Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hashimoto, Makoto; Usui, Toshihide
Proceedings of 2nd Asian and Oceanic Congress Radiological Protection (AOCRP-2) (CD-ROM), p.1175 - 1181, 2006/10
no abstracts in English
Kinase, Sakae; Watanabe, Ritsuko; Saito, Kimiaki
Proceedings of 2nd Asian and Oceanic Congress Radiological Protection (AOCRP-2) (CD-ROM), p.509 - 513, 2006/10
The aim of the present work is the development of logical dosimetry for human alimentary tract. In this work, specific absorbed fractions for both photon and electron to a stomach model with stem cells have been evaluated in the energy range from 10 keV to 4 MeV using Monte Calro simulation. Furthermore, S values to the stomach model have been evaluated for several positron sources:  C,
C,  N,
N,  O and
O and  F. Consequently, it was found that photon SAFs to stem cells in the stomach are greater than those to the whole stomach wall. Electron SAFs to stem cells in the stomach were also found to be less than those used in the radiological protection. The stomach wall S values are less than those used in the radiological protection. It is concluded that the determination of target tissue in the stomach is very important for the SAF and S value evaluations.
F. Consequently, it was found that photon SAFs to stem cells in the stomach are greater than those to the whole stomach wall. Electron SAFs to stem cells in the stomach were also found to be less than those used in the radiological protection. The stomach wall S values are less than those used in the radiological protection. It is concluded that the determination of target tissue in the stomach is very important for the SAF and S value evaluations.
 Cs and
Cs and 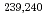 Pu in the Japan Sea
Pu in the Japan SeaNakano, Masanao; Takeishi, Minoru; Furuta, Sadaaki
Proceedings of 2nd Asian and Oceanic Congress Radiological Protection (AOCRP-2) (CD-ROM), p.795 - 799, 2006/10
In order to assess the worldwide and long-term effects from nuclear facilities, LAMER (Long-term Assessment ModEl for Radioactivity in the oceans) has been developed. As a part of LAMER, an advection-diffusion-scavenging model incorporated into the OGCM concerned the Japan Sea has been developed and validated by calculating  Cs and
Cs and 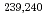 Pu water profiles in the Japan Sea and comparing them with experimental data. The concentrations of
Pu water profiles in the Japan Sea and comparing them with experimental data. The concentrations of  Cs and
Cs and 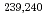 Pu have generally shown reasonable agreement between calculated and observed data. The best agreement between the experimental and calculated water profiles in the Japan Sea was obtained with the horizontal and vertical diffusion coefficients of 3
Pu have generally shown reasonable agreement between calculated and observed data. The best agreement between the experimental and calculated water profiles in the Japan Sea was obtained with the horizontal and vertical diffusion coefficients of 3 10
10 cm
cm s
s and 0.3 cm
and 0.3 cm s
s , respectively. The simulation in this study make them sure the quantitative origins and behaviours of
, respectively. The simulation in this study make them sure the quantitative origins and behaviours of  Cs and
Cs and 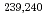 Pu in the Japan Sea. The behaviours of
Pu in the Japan Sea. The behaviours of  Cs and
Cs and 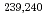 Pu in the Japan Sea have been much different from the behaviours in the Pacific Ocean.
Pu in the Japan Sea have been much different from the behaviours in the Pacific Ocean.
Sekiguchi, Masato; Takahashi, Masa; Miyauchi, Hideaki; Tachibana, Haruo; Komuro, Yuji*; Nemoto, Kiyoko*; Okawa, Ikuko*; Yoshizawa, Michio
Proceedings of 2nd Asian and Oceanic Congress Radiological Protection (AOCRP-2) (CD-ROM), p.114 - 117, 2006/10
In the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI), which was merged with the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute into the Japan Atomic Energy Agency in 2005, individual monitoring and dose record keeping for radiation workers have been conducted since 1957. This report outlines the statistics of the number of radiation workers and individual doses, such as annual collective doses, annual average doses, the maximum doses and dose distributions, over the past 48 years from 1957 to 2005. Individual doses were increased due to the augment of trouble and maintenance of new experimental facilities in 1960's. The collective doses and annual average doses in 1960's exceeded 1,200 man-mSv and 0.4mSv, respectively, in some years. Then, consecutive dose reduction efforts made the collective dose significantly decrease to less than 400 man-mSv ( 1/3 of the highest) and the average dose to
1/3 of the highest) and the average dose to  0.04 mSv (
0.04 mSv ( 1/10 of the highest). The collective doses in recent years keep almost constant even though radiation works increase in some high-contaminated hot laboratories for the decontamination and maintenance of experimental equipments. It was found from the analysis of cumulative distributions that there was a specific work-group exposed to significantly high dose compared with other workers.
1/10 of the highest). The collective doses in recent years keep almost constant even though radiation works increase in some high-contaminated hot laboratories for the decontamination and maintenance of experimental equipments. It was found from the analysis of cumulative distributions that there was a specific work-group exposed to significantly high dose compared with other workers.
Mikami, Satoshi; Koarashi, Jun; Miyauchi, Toru; Akiyama, Kiyomitsu; Kobayashi, Hirohide
Proceedings of 2nd Asian and Oceanic Congress Radiological Protection (AOCRP-2) (CD-ROM), p.308 - 312, 2006/10
As airborne radioiodine effluent monitoring in Tokai reprocessing plant (TRP), not only a weekly evaluation of exact discharged amount of radioiodine ( I) for assessing environmental impact, but also continuous monitoring of radioiodine being discharged are performed for quick recognition of unexpected effluent tendency. Furthermore, to enhance effluent monitoring activity corresponding to features reprocessing plant, sequential radioiodine monitoring system without interference by the mingled
I) for assessing environmental impact, but also continuous monitoring of radioiodine being discharged are performed for quick recognition of unexpected effluent tendency. Furthermore, to enhance effluent monitoring activity corresponding to features reprocessing plant, sequential radioiodine monitoring system without interference by the mingled  Kr has been developed and effectively functioned as an assist during plant operation. The systematic configurations having these functions for airborne radioiodine monitoring corresponding to nuclear fuel reprocessing plant have been established.
Kr has been developed and effectively functioned as an assist during plant operation. The systematic configurations having these functions for airborne radioiodine monitoring corresponding to nuclear fuel reprocessing plant have been established.
Sanada, Yukihisa; Kobayashi, Hirohide; Hashimoto, Tetsuo*
Proceedings of 2nd Asian and Oceanic Congress Radiological Protection (AOCRP-2) (CD-ROM), p.313 - 317, 2006/10
The dust monitor for rapid detection of artificial nuclides such as Plutonium with Rn-progeny background compensation system was developed to apply a time interval analysis (TIA). The TIA method was applied to beta and  decay events with microsecond scale (half-life of
decay events with microsecond scale (half-life of  Po: 164 microsecond). In actual experiments, dust sample on the filter (HE-40T pore size: 8micrometer) was collected in a workspace at the JAEA reprocessing facility to compensate
Po: 164 microsecond). In actual experiments, dust sample on the filter (HE-40T pore size: 8micrometer) was collected in a workspace at the JAEA reprocessing facility to compensate  Bi-
Bi- Po correlated events. As a result, total alpha-ray counting rate except for
Po correlated events. As a result, total alpha-ray counting rate except for  Po was 0
Po was 0  0.05 cps. The small
0.05 cps. The small  Am source with dust sampling was measured for simulation of unexpected additional
Am source with dust sampling was measured for simulation of unexpected additional  -ray emitted radionuclides. The increment for
-ray emitted radionuclides. The increment for  -ray counting rate due to the
-ray counting rate due to the  Am source could be clearly detected. The present method will apply for on-line monitoring of
Am source could be clearly detected. The present method will apply for on-line monitoring of  -ray measurement, because the method is able to detect artificial nuclides by compensating any changes of background due to Rn-progeny.
-ray measurement, because the method is able to detect artificial nuclides by compensating any changes of background due to Rn-progeny.
Oda, Keiji*; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Expert Committee on Concepts of Dosimetric Quantities Used in Radiological protection, Japan Health
Proceedings of 2nd Asian and Oceanic Congress Radiological Protection (AOCRP-2) (CD-ROM), p.52 - 55, 2006/10
no abstracts in English
Takeyasu, Masanori; Iida, Takao*; Takeishi, Minoru
Proceedings of 2nd Asian and Oceanic Congress Radiological Protection (AOCRP-2) (CD-ROM), p.754 - 757, 2006/10
The atmospheric Rn-222 concentration in rain clouds was estimated using the wet scavenging model of Rn-222 decay products with the observed data of the environmental  ray dose rate. In this method, the pattern of the increase of the dose rate calculated by the model was adjusted to the observed one, in order to estimate the atmospheric Rn-222 concentration which was one of parameter of the model. The Rn-222 concentration was estimated for the rainfall event on Dec. 27, 2003, when a large increase of the dose rate was observed in Tokai-mura. The concentration was estimated to be 24 Bq m
ray dose rate. In this method, the pattern of the increase of the dose rate calculated by the model was adjusted to the observed one, in order to estimate the atmospheric Rn-222 concentration which was one of parameter of the model. The Rn-222 concentration was estimated for the rainfall event on Dec. 27, 2003, when a large increase of the dose rate was observed in Tokai-mura. The concentration was estimated to be 24 Bq m , which was higher than the measured one at a height of a few kilometers around central Japan by aircraft. From a back trajectory analysis, the origin of Rn-222 atoms for the events on Dec. 27 was back-tracked to the northeastern part of China, and it was guessed that the large amount of Rn-222 was transported by the Eurasian continental air mass.
, which was higher than the measured one at a height of a few kilometers around central Japan by aircraft. From a back trajectory analysis, the origin of Rn-222 atoms for the events on Dec. 27 was back-tracked to the northeastern part of China, and it was guessed that the large amount of Rn-222 was transported by the Eurasian continental air mass.
Furuta, Sadaaki; Miyabe, Kenjiro
Proceedings of 2nd Asian and Oceanic Congress Radiological Protection (AOCRP-2) (CD-ROM), p.928 - 932, 2006/10
In 1972, production of nuclear fuels for experimental fast breeder reactor "JOYO" started at MOX fuel fabrication facilities in the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of JAEA. And in 1977 Tokai reprocessing plant "TRP" was launched as the first nuclear reprocessing plant in Japan with a capacity of 0.7tU/day spent fuel, and successfully reprocessed 1,116tU fuel mainly spent by light water reactor up to March 2006. A lot of other nuclear facilities associated with them are located at the same Laboratories' site. A feature of radiation protection and its recent relevant researches at the Laboratories are described in this paper.
Sanada, Yukihisa; Kobayashi, Hirohide; Hashimoto, Tetsuo*
no journal, ,
A dust monitor for rapid detection of artificial nuclides with Rn-progeny background compensation system was developed by applying a time interval analysis (TIA). A dust monitor with silicon semiconductor detector was constructed in combination with a special time recording device and a personal computer. Data of time intervals of neighboring pulses was analyzed by single time interval analysis (STA), which is one kind of the TIA method. Aerosol sample of natural nuclides was measured by this system. As a result, the counts derived from  Bi-
Bi- Po correlated events were certainly observed from 0 to 1ms of time interval region. This result suggested that selective detection of
Po correlated events were certainly observed from 0 to 1ms of time interval region. This result suggested that selective detection of  Bi-
Bi- Po correlated events could be measured with this system. The present method will be applied for on-line monitoring of alpha-ray measurement, because the method is able to detect any additional artificial nuclides by compensating any changes of background due to Rn-progeny.
Po correlated events could be measured with this system. The present method will be applied for on-line monitoring of alpha-ray measurement, because the method is able to detect any additional artificial nuclides by compensating any changes of background due to Rn-progeny.
Tsujimura, Norio; Momose, Takumaro; Yoshizawa, Michio; Yamamoto, Hideaki; Cruz-Suarez, R.*; Murakami, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
As one of the IAEA/RCA projects, three phases of personal dosimetry intercomparison programs had been conducted during the years of 1990 to 2004. The purpose of the program was to assess the ability of the personal dosimetry services in the RCA Member States and also to provide technical help in improving a performance of their dosimetry systems and in implementing the operational quantities recommended by ICRU. The purpose of this paper is to trace the history of and to present a summarized review of the results of the intercomparison programs. The trend of the phase-by-phase results showed that the quality of individual monitoring in most of the Member States has become dramatically improved to an acceptable level. There was a successful achievement and advancement over the 15 years effort.
Mikami, Satoshi; Koarashi, Jun; Miyauchi, Toru; Akiyama, Kiyomitsu; Kobayashi, Hirohide
no journal, ,
For airborne radioiodine effluent monitoring in Tokai reprocessing plant (TRP), not only a weekly evaluation of exact discharged amount of radioiodine (I-129) for assessing environmental impact, but also continuous monitoring of radioiodine being discharged are performed for quick recognition of unexpected effluent tendency. Furthermore, to enhance effluent monitoring activity corresponding to features of reprocessing plant, continuous radioiodine monitoring system without interference by the mingled Kr-85 has been developed and effectively functioned as an assist during plant operation. The systematic configurations having these functions for airborne radioiodine monitoring corresponding to nuclear fuel reprocessing plant have been established.
Furuta, Sadaaki; Miyabe, Kenjiro
no journal, ,
The first nuclear cycle plants in Japan, such as fuel reprocessing plant launched in 1977 and MOX fuel fabrication facilities in 1972, including other nuclear facilities, are located at Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, JAEA. A feature of radiation protection and its recent relevant researches performed in the Laboratories will be introduced.