Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Minato, Futoshi; Nagai, Yasuki; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu
no journal, ,
Various kinds of radioactive isotopes (RIs) are widely used in nuclear medicine for diagnostics and therapy. Since the RIs are not usually present in the nature, they must be produced by nuclear reactors and accelerators. For instance,  Tc is mainly produced by fission of highly enriched
Tc is mainly produced by fission of highly enriched  U (HEU) in nuclear reactors. However, use of the HEU is unfavorable in terms of nuclear security. Therefore, many methods without
U (HEU) in nuclear reactors. However, use of the HEU is unfavorable in terms of nuclear security. Therefore, many methods without  U have been studied in order to produce RIs for medical use; for example, thermal neutron capture,
U have been studied in order to produce RIs for medical use; for example, thermal neutron capture,  disintegration, and proton induced reactions. We also have proposed an alternative method using accelerator neutron besides the above methods. In this talk, we will show the features of RI productions with accelerator neutron which we have ever investigated and found, along with numerical results of RI yields calculated with Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library (JENDL-4.0).
disintegration, and proton induced reactions. We also have proposed an alternative method using accelerator neutron besides the above methods. In this talk, we will show the features of RI productions with accelerator neutron which we have ever investigated and found, along with numerical results of RI yields calculated with Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library (JENDL-4.0).
Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi
no journal, ,
While the existence of kaonic nuclei has been intensively studied both theoretically and experimentally, there is no conclusive result establishing its existence.Here, we have searched for the 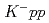 , a bound state of a
, a bound state of a 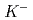 with two protons, in the
with two protons, in the 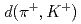 reaction at 1.69 GeV/
reaction at 1.69 GeV/ at J-PARC K1.8 beam line with a missing-mass resolutionof 2.7 MeV/
at J-PARC K1.8 beam line with a missing-mass resolutionof 2.7 MeV/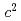 (FWHM). In this reaction, the
(FWHM). In this reaction, the 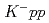 is assumed to be produced as
is assumed to be produced as 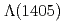 as a doorwaysuch as
as a doorwaysuch as 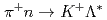 ,
, 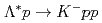 .Since the sticking probability of the
.Since the sticking probability of the  on proton would not be so large, coincidence of high-momentum (
on proton would not be so large, coincidence of high-momentum ( 250 MeV/
250 MeV/ ) proton(s) in large emission angles (
) proton(s) in large emission angles (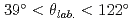 ) was requested to enhance the signal-to-background ratio. We have obtained an inclusive
) was requested to enhance the signal-to-background ratio. We have obtained an inclusive 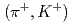 spectrum in a wide missing-mass range from
spectrum in a wide missing-mass range from  ,
,  to
to 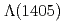 /
/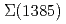 , for the first time. A proton coincidence spectrum shows a large proton-emission probability at around 2.27 GeV/
, for the first time. A proton coincidence spectrum shows a large proton-emission probability at around 2.27 GeV/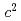 as a broad bump. It might be attributed to the
as a broad bump. It might be attributed to the 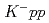 production. A study of decay branch suggests non-mesonic decays of
production. A study of decay branch suggests non-mesonic decays of 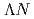 and
and 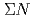 are dominant rather than mesonic decays.
are dominant rather than mesonic decays.
 Sn studied via the
Sn studied via the  Sn(d,t)
Sn(d,t) Sn reaction
Sn reactionOrlandi, R.; Pain, S. D.*; Bardayan, D. W.*; Gross, C. J.*; Smith, M. S.*; Jungclaus, A.*; Ahn, S.*; Jones, K. L.*; Pittman, S. T.*; Schmitt, K. T.*; et al.
no journal, ,
L guillon, R.; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Orlandi, R.; Makii, Hiroyuki; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Ishii, Tetsuro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Chiba, Satoshi*; et al.
guillon, R.; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Orlandi, R.; Makii, Hiroyuki; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Ishii, Tetsuro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Chiba, Satoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Hayakawa, Takehito; Negm, H.*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Daito, Izuru*; Kii, Toshiteru*; Zen, H.*; Omer, M.*; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hajima, Ryoichi
no journal, ,
Recently, a nondestructive measurement method of shielded fissional isotopes such as  U or
U or  Pu has been proposed for the nuclear security. These isotopes are measured by using nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) with monochromatic energy
Pu has been proposed for the nuclear security. These isotopes are measured by using nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) with monochromatic energy  -ray beams generated by laser Compton-scattering (LCS). We have proposed that one measure scattered
-ray beams generated by laser Compton-scattering (LCS). We have proposed that one measure scattered  -rays from NRF with LCS
-rays from NRF with LCS  -ray beams using the LaBr
-ray beams using the LaBr (Ce) detectors. The LaBr
(Ce) detectors. The LaBr (Ce) crystals include internal radioisotopes of a meta-stable isotope
(Ce) crystals include internal radioisotopes of a meta-stable isotope 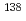 La and alpha decay chains from some actinides as
La and alpha decay chains from some actinides as 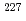 Ac. There is a broad pump at about 2 MeV. This pump is considered to be an overlap of
Ac. There is a broad pump at about 2 MeV. This pump is considered to be an overlap of  -rays from decay chains of some actinides but its detailed structure has not been established. Here we have measured NRF spectra of
-rays from decay chains of some actinides but its detailed structure has not been established. Here we have measured NRF spectra of  U using the LCS
U using the LCS  -rays with energy of about 2.5 MeV at the HIgS facility of the Duke University. The background has been evaluated using a simulation code GEAT4. The 9 peaks, 8 NRF
-rays with energy of about 2.5 MeV at the HIgS facility of the Duke University. The background has been evaluated using a simulation code GEAT4. The 9 peaks, 8 NRF  -rays plus the Compton scattered
-rays plus the Compton scattered  -ray of the incident beam, are finally assigned in an energy range of about 200 keV at about 2.5 MeV. The 8 integrated NRF cross-sections measured by LaBr
-ray of the incident beam, are finally assigned in an energy range of about 200 keV at about 2.5 MeV. The 8 integrated NRF cross-sections measured by LaBr (Ce) have been consistent with results by an HPGe detector. The three levels are newly assigned using the HPGe detector. Two of them are also measured by LaBr
(Ce) have been consistent with results by an HPGe detector. The three levels are newly assigned using the HPGe detector. Two of them are also measured by LaBr (Ce).
(Ce).
 Tc obtained from
Tc obtained from  Mo produced by
Mo produced by  Mo(n,2n) using accelerator neutrons
Mo(n,2n) using accelerator neutronsNagai, Yasuki; Kawabata, Masako; Sato, Nozomi*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Saeki, Hideya; Motoishi, Shoji*; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Ota, Akio; Shiina, Takayuki; Kawauchi, Yukimasa
no journal, ,
 Tc, the daughter nuclide of
Tc, the daughter nuclide of  Mo, is widely used for medical diagnosis. In Japan, about 0.9 million diagnostic procedures are carried out using
Mo, is widely used for medical diagnosis. In Japan, about 0.9 million diagnostic procedures are carried out using  Tc.
Tc.  Mo has been mostly produced using
Mo has been mostly produced using  U in research reactors. Because of recent shortages of
U in research reactors. Because of recent shortages of  Mo, a variety of alternative production methods of
Mo, a variety of alternative production methods of  Mo or
Mo or  Tc were proposed. We proposed to produce
Tc were proposed. We proposed to produce  Mo by
Mo by  Mo(n,2n) using neutrons from an accelerator. The route is characterized to produce a large quantity of high-quality
Mo(n,2n) using neutrons from an accelerator. The route is characterized to produce a large quantity of high-quality  Mo with a minimum level of radioactive wastes, since the cross section of the
Mo with a minimum level of radioactive wastes, since the cross section of the  Mo(n,2n)
Mo(n,2n) Mo reaction at 11
Mo reaction at 11  En
En  18 MeV is large, and the cross sections of the (n,He), (n,n'p), and (n,p) reactions on
18 MeV is large, and the cross sections of the (n,He), (n,n'p), and (n,p) reactions on  Mo are quite small. Intense neutrons are available because of recent progresses of accelerator and target technologies. In the talk, we show our recent experimental results to obtain
Mo are quite small. Intense neutrons are available because of recent progresses of accelerator and target technologies. In the talk, we show our recent experimental results to obtain  Tc with high-quality using
Tc with high-quality using  Mo produced by
Mo produced by  Mo(n,2n).
Mo(n,2n).
Ekawa, Hiroyuki; Imai, Kenichi
no journal, ,
 Cu and
Cu and  Cu using zinc target irradiated with accelerator neutrons
Cu using zinc target irradiated with accelerator neutronsKawabata, Masako; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Saeki, Hideya; Sato, Nozomi*; Motoishi, Shoji*; Nagai, Yasuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Imai, Kenichi
no journal, ,
Recent Lattice QCD calculations have suggested a possible existence of H-dibaryon near the threshold. In the previous experiments at KEK-PS, a hint of peak structure was observed in the invariant mass spectrum at just above the threshold. An experiment to search for the H-dibaryon through  p
p 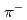 and
and 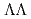 mass spectra was proposed at J-PARC (E42). Much better statistics and mass resolution than the previous data are expected. For this experiment, we have been constructing a novel hyperon spectrometer with use of a GEM-TPC and a superconducting Helmholtz magnet. The expected performance of the spectrometer and the proposed experiment is reported based on the R&D results of the TPC and simulations. Possible physics with the hyperon spectrometer other than the H-dibaryon is also discussed.
mass spectra was proposed at J-PARC (E42). Much better statistics and mass resolution than the previous data are expected. For this experiment, we have been constructing a novel hyperon spectrometer with use of a GEM-TPC and a superconducting Helmholtz magnet. The expected performance of the spectrometer and the proposed experiment is reported based on the R&D results of the TPC and simulations. Possible physics with the hyperon spectrometer other than the H-dibaryon is also discussed.
 82 nuclei at the JAEA Tandem Facility
82 nuclei at the JAEA Tandem FacilitySmallcombe, J.; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Makii, Hiroyuki; Orlandi, R.; Tamura, Nobuyuki*; Goto, Shinichi*; Otsuki, Tsutomu*; Andreyev, A.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Koura, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
An improvement of the gross theory of the  decay has been carried out on
decay has been carried out on  -decay rate,
-decay rate,  , and beta-delayed neutron emission probability,
, and beta-delayed neutron emission probability, 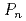 . The gross theory is based on the sum rule of the
. The gross theory is based on the sum rule of the  -decay strength function, and has succeeded in describing
-decay strength function, and has succeeded in describing  -decay rate of nuclei in the entire nuclear region. The gross theory includes not only the allowed (Fermi and Gamow-Teller) transition, but also the 1st-forbidden transition. In this work, some improvements are introduced as the nuclear shell correction for the nuclear level density and the nuclear deformation for the strength function, those effects were not included in the original gross theory. Considering the properties of the integrated Fermi function, three energy regions of the
-decay rate of nuclei in the entire nuclear region. The gross theory includes not only the allowed (Fermi and Gamow-Teller) transition, but also the 1st-forbidden transition. In this work, some improvements are introduced as the nuclear shell correction for the nuclear level density and the nuclear deformation for the strength function, those effects were not included in the original gross theory. Considering the properties of the integrated Fermi function, three energy regions of the  decay are classified: a higher energy region, which fully affects
decay are classified: a higher energy region, which fully affects 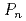 , a middle energy region, which contributes the decay heat, and a region neighboring the ground-state, which determines
, a middle energy region, which contributes the decay heat, and a region neighboring the ground-state, which determines  . Some results will be given in the presentation.
. Some results will be given in the presentation.
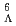 H hypernucleus via the (
H hypernucleus via the (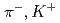 ) reaction at J-PARC
) reaction at J-PARCSugimura, Hitoshi; Imai, Kenichi; Sako, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
The research for neutron-rich hypernuclei are mainly studying at Japan and Europe. We have conducted the production experiment of 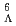 H at J-PARC.
H at J-PARC.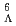 H consists of four neutrons, one proton and one
H consists of four neutrons, one proton and one  particle. Therefore N/Z ratio is very high. In such case,
particle. Therefore N/Z ratio is very high. In such case, 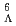 H makes very important role for researching the neutron star. So, We attempted to produce the hypernucleus and decided the upper limit of production cross section.
H makes very important role for researching the neutron star. So, We attempted to produce the hypernucleus and decided the upper limit of production cross section.