Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Abe, Hiroshi; Shimomura, Takuya; Tokuhira, Shinnosuke*; Shimada, Yukihiro*; Takenaka, Yusuke*; Furuyama, Yuta*; Nishimura, Akihiko; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Oshima, Takeshi
Proceedings of 7th International Congress on Laser Advanced Materials Processing (LAMP 2015) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2015/08
A short pulse laser (the nanosecond and femtosecond) was applied to hydrogen absorbing alloys surface layer, and a surface modification experiment was put into effective to aim at improvement of hydrogen adsorption functionally. It was investigated about correlation between an initial hydrogen absorption reaction rate of hydrogen alloys and a laser irradiation in this research. The laser irradiation condition was done with pulse width 100 fsec and energy 0.2 - 3.4 mJ/pulse. It blazed down on hydrogen absorbing alloys (LaNi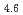 Al
Al ) and changed local order in the surface. As a result, the initial hydrogen absorption reaction rate was 1.5 - 3.0 times as fast as a irradiated sample, and the result and laser irradiated sample found out that a hydrogen absorption function improves. A laser irradiation can conclude to be effective in surface modification of the hydrogen storage materials.
) and changed local order in the surface. As a result, the initial hydrogen absorption reaction rate was 1.5 - 3.0 times as fast as a irradiated sample, and the result and laser irradiated sample found out that a hydrogen absorption function improves. A laser irradiation can conclude to be effective in surface modification of the hydrogen storage materials.
Iwai, Hiroki; Nakamura, Yasuyuki; Mizui, Hiroyuki; Sano, Kazuya; Morishita, Yoshitsugu
Proceedings of 7th International Congress on Laser Advanced Materials Processing (LAMP 2015) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2015/08
The reactor of FUGEN is characterized by its tube-cluster construction that contains 224 channels arranging both the pressure and the calandria tubes coaxially in each channel. And the periphery part of the core has the laminated structure of up to 150 mm thickness of carbon steel for radiation shielding. Method for dismantling the reactor core is also being studied with considering processes of dismantlement by remote-handling devices under the water for the radiation shielding. In order to shorten the term of the reactor dismantlement work and reduce the secondary waste, some cutting tests and literature research for various cutting methods had been carried out. As the result, the laser cutting method, which has feature of the narrow cutting kerf and the fast cutting velocity, was mainly selected for dismantling the reactor. In this presentation, current activities of FUGEN decommissioning and R&D of laser cutting tests are introduced.
Terada, Takaya; Kitsunai, Daisuke; Nishimura, Akihiko; Ito, Fuyumi*
no journal, ,
Shimomura, Takuya; Nishimura, Akihiko; Terada, Takaya; Takenaka, Yusuke*; Daido, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English