Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Villard, L.*; Bottino, A.*; Brunner, S.*; Casati, A.*; Chowdhury, J.*; Dannert, T.*; Ganesh, R.*; Garbet, X.*; G rler, T.*; Grandgirard, V.*; et al.
rler, T.*; Grandgirard, V.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 52(12), p.124038_1 - 124038_18, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:60.27(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Miyato, Naoaki; Scott, B. D.*
Proceedings of 37th European Physical Society Conference on Plasma Physics (EPS 2010) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2010/06
Reduced kinetic models such as gyrokinetic models are constructed by phase space transformation from particle phase space to guiding-centre phase space. In the reduced quasi-neutrality condition or the Poisson equation for electrostatic potential, particle density should be represented in terms of guiding-centre things. It is called push-forward representation of particle density. Recently a reduced kinetic model with large flow was derived by modifying the standard guiding-centre transformation. The model can be regarded as a natural extension of the standard model to the large flow regime because the symplectic part in the guiding-centre phase space Lagrangian is the same as the standard one formally. The push-forward representation of particle density or the reduced quasi-neutrality condition in the transonic case is derived by the variational method. It is found that corrections due to the flow appear in the polarisation density.
 dependence of the growth rate of the edge localized MHD modes
dependence of the growth rate of the edge localized MHD modesAiba, Nobuyuki; Hirota, Makoto
Proceedings of 37th European Physical Society Conference on Plasma Physics (EPS 2010) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2010/06
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Takahiro; Oyama, Naoyuki; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Fujita, Takaaki
Proceedings of 37th European Physical Society Conference on Plasma Physics (EPS 2010) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2010/06
Since transient heat and particle loads by the type-I ELMs are significantly high for the plasma facing components of the fusion reactor, understanding propagation of plasma ejected by ELMs (ELM pulse) in SOL is important. Increase in the SOL plasma density due to the ELM pulse has been measured through the increase in beam emission (BE) at various radial locations in SOL near equatorial plane, using MSE diagnostics as beam emission spectroscopy (BES) diagnostics. From the temporal delay of the increase of BE as a function of major radius in the SOL, radial velocity of the ELM pulse propagation has been evaluated as 0.8-1.8 km/s. In accurately evaluating the velocity, elimination of background (BG) light from the BES signal is found essential since the delay of the net BE is veiled by the BG light that increases in synchronous to the ELM pulse. The intermittent increase in the BG light synchronized with ELMs has been observed in MSE channels viewing not only the SOL but also the main plasma. Since this BG light affects the magnetic pitch angle measurement by MSE diagnostics as was reported in JET, the impact of the intermittent BG light by ELMs on MSE diagnostics has been investigated numerically. When intermittent BG light by ELMs mixes with PEM modulation for MSE diagnostics, broadband spectrum of the impulse-like BG light disturbs the spectrum intensities, even if the BG light is not polarized. Numerical simulation shows that error induced by ELMs piles up if ELM frequency is higher than 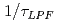 , where
, where 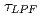 is time constant of lock-in amplifier detecting PEM modulation, and then, the error remains even between ELMs.
is time constant of lock-in amplifier detecting PEM modulation, and then, the error remains even between ELMs.
Koubiti, M.*; Nakano, Tomohide; Capes, H.*; Marandet, Y.*; Mouret, L.*; Rosato, J.*; Stamm, R.*
Proceedings of 37th European Physical Society Conference on Plasma Physics (EPS 2010) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2010/06
The C IV ( = 6-7) spectral lines emitted from the JT-60U detachedplasmas were observed with a high-wavelength resolution spectrometer and theprofiles were analyzed with a PPP code. The analysis indicates that thespectral profiles were broadened with both the Doppler and the Starkeffects. From these effects, the electron temperature and density wereevaluated. Along the viewing chord for the X-point, the electron temperatureand density was determined to be 3 eV and 7
= 6-7) spectral lines emitted from the JT-60U detachedplasmas were observed with a high-wavelength resolution spectrometer and theprofiles were analyzed with a PPP code. The analysis indicates that thespectral profiles were broadened with both the Doppler and the Starkeffects. From these effects, the electron temperature and density wereevaluated. Along the viewing chord for the X-point, the electron temperatureand density was determined to be 3 eV and 7 10
10 m
m , respectively. These are similar to those determined from the intensity ratioof C IV lines (6.3 eV and 7.8
, respectively. These are similar to those determined from the intensity ratioof C IV lines (6.3 eV and 7.8  10
10 m
m , respectively). The high density plasma around the X-point was confirmed withthese independent methods.
, respectively). The high density plasma around the X-point was confirmed withthese independent methods.
Nakamura, Yukiharu*; Pautasso, G.*; Sugihara, Masayoshi*; Miyamoto, Seiji; Toshimitsu, Shinichi; Yoshino, Ryuji; ASDEX Upgrade Team*
Proceedings of 37th European Physical Society Conference on Plasma Physics (EPS 2010) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2010/06
Of particular importance for the assessment of electromagnetic loads on vacuum vessel and in-vessel components of ITER is the halo current which achieves a maximum during VDEs (VDE: vertical displacement event). However, halo current models have a limited development so far with a few exceptions such as a validation study of the JT-60U halo current modelling using the DINA code. Recently, several experimental groups have prepared systematic halo current data, and further model development and validation with these data need to be performed using an axisymmetric, two-dimensional, free boundary code, TSC. To enhance an understanding of the maximum halo current and large vertical shifts, a reference discharge was selected from those included in the ASDEX upgrade disruption database. Systematic TSC simulations were performed to mimic the observation of a slow VDE of hot plasma and an ensuing fast downward-going VDE during a subsequent plasma current quench. Careful parameter adjustment of the temperature and width of the halo region was examined to mimic measurements of the halo current. A spontaneous, downward-going VDE was reproduced accurately in a manner that closely resembled experimental observations.
Takechi, Manabu; Bolzonella, T.*; Baruzzo, M.*; Ide, Shunsuke; Matsunaga, Go; JT-60SA Team
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (Internet), 34A, p.P2.192_1 - P2.192_4, 2010/00
Ide, Shunsuke; Kamada, Yutaka; Lackner, K.*; Bolzonella, T.*; Fujita, Takaaki; JT-60SA Team
no journal, ,
Snipes, J. A.*; Schaffer, M. J.*; Gohil, P.*; de Vries, P.*; Fenstermacher, M. E.*; Evans, T. E.*; Gao, X. M.*; Garofalo, A.*; Gates, D. A.*; Greenfield, C. M.*; et al.
no journal, ,
A series of experiments was performed on DIII-D to mock-up the field that will be induced in a pair of ferromagnetic Test Blanket Modules (TBMs) in ITER to determine the effects of such error fields on plasma operation and performance. A set of coils producing both poloidal and toroidal fields was placed inside a re-entrant horizontal port close to the plasma. The coils produce a localized ripple due to the toroidal field (TF) + TBM up to 5.7%, which is more than four times that expected from a pair of representative 1.3 ton TBMs in ITER. The experiments show that the reduction in the toroidal rotation is sensitive to the ripple. On the other hand, the confinement is reduced by up to 15-18% for local ripple 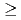 3% but is hardly affected at 1.7% local ripple.
3% but is hardly affected at 1.7% local ripple.