effect of the wrapping wire on the flow field in the subchannel was understood. There experimental results useful not only for understanding of pin bundle thermal hydraulics but also code validation.
number in the region away from the wrapping wire. Moreover, the PIV measurements by using the 3-pin bundle geometry without the wrapping wire were conducted. From the results, the effect of the wrapping wire on the flow field in the subchannel was understood. There experimental results useful not only for understanding of pin bundle thermal hydraulics but also code validation.
Miyahara, Shinya*; Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Seino, Hiroshi
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2020/08
In a postulated accident of fuel pin failure of sodium cooled fast reactor, a fission product cesium will be released as an aerosol such as cesium iodide and/or oxide together with xenon and/or krypton. In this study, cesium aerosol removal behavior due to inertial deposition, sedimentation and diffusion was analyzed by a computer program which deals with the expansion and the deformation of the bubble together with the aerosol absorption. Initial bubble diameter, sodium pool depth and temperature, aerosol particle diameter and density, initial aerosol concentration were changed as parameter. From the results, it was concluded that the initial bubble diameter was most sensitive parameter to the decontamination factor (DF). It was found that the sodium pool depth, the aerosol particle diameter and density have also important effect on the DF, but the sodium temperature has a marginal effect. To meet these results, the experiments are under planning to validate the results.
Aoki, Takeshi; Isaka, Kazuyoshi; Sato, Hiroyuki; Ohashi, Hirofumi
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2020/08
The flow distribution analysis performed in the HTGR design has to take into account the interaction thermal and radiation deformations of the graphite structure, and the gaps between the graphite structures forming unintended flow. In the present study, a user-friendly flow network calculation code (FNCC) has been developed on the basis of experiences of High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) design for HTGR design with enhanced compatibility with other HTGR design codes and with considering graphite block deformation in iteration process without manual control. The validation of FNCC was performed for the one-column flow distribution test. The analytical results using FNCC showed good agreement with the experimental results. It is concluded that FNCC was validate for the analysis of distributions of flowrate and pressure for the flow network model including the unintended flow paths in prismatic-type HTGRs.
Tsuji, Mitsuyo; Aizawa, Kosuke; Kobayashi, Jun; Kurihara, Akikazu; Miyake, Yasuhiro*
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2020/08
The water experiments using a 1/10 scale experimental apparatus simulating the reactor vessel of SFR were conducted to investigate the natural circulation phenomena in a reactor vessel. In this paper, the natural circulation flow field in the reactor vessel was measured by the Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) method. The PIV measurement was carried out under the operation of the dipped-type direct heat exchanger (DHX) installed in the upper plenum when 20% of the core fuel fell to the lower plenum and accumulated on the core catcher. From the results of PIV measurement, it was quantitatively confirmed that the upward flow occurred at the center region of the lower and upper plenums. In addition, the downward flows were confirmed near the reactor vessel wall in the upper plenum and through outermost layer of the simulated core in the lower plenum. Moreover, the relationship between the temperature field and the velocity field was investigated in order to understand the natural circulation phenomenon in the reactor vessel. From the above results, it was confirmed that the natural circulation cooling path was established under the dipped-type DHX operation.
Abe, Yuta; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Oishi, Yuji*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Nagae, Yuji; Sato, Ikken
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2020/08
Uchibori, Akihiro; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Takata, Takashi; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2020/08
The multi-scenario simulation system named SPECTRA has been developed for integrated analysis of in- and ex-vessel phenomena during a severe accident in sodium-cooled fast reactors. The base module computing ex-vessel compressible gas behavior by a lumped mass model and a sodium-concrete interaction module were verified through the basic analyses individually. A validity of the system including the base module and the individual physical module such as the sodium-concrete interaction module was confirmed through the analysis assuming sodium leakage from a reactor vessel and a primary cooling loop.
Sonehara, Masateru; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Uchibori, Akihiro; Takata, Takashi; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Clark, A. J.*; Louie, D. L. Y.*
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2020/08
In order to investigate the multi-dimensional effects of sodium combustion, a benchmark analysis of the SNL Surtsey spray combustion experiment (SNL T3 experiments) using AQUA-SF and SPHINCS is conducted in JAEA. As a best estimate analysis, the spray burning duration is adjusted in the computation in order to take into account the temporary suppression of the spray combustion observed in the experiment. Furthermore, droplet size of SPHINCS and AQUA-SF are optimized to represent the T3 experimental results. The best estimate of AQUA-SF results in the droplet diameter of 2.5 mm, which agrees quite well with the spatial temperature measurements, and the sodium droplet diameter measurement with a high speed camera.