Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Igawa, Naoki; Shamoto, Shinichi
IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering, 18, p.062020_1 - 062020_4, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:75.61(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)SiC nanowires and nanotubes sheathed with BN were synthesized by annealing C-SiC and SiC nanotubes at 1600 and 1700  C for 5 h with BN powder in Ar gas. According to TEM observation, the BN coating was very thin and the layer number of BN coating was less than 10. The BN coating on the surface of SiC nanotubes was not produced by the heat treatment at 1500
C for 5 h with BN powder in Ar gas. According to TEM observation, the BN coating was very thin and the layer number of BN coating was less than 10. The BN coating on the surface of SiC nanotubes was not produced by the heat treatment at 1500  C. This result revealed that BN on the surface of SiC nanomaterials produced by heat treatment of higher than 1600
C. This result revealed that BN on the surface of SiC nanomaterials produced by heat treatment of higher than 1600  C. After the heat treatment of higher than 1600
C. After the heat treatment of higher than 1600  C, many nanotubes transformed to nanowires because the inner space of nanotubes was occluded due to the SiC grain growth by heat treatment.
C, many nanotubes transformed to nanowires because the inner space of nanotubes was occluded due to the SiC grain growth by heat treatment.
 pellets for production of
pellets for production of  Mo medical isotope
Mo medical isotopeKimura, Akihiro; Sato, Yuichi*; Tanase, Masakazu*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering, 18(4), p.042001_1 - 042001_4, 2011/10
In the medical field, the radioisotopes are indispensable. Especially,  Tc is most commonly used as a radiopharmaceutical. However, the supply of
Tc is most commonly used as a radiopharmaceutical. However, the supply of  Mo in Japan depends fully on the import from foreign countries. JMTR has a plan to produce a medical isotope of
Mo in Japan depends fully on the import from foreign countries. JMTR has a plan to produce a medical isotope of  Mo, the parent nuclide of
Mo, the parent nuclide of  Tc by the (n,
Tc by the (n, ) method and a part of the import volume can be covered of the home country. In this plan, it is important to develop the production method of the irradiation targets such as the Molybdenum oxide (MoO
) method and a part of the import volume can be covered of the home country. In this plan, it is important to develop the production method of the irradiation targets such as the Molybdenum oxide (MoO ) pellets. However, MoO
) pellets. However, MoO is low sublime temperature and it is difficult to produce the pellets with high density. In this study, MoO
is low sublime temperature and it is difficult to produce the pellets with high density. In this study, MoO pellets were produced by two kinds of production methods. As a result, MoO
pellets were produced by two kinds of production methods. As a result, MoO pellet of about 70% TD was obtained by CIP and MoO
pellet of about 70% TD was obtained by CIP and MoO pellet of over 95% TD was obtained by SPS.
pellet of over 95% TD was obtained by SPS.
Nozawa, Takashi; Choi, Y.-B.*; Hinoki, Tatsuya*; Kishimoto, Hirotatsu*; Koyama, Akira*; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu
IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering, 18, p.162011_1 - 162011_4, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:97.12(Materials Science, Ceramics)A SiC/SiC composite is one of attractive candidates for fission and nuclear fusion due to the proven irradiation tolerance coupled with the excellent baseline properties as refractory ceramics. Considering the inherent anisotropy of composites due to the variety of fabric architecture, it is required to identify the crack propagation behavior of SiC/SiC composites by various failure modes. This study aims to evaluate crack propagation behavior by the axial and off-axial tensile/compressive tests, Iosipescu test for in-plane shear, double-notch-shear test for inter-laminar shear and diametral compression test for inter-laminar detachment. Preliminary test results identified strength anisotropy maps, implying that the composites failed by the mixed modes. Specifically, it was found that the in-plane/inter-laminar shear modes had significant impacts on the results.
Sumita, Junya; Fujita, Ichiro; Shibata, Taiju; Makita, Taiyo*; Takagi, Takashi*; Kunimoto, Eiji*; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Kim, W. J.*; Park, J. Y.*
IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering, 18(16), p.162010_1 - 162010_4, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:50.51(Materials Science, Ceramics)For control rod element of Very High Temperature Reactor, carbon fiber reinforced carbon matrix composite (C/C composite) is one of the major candidate materials for its high strength and thermal stability. Since the crack propagation of the C/C composite is complicated, the fracture behavior is one of the most important subjects of the design methodology for the control rod with the C/C composite. In this study, in order to assess the Mode-II fracture behavior of the two-dimensional (2D-) C/C composite which has the layer structure of laminas composed of fibers and matrix, bending test with oxidized end notched flexure specimen was carried out. The interlaminar fracture toughness decreased with increasing the oxidation for the 2D-C/C composite. The oxidized matrix causes reduction of fracture toughness and the reduction ratio is dependent on the matrix type. The crack initiates at the boundary between fiber bundles and grows along them without breaking the fiber. It is thought that the cracks which were initiated at the interface between matrix and fiber were gathered into the voids in the boundary between fiber bundles, and then the crack grows up in the matrix.
Eto, Motokuni*; Konishi, Takashi*; Shibata, Taiju; Sumita, Junya
IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering, 18(16), p.162003_1 - 162003_6, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:89.61(Materials Science, Ceramics)High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) and Very High Temperature Reactor (VHTR) are attractive nuclear reactors to obtain high temperature helium gas to the reactor outlet. To enhance the thermal efficiency, the core internals of HTGR/VHTR are subjected to the very severe high temperature condition. The carbon fiber reinforced carbon-carbon composite (C/C composite) is one of the advanced material candidates for the control rod sheath of the reactors because of its excellent thermal resistance and stability in the severe condition. The R&Ds on the C/C composite application to HTGR have been carried out since 1990'. JAEA and Toyo Tanso have been in collaboration with each other in the R&Ds. The development of control rod made of C/C composite is recently focused as one of the important subjects to develop the VHTR in the international R&Ds. The scheme of the development of JAEA is categorized as the following phases; (1) Database establishment, (2) Design and manufacturing of component and (3) Demonstration test by HTTR. At the initial stage of the development in 1990' in JAERI, the feasibility of the control rod using C/C composite was demonstrated by a conceptual design. The phase (2) is planned to be completed within 5 years. This paper presents the review of the development of the control rod made of C/C composite and the recent R&D results.
Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Kunimoto, Eiji*; Yamaji, Masatoshi*; Konishi, Takashi*; Sawa, Kazuhiro
IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering, 18(16), p.162012_1 - 162012_4, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:50.51(Materials Science, Ceramics)For control rod element of Very High Temperature Reactor, carbon fiber reinforced carbon matrix composite (C/C composite) is one of the major candidate materials for its high strength and thermal stability. The development of a property prediction model of the two-dimensional (2D)-C/C composite is one of the most important subjects for the design methodology for control rod. Since the property of the 2D-C/C composite is strongly dependent on its microstructure, fiber/matrix, it would be possible to evaluate the properties of the 2D-C/C composite from its microstructure. In this study, in order to develop the property prediction model of the 2D-C/C composite base on its microstructure, pore distribution was investigated by using the X-ray computed tomography (X-ray CT) images and developed image based voxcel model. The compressive strength of the 2D-C/C composite was measured and evaluated by the voxcel model. This study shows that the pore distribution in the 2D-C/C composite can be confirmed visually and the volume and shape of the pores can be estimated from X-ray CT images. It is also shown that evaluation of the compressive strength by using the voxel model is useful to simulate the trend of the stress distribution of the 2D-C/C composite. However, it is necessary to characterize the property of the 2D-C/C composite and to set up the appropriate mesh to simulate the absolute stress value precisely.
 O
O
Matsumoto, Keisuke*; Koyama, Tsukasa*; Mori, Shigeo*; Yoshii, Kenji; Kambe, Takashi*; Ikeda, Naoshi*
IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering, 18(9), p.092047_1 - 092047_4, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:50.51(Materials Science, Ceramics)Changes of charge ordered (CO) structure by partial substitution of Mn for Fe in YbFe O
O were investigated by a transmission electron microscope (TEM), incombination with conventional dielectric measurement. It is revealed that partial substitution of Mn
were investigated by a transmission electron microscope (TEM), incombination with conventional dielectric measurement. It is revealed that partial substitution of Mn for Fe
for Fe in YbFe
in YbFe O
O destroyed drastically the CO structure with the wave vector of q=
destroyed drastically the CO structure with the wave vector of q= 1/3 1/3 1/2
1/3 1/3 1/2 . Consequently polar clustering structure giving rise to honeycomb-shaped diffuse streaks was found in YbFeMnO
. Consequently polar clustering structure giving rise to honeycomb-shaped diffuse streaks was found in YbFeMnO . The random distribution of polar clustering structure gives rise to characteristic broad dielectric dispersion.
. The random distribution of polar clustering structure gives rise to characteristic broad dielectric dispersion.
Igawa, Naoki; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Birumachi, Atsushi; Ishii, Yoshinobu*
IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering, 18, p.022021_1 - 022021_4, 2011/05
The neutron scattering length density distributions of Xe deuterohydrate were analyzed by Rietveld and MEM analysis applied to neutron powder diffraction data to clarify the Xe behavior in the temperature range from 10 to 245 K. A spherical positive scattering length density attributed to the Xe atom was observed at the center of the small cage of the hydrate. On the other hand, an ellipsoid shaped scattering length density distribution at the center of the large cage was observed; the major axis of the ellipsoid scattering length density was directed toward the center of a hexagonal facet of the large cage. The distributions of the Xe atom in the both cages were almost the same at any temperature.
Suzuya, Kentaro; Kohara, Shinji*; Okamura, Kiyohito*; Ichikawa, Hiroshi*; Suzuki, Kenji*
no journal, ,
Polymer-derived Si-C-O fibers have high tensile strength and characteristic electrical properties. The atomic scale structure of the polymer (Polycarbosilane) and the polymer-derived Si-C-O ceramics amorphous fibers has been investigated by high-energy X-ray diffraction. In addition, we applied the reverse Monte Carlo (RMC) modelling method to the diffraction data to visualize for better understanding of the complex structure. By the RMC modelling, the basic structures of the Si-C-O fibers are the three-dimensionally connected SiC
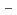
 O
O (x = 0-4) tetrahedral random-network structure which is the successive assembly of the SiC
(x = 0-4) tetrahedral random-network structure which is the successive assembly of the SiC
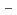
 O
O tetrahedral unit which share elements (corners and edges) and the excess carbon atoms which are interconnected and distributed widely in the network cage.
tetrahedral unit which share elements (corners and edges) and the excess carbon atoms which are interconnected and distributed widely in the network cage.
Kitagishi, Shigeru; Saito, Takashi; Omi, Masao; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
no journal, ,
The Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) has been utilized for the various neutron irradiation tests of fuels and materials, as well as for radioisotope (RI) production since achieving the first criticality in March 1968. The JMTR was stopped at the beginning of 2006 to conduct refurbishment works, and the reoperation will be planned from 2011. The new JMTR is expected to contribute of many fields such as the lifetime extension of light water reactors (LWRs), progress of science and technology for fusion reactors and expansion of industry for RI production. It is important for neutron irradiation test of materials and fuels to clarify the irradiation environment. For example, the oxygen and hydrogen peroxide concentrations in the cooling water are required to measure in the analysis of corrosion mechanism of the structure materials under LWR conditions. However, the outer diameter of the irradiation capsule used in JMTR is limited below  65mm. Therefore, it is necessary for the measurement of irradiation environment to develop the small ceramic oxygen sensors. In this study, properties of the element of ceramic oxygen sensor fabricated by the Spark Plasma Sintering method were evaluated under a high temperature gas environment and a high pressure water environment.
65mm. Therefore, it is necessary for the measurement of irradiation environment to develop the small ceramic oxygen sensors. In this study, properties of the element of ceramic oxygen sensor fabricated by the Spark Plasma Sintering method were evaluated under a high temperature gas environment and a high pressure water environment.