Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Sakasai, Kaoru; Honda, Katsunori; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Katagiri, Masaki*
JAEA-Conf 2015-002, p.391 - 398, 2016/02
Development of position-sensitive scintillator detectors at the J-PARC/MLF is briefly reviewed. The detector development for the neutron scattering instruments in the J-PARC/MLF initiated back in 2001. After the basic experiments and design study we have produced first beam line detectors in 2008 both with the one and two-dimensional position-sensitivity. With an extension of the fiber detector technology the detector that has an active area of 256  256 mm
256 mm with a 4-mm spatial resolution was designed and made for the single crystal diffractometer, SENJU, in 2011. In the presentation recent development work including the alternative detectors to
with a 4-mm spatial resolution was designed and made for the single crystal diffractometer, SENJU, in 2011. In the presentation recent development work including the alternative detectors to  He gas is also introduced as well as the new detector development for the nextiBIX instrument.
He gas is also introduced as well as the new detector development for the nextiBIX instrument.
Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Kambara, Wataru; Krist, T.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Arai, Masatoshi; Iida, Kazuki*; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2015-002, p.339 - 348, 2016/02
We have developed a new Fermi chopper referred to as Magic chopper to realize the full optimization of the experimental condition for Multi-Ei method in a chopper spectrometer. In this study, the theoretical aspects of MAGIC chopper concept will be initially presented, and the performances of MAGIC chopper will be evaluated by both Monte Carlo simulation and neutron transmission experiment.
Sakai, Kenji; Oi, Motoki; Watanabe, Akihiko; Kai, Tetsuya; Kato, Yuko; Meigo, Shinichiro; Takada, Hiroshi
JAEA-Conf 2015-002, p.593 - 598, 2016/02
For safe and stable beam operation, a MLF general control system (GCS) consists of several subsystems such as an integral control, interlock, server, network, and timing distribution systems. Since the first beam injection in 2008, the GCS has operated stably without any serious troubles in comparison with upgrade of target devices for ramping up beam power and increment of user apparatuses year by year. In recent years, however, it has been improved significantly in view of sustainable long-term operation and maintenance. The monitor and operation system of the GCS has been upgraded by changing its framework software to improve potential flexibility in its maintenance. Its interlock system was also modified in accordance with the re-examination of the risk management system of J-PARC. This paper reports recent progress of the MLF-GCS.
Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Iida, Kazuki*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakatani, Takeshi; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2015-002, p.319 - 329, 2016/02
Wan, T.; Naoe, Takashi; Wakui, Takashi; Haga, Katsuhiro; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Futakawa, Masatoshi
JAEA-Conf 2015-002, p.76 - 87, 2016/02
High power accelerator driven pulsed spallation neutron sources are being developed in the world. Mercury is used as a target material to produce neutrons via the spallation reaction induced by injected protons. At the moment of the proton injection, the mercury vessel with a double wall structure is impulsively excited by the interaction between mercury and solid wall. The vibrational signals were measured in noncontact and remotely by using a Laser Doppler Vibrometer (LDV) system to evaluate the structure integrity. The extreme damages were assumed as the first step, i.e., the inner structure was partly broken by erosion. The dependency of vibrational behaviors on the damage was systematically investigated through numerical simulations and experiments. A LDV was installed to monitor the dependency of an electro-Magnetic Impact Testing Machine (MIMTM) vibration on the damage size. Through the numerical simulation, it was found that the target vessel vibration depends on the damage size. A technique referred to a Wavelet Differential Analysis (WDA) has been developed to enhance the effect of damages on the impulsive vibration behavior. However, the vibration signals obtained from MIMTM contain considerable noise. In order to reduce the noise effect on the impulsive vibration behavior, the statistical methods referred to an Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) and an Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA) was applied. Numerical simulation results that obtained from controlling the damage size, were firstly added to random noise with various levels manually, and then were analyzed by the statistic methods. Then, the field data that measured from the real mercury target was analyzed. The results represent that the combination of WDA and ANOVA/ANCOVA could effectively indicate the damage dependency.
Haga, Katsuhiro; Naoe, Takashi; Wakui, Takashi; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Futakawa, Masatoshi
no journal, ,
For the mercury target of a pulsed spallation neutron source of J-PARC, cavitation damage of the target vessel wall which is caused by the pressure wave in mercury induced by high power pulsed proton beam of 1 MW is the crucial issue. So far, the analytical and experimental studies and the operational experiences of SNS suggest that the rapid mercury flow can mitigate the cavitation damages. In order to include this effect into the target design of J-PARC, we adopted doubled-walled structure to the beam window of the target vessel. The mercury flow channel with a narrow gap of 2 mm was made by adding an inner wall to just inside of the beam window. In order to investigate the mercury flow distribution and flow field, numerical simulations were carried out using the conventional code, ANSYS FLUENT. While the mercury velocity outside of the narrow channel was 1.2 m/s, the mercury velocity in the narrow channel increased to almost 4 m/s, which was promising to suppress the cavitation damages. The effect of the inner wall failure of the narrow channel on the mercury flow was also evaluated. The round hole was created on the inner wall at the center of the beam window. The simulation results and the water experimental results showed that the mercury flow velocity in the narrow channel was almost the same with the case without a hole if the hole diameter is around 10 mm.
Takata, Shinichi; Suzuki, Junichi*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Iwase, Hiroki*; Shinohara, Takenao; Oku, Takayuki; Nakatani, Takeshi; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Ito, Takayoshi*; Tominaga, Taiki*; et al.
no journal, ,
The small and wide angle neutron scattering instrument, 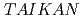 , was installed at the
, was installed at the 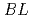 15 in the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility,
15 in the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility, 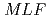 , of
, of 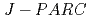 .
. 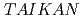 is designed for efficient measurement in wide-q range by using of the wide wavelength and the four detector banks which cover small-, middle-, high-, and backward-angle. At the present stage, 1,216
is designed for efficient measurement in wide-q range by using of the wide wavelength and the four detector banks which cover small-, middle-, high-, and backward-angle. At the present stage, 1,216 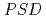 s are mounted on
s are mounted on 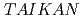 , where the number is about 50% of the installable total
, where the number is about 50% of the installable total 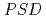 s number. On beam commissioning started in January 2012, and user program began in March 2012. The software of data reduction has newly developed and some sample environment devices such as a sample changer, tension tester, and refrigerator have been improved. In this presentation, we present the current status of
s number. On beam commissioning started in January 2012, and user program began in March 2012. The software of data reduction has newly developed and some sample environment devices such as a sample changer, tension tester, and refrigerator have been improved. In this presentation, we present the current status of 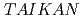 about the new software, sample environment devices, and the results on some samples to show the instrument performance of
about the new software, sample environment devices, and the results on some samples to show the instrument performance of 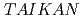 .
.
Kambara, Wataru; Aoyama, Kazuhiro; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro; Iwahashi, Takaaki; Ono, Shino; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Shibata, Kaoru; Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; et al.
no journal, ,
Yamazaki, Dai; Maruyama, Ryuji; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Harada, Masahide; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Nagano, Mikinori*; Tabata, Takaaki*; Mitsushima, Naoki*; Yamamura, Kazuya*
no journal, ,
We have been developing focusing supermirrors by depositing a supermirror on a precisely figured aspheric surface. Surface of a quartz substrate is figured using the "numerically-controlled local wet etching" technique. The figured surface shows a figure error of less than 1 micrometer p-v and an RMS roughness of less than 0.2 nm. Deposition of NiC/Ti supermirror (m=4) with ion beam sputtering keeps the figure error within several micrometers p-v and the roughness almost unchanged. A one-dimensional elliptical supermirror of 400mm in length was developed and it successfully achieved focused peak width (FWHM) of 0.128 mm and peak intensity 52 times that of unfocused (divergent) beam. We also tried two-dimensional focusing using two (vertical and lateral) focusing mirrors in a Kirkpatric-Baez configuration and successfully focused the beam to a spot of 0.5 mm in diameter.
Aso, Tomokazu; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Munakata, Koji*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Kawamura, Seiko; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Watanabe, Masao; Takata, Shinichi; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
no journal, ,
In FY2013, the SE team was officially organized in Technology Development Section in MLF with succeeding the previous ad hoc SE team. We are working on operation of so-called beam-line (BL)-common SE equipment and development of the SE devices as well as the previous SE team. We have already prepared a vertical-field superconducting magnet, a dilution refrigerator insert, a furnace with Nb heater and 2K cryostat as the BL-common SE equipment. In this fiscal year, a bottom-loading type  He cryostat will be introduced. Moreover, we have just started developing high pressure system by collaborating with High Pressure Group in MLF, to comply with users' requests. We have also discussed the general purpose of apparatus for pulse magnet and for hydrogen environment. We plan to prepare more working area for the SE equipment, whose number gradually increases, and sample preparation and characterization rooms for users in the new building, which is under construction.
He cryostat will be introduced. Moreover, we have just started developing high pressure system by collaborating with High Pressure Group in MLF, to comply with users' requests. We have also discussed the general purpose of apparatus for pulse magnet and for hydrogen environment. We plan to prepare more working area for the SE equipment, whose number gradually increases, and sample preparation and characterization rooms for users in the new building, which is under construction.
Yamamoto, Kazami
no journal, ,
An accelerator system of Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) operated since May 2008 for neutron experiments. The accelerator system consists Linac, Rapid Cycling synchrotron (RCS) and Main Ring. The original design of RCS injection energy is 400 MeV, but first operation was started by 181 MeV for budget reason. New acceleration cavities were installed in J-PARC linac summer shutdown of 2013, and user operation to Material and Life science Facility (MLF) with 400 MeV injection energy was started from February 2014. Owing to the beam commissioning with 400 MeV injection energy, the amount of the beam loss was enough small and we established 300 kW continuous operation. In this paper, we report the present status and future plan of J-PARC linac and RCS.
Kurihara, Kazuo; Tomoyori, Katsuaki; Tamada, Taro; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
Many proteins, especially membrane proteins and protein complexes, have larger molecular weight and then unit cells of their crystals have larger volume. Therefore, our group had designed the diffractometer which can cover such crystals with large unit cell volume (target lattice length: 250 ) at J-PARC. In order to separate spots closer to each other in spatial as well as time dimension in diffraction images, our proposed diffractometer adopts longer camera distance (
) at J-PARC. In order to separate spots closer to each other in spatial as well as time dimension in diffraction images, our proposed diffractometer adopts longer camera distance ( 2 = 800mm) and selects decoupled hydrogen moderator as neutron source which has shorter pulse width. Under the conditions that
2 = 800mm) and selects decoupled hydrogen moderator as neutron source which has shorter pulse width. Under the conditions that  1 is 33.5m, beam divergence 0.4
1 is 33.5m, beam divergence 0.4 and crystal edge size 2mm, this diffractometer is estimated to afford the resolution (
and crystal edge size 2mm, this diffractometer is estimated to afford the resolution (
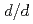 ) of 1% at the middle and high 2
) of 1% at the middle and high 2
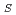 angles and be able to resolve spots diffracted from crystals with a lattice length of 220
angles and be able to resolve spots diffracted from crystals with a lattice length of 220 in each axis at
in each axis at  -space of 2.0
-space of 2.0 . In order to increase measurement efficiency, novel large-area detector (larger than 300mm
. In order to increase measurement efficiency, novel large-area detector (larger than 300mm  300mm) with a spatial resolution of better than 2.5mm is under development. More than 40 detectors plan to be installed, providing the total solid angle coverage of larger than 33%.
300mm) with a spatial resolution of better than 2.5mm is under development. More than 40 detectors plan to be installed, providing the total solid angle coverage of larger than 33%.
Kato, Shinichi; Yamamoto, Kazami; Harada, Hiroyuki; Hotchi, Hideaki; Kinsho, Michikazu
no journal, ,
The J-PARC 3-GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) accelerates proton beams from 400 MeV to 3 GeV and the designed output beam power is 1 MW. To achieve a high-intensity output beam power, the RCS adapts H charge-exchange multi-turn injection. The H
charge-exchange multi-turn injection. The H beam from the Linac is delivered to the RCS injection point, where it is injected through a carbon stripper foil in order to strip two electrons and to convert into proton. This injection is divided into 308 turns. Therefore, the both injection and circulating beams hit the foil repeatedly and scattering occur during the injection. Especially, large-scattered particles cause uncontrolled beam losses at downstream area. Thus, a new collimation system was developed and installed downstream of the foil to localize these losses in 2011. In the beam commissioning at 181 MeV and 400 MeV injection energy, unique tuning method of the collimator has been established and consequently these uncontrolled beam losses were localized successfully.
beam from the Linac is delivered to the RCS injection point, where it is injected through a carbon stripper foil in order to strip two electrons and to convert into proton. This injection is divided into 308 turns. Therefore, the both injection and circulating beams hit the foil repeatedly and scattering occur during the injection. Especially, large-scattered particles cause uncontrolled beam losses at downstream area. Thus, a new collimation system was developed and installed downstream of the foil to localize these losses in 2011. In the beam commissioning at 181 MeV and 400 MeV injection energy, unique tuning method of the collimator has been established and consequently these uncontrolled beam losses were localized successfully.
Harjo, S.; Aizawa, Kazuya; Kawasaki, Takuro; Gong, W.; Iwahashi, Takaaki; Ito, Takayoshi*; Abe, Jun*; Nakatani, Takeshi
no journal, ,
Uesaka, Mitsuru*; Tagi, Kazuhiro*; Matsuyama, Daiki*; Fujiwara, Takeshi*; Dobashi, Katsuhiro*; Yamamoto, Masashi*; Harada, Hideo
no journal, ,
Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Oikawa, Kenichi; Segawa, Mariko; Harada, Masahide; Nakatani, Takeshi; Oi, Motoki; Sato, Hirotaka*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Yokota, Hideo*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori; Nagai, Takaya*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Machida, Akihiko; Saito, Hiroyuki; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Abe, Jun*; Machida, Shinichi*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*
no journal, ,
We developed a six-axis multi-anvil press and the beamline dedicated for the press to realize high-PT neutron experiments. ATUSHIME has six hydraulic rams with a maximum load of 5000 kN per each. The six anvils are synchronized within the precision of 2 micron and compress the cubic sample isotropically. The press can generate high-PT condition of 10 GPa and 2000 K with the sample volume of 20 mm3 volume. To obtain a clear diffraction pattern from a compressed sample surrounded by a heater and pressure-transmitting medium, the beamline is equipped with fine incident collimator and radial collimators. These collimation devices enable us to selectively obtain the diffraction in the region of 3 mm cube in the high-pressure assembly.
Kikuchi, Tatsuya
no journal, ,
Dynamic structure factor, S(Q,E), which can be obtained by Inelastic neutron scattering directly, is a function of scattering vector, Q, and energy transfer, E. In recent years, importance of the studies on dynamics that cannot be well described by Q and E in substances such as battery materials has increased. S(Q,E) is defined as a Fourier-transformed function from van Hove's space-time correlation function, G(r,t), which is a function in real space and time. G(r,t) is important to express local motions of atoms and molecules directly on these substances. However, the calculation of G(r,t) has been hardly performed even though it is so easy mathematically, because it requires spectrum in both high resolution and wide range in Q-E space. By the progress of the recent neutron sources and spectrometers, the measurements with wide range and high resolution in Q-E space are becoming easy. We measured high-resolution S(Q,E)s using AMATERAS spectrometer installed at J-PARC and calculated G(r,t)s. We used the maximum entropy method to lower the bias of truncation errors for the calculation of G(r,t).
Futakawa, Masatoshi
no journal, ,
A very preliminary plan associated with second target station in J-PARC is introduced in the presentation.