Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shimada, Asako; Tsukahara, Takehiko*; Nomura, Masao*; Takeda, Seiji
no journal, ,
Because of the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), a large area of eastern Japan was contaminated by radiocesium. There are many old nuclear facilities in the area. When the old nuclear facilities will be decommissioned in three decades, the radioactive level of radiocesium from 1F would be more than clearance level. When radiocesium would be detected at the completion of their decommissioning in the site, estimation of the origin of which is from background originated 1F and fallout of atmospheric nuclear test or from decommissioned facilities will be important. Therefore, soils of 3 sites were collected by using U8 containers and by core boring, and  Cs radioactivity,
Cs radioactivity,  Cs/
Cs/ Cs radioactivity ratios,
Cs radioactivity ratios,  Cs/
Cs/ Cs isotope ratios were determined. Separation method of Cs from soil materials were developed based on the reported methods. The
Cs isotope ratios were determined. Separation method of Cs from soil materials were developed based on the reported methods. The  Cs radioactivity concentrations were varied in not only between sites but also in the same site, however,
Cs radioactivity concentrations were varied in not only between sites but also in the same site, however,  Cs/
Cs/ Cs radioactivity ratio was approximately constant in all sites. In case of highly contaminated soils,
Cs radioactivity ratio was approximately constant in all sites. In case of highly contaminated soils,  Cs/
Cs/ Cs isotope ratio was almost comparable to that for the soil collected at near the 1F. On the other hand, in case of lower contaminated soils,
Cs isotope ratio was almost comparable to that for the soil collected at near the 1F. On the other hand, in case of lower contaminated soils,  Cs/
Cs/ Cs isotope ratio was slightly higher than that for soil collected at near the 1F. It is possibly that fallout before the 1F accident contained
Cs isotope ratio was slightly higher than that for soil collected at near the 1F. It is possibly that fallout before the 1F accident contained  Cs to increase the
Cs to increase the  Cs/
Cs/ Cs isotope ratio. In the presentation, vertical distribution will also be discussed.
Cs isotope ratio. In the presentation, vertical distribution will also be discussed.
 Sr in environmental samples at the attogram-level by accelerator mass spectrometry
Sr in environmental samples at the attogram-level by accelerator mass spectrometryMartschini, M.*; Honda, Maki; Merchel, S.*; Winkler, S.*; Golser, R.*
no journal, ,
The quantitative analysis of  Sr is cumbersome and time-consuming because it is a pure
Sr is cumbersome and time-consuming because it is a pure  -ray emitter. The detection limit of
-ray emitter. The detection limit of  Sr by conventional accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) methods is comparable to the typical detection limit of 3 mBq for
Sr by conventional accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) methods is comparable to the typical detection limit of 3 mBq for  -ray detection methods, mainly due to the interference of the isobaric
-ray detection methods, mainly due to the interference of the isobaric  Zr. The worldwide unique Ion Laser Interaction Mass Spectrometry (ILIAMS), performed at the University of Vienna, effectively removes
Zr. The worldwide unique Ion Laser Interaction Mass Spectrometry (ILIAMS), performed at the University of Vienna, effectively removes  Zr with a laser and reaction gases. Therefore, the detection limits of
Zr with a laser and reaction gases. Therefore, the detection limits of  Sr is superior (
Sr is superior ( 0.1 mBq) to conventional AMS systems not equipped with such an ion-laser interaction isobaric removal system. In this study,
0.1 mBq) to conventional AMS systems not equipped with such an ion-laser interaction isobaric removal system. In this study,  Sr analysis in coral samples etc., an environmental sample under extreme conditions (e.g. low concentrations of
Sr analysis in coral samples etc., an environmental sample under extreme conditions (e.g. low concentrations of  Bq/g and limited sample volumes of grams), was tried. To lower the detection limit
Bq/g and limited sample volumes of grams), was tried. To lower the detection limit  0.1 mBq, Sr was purified (Sr carrier) from old age coral with almost no
0.1 mBq, Sr was purified (Sr carrier) from old age coral with almost no  Sr contamination from atmospheric nuclear tests, chemical separation of environmental samples were conducted, and
Sr contamination from atmospheric nuclear tests, chemical separation of environmental samples were conducted, and  Sr was measured by AMS. The results showed that the detection limit of
Sr was measured by AMS. The results showed that the detection limit of  Sr achieved in the analysis was
Sr achieved in the analysis was  0.03 mBq (
0.03 mBq ( Sr/Sr
Sr/Sr  5
5 10
10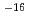 , 1/100 of the
, 1/100 of the  -ray detection methods). The detection limit achieved in this study corresponds to 2 ag of
-ray detection methods). The detection limit achieved in this study corresponds to 2 ag of  Sr in 1 mg of Sr target. The latest results of highly sensitive
Sr in 1 mg of Sr target. The latest results of highly sensitive  Sr analysis in small amounts of general environmental samples (coral, seawater, etc.) are mainly presented.
Sr analysis in small amounts of general environmental samples (coral, seawater, etc.) are mainly presented.
Sakoda, Akihiro; Ishimori, Yuu; Hasan, Md. M.*; Jin, Q.*; Kanzaki, Norie; Iimoto, Takeshi*
no journal, ,
Building materials such as brick and concrete are known to be one of indoor radon (Rn-222) and thoron (Rn-220) sources. Most radon and thoron exhalation studies have been based on laboratory tests using pieces and blocks of such materials. To elucidate how laboratory findings can be used in a real-world environment, we conducted intensive in-situ radon and thoron exhalation tests on interior walls, with different structure types of an apartment (i.e., solid wall and cavity wall) for over a year. This study provides an insight into parameterizing a radon source input in modeling the spatial and temporal dynamics of indoor radon and thoron air concentrations.
Mori, Airi; Johansen, M. P.*; Takahara, Shogo
no journal, ,
Johansen, M. P.*; Carpenter, J. G.*; Charmasson, S.*; Gwynn, J. P.*; McGinnity, P.*; Mori, Airi; Orr, B.*; Simon-Cornu, M.*; Osvath, I.*
no journal, ,