Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Noda, Yohei; Kumada, Takayuki; Hashimoto, Takeji; Koizumi, Satoshi
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(17), p.2572 - 2574, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:35.37(Physics, Condensed Matter)We polarized hydrogen nuclear spins of polyethylene samples, doped with organic radical (TEMPO), by use of a dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) technique, in which the sample was irradiated by microwave (94 GHz) at 3.3 Tesla and 1.4 K. For the samples under the DNP state, we conducted small-angle scattering experiments with polarized neutrons. For the sample with low crystallinity (polarization: 32%), the shift of the incoherent scattering level was observed. For the sample with high crystallinity (polarization: 23%), the enhancement of the coherent scattering due to the crystalline structure was observed.
 O
O (
( = Ho, Er)
= Ho, Er)Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Fukunaga, Mamoru*; Nishihata, Keisuke*; Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Noda, Yukio*; Tokura, Yoshinori*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(17), p.2513 - 2516, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:24.59(Physics, Condensed Matter)Maruyama, Ryuji; Hino, Masahiro*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Achiwa, Norio*; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(17), p.2594 - 2599, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:15.86(Physics, Condensed Matter)Neutron resonance spin echo (NRSE) is one of the most useful techniques for quasi-elastic scattering with high energy resolution. The path length variation due to the beam divergence has to be corrected in high resolution NRSE measurement because it gives the limit in the energy resolution. A neutron focusing technique using neutron supermirrors is effective to overcome this problem. When a cylindrical shaped neutron supermirror placed in the center of the flight path with a pair of RSFs has the object and the image plane corresponding to the each coil plane of the first and the second RSF, the path length difference can be corrected for the neutron beam with large divergent angle, which leads to the realization of high intensity as well as high resolution in NRSE measurement. In this study, the correction method of the beam divergence with a cylindrical shaped supermirror and its experimental results are discussed.
 lattice antiferromagnet KFe
lattice antiferromagnet KFe (OH)
(OH) (SO
(SO )
)
Matan, K.*; Helton, J. S.*; Grohol, D.*; Nocera, D. G.*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Lee, Y. S.*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(17), p.2529 - 2531, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.32(Physics, Condensed Matter) N
N nano-particles for magnetic recording tape
nano-particles for magnetic recording tapeOku, Takayuki; Kikuchi, Takayuki*; Shinohara, Takenao; Suzuki, Junichi; Ishii, Yuya*; Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Sasaki, Yuji*; Kishimoto, Mikio*; Yokoyama, Makoto*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(17), p.2575 - 2577, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:35.37(Physics, Condensed Matter)The microscopic determination of the magnetic moment in the Fe N
N nano-particles by means of polarized neutron diffraction experiment is reported. These particles had been developed by industrial researchers for use in high-density magnetic tape, and the particles were coated with proprietary nonmagnetic material. Polarized neutrons were used to measure the magnetic-nuclear interference contributions and, given the known crystal structure, the detailed analysis allowed to determine the magnetic moments on the different Fe-sites. The future perspectives of this technique using the high-intensity powder instrument in combination with pulsed magnetic high-field at J-PARC including the possible industrial application is discussed.
nano-particles by means of polarized neutron diffraction experiment is reported. These particles had been developed by industrial researchers for use in high-density magnetic tape, and the particles were coated with proprietary nonmagnetic material. Polarized neutrons were used to measure the magnetic-nuclear interference contributions and, given the known crystal structure, the detailed analysis allowed to determine the magnetic moments on the different Fe-sites. The future perspectives of this technique using the high-intensity powder instrument in combination with pulsed magnetic high-field at J-PARC including the possible industrial application is discussed.
Kumada, Takayuki; Noda, Yohei; Hashimoto, Takeji; Koizumi, Satoshi
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(17), p.2637 - 2639, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:54.68(Physics, Condensed Matter)We have developed dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) system for SANS-J-II at the JRR-3 atomic research reactor at Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Our system is composed of superconducting magnet (3.3 Tesla), Gunn oscillator as a microwave source (94 GHz), and cryostat (1.2 K). We succeeded in polarizing polyethylene sample up to 0.32 and observing effects of polarization on SANS profile. We plan to use the DNP and SANS system in order to determine structure factors of multi-component systems.
Yamazaki, Dai; Maruyama, Ryuji; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Takai, Hiroyuki*; Yamamura, Kazuya*
no journal, ,
 B sintered magnets
B sintered magnetsTakeda, Masayasu; Suzuki, Junichi; Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Akiya, Takahiro*; Kato, Hiroaki*; Sagawa, Masato*; Koyama, Keiichi*
no journal, ,
Nd-Fe-B magnets are now widely used because of the highest BH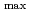 of them in the commercially available magnets. At the present, Dy, which is one of the rare metals, has to be added to maintain the coercivity especially in the operational temperatures higher than the room temperature. The key to achieve the Dy-free Nd-Fe-B magnets is how to control the grain size and the structure near the grain boundary. We have performed the small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) measurements of the sintered Nd-Fe-
of them in the commercially available magnets. At the present, Dy, which is one of the rare metals, has to be added to maintain the coercivity especially in the operational temperatures higher than the room temperature. The key to achieve the Dy-free Nd-Fe-B magnets is how to control the grain size and the structure near the grain boundary. We have performed the small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) measurements of the sintered Nd-Fe- B magnets using unpolarized and polarized neutrons to obtain the averaged internal structures of samples with the different coercivity introduced by applying different high magnetic fields during the annealing. We found that inhomogeneity was induced by the magnetic fields applied parallel to
B magnets using unpolarized and polarized neutrons to obtain the averaged internal structures of samples with the different coercivity introduced by applying different high magnetic fields during the annealing. We found that inhomogeneity was induced by the magnetic fields applied parallel to 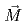 . The relation between the inhomogeneity and the coercivity force is unclear at the moment, but we will present possible interpretation.
. The relation between the inhomogeneity and the coercivity force is unclear at the moment, but we will present possible interpretation.
 studied with spherical neutron polarimetry
studied with spherical neutron polarimetryKajimoto, Ryoichi; Matsuda, Masaaki; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Mitsui, Yukari*; Yoshizawa, Hideki*
no journal, ,
 Sr
Sr CuO
CuO
Matsuda, Masaaki; Fujita, Masaki*; Takeda, Masayasu; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
no journal, ,
Polarized neutron scattering is an important tool to clarify the existence of chirality. Furthermore, it also gives useful information on magnetic anisotropy of the spin fluctuations in the diagonal incommensurate phase. We performed polarized neutron scattering experiments in lightly-doped La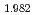 Sr
Sr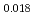 CuO
CuO . The results showed that the chiral terms are almost negligible, indicating that there is no chirality or that the two chirality domains are equally populated. The diagonal terms originate from the magnetic anisotropy in the antiferromagnetically ordered phase. It was found that the spins lie almost in the CuO
. The results showed that the chiral terms are almost negligible, indicating that there is no chirality or that the two chirality domains are equally populated. The diagonal terms originate from the magnetic anisotropy in the antiferromagnetically ordered phase. It was found that the spins lie almost in the CuO plane although a finite out-of-plane component was observed. It was also found that there exists a small anisotropy in the CuO
plane although a finite out-of-plane component was observed. It was also found that there exists a small anisotropy in the CuO plane and the spin component is larger along the b axis, suggesting the remnant of anisotropy in pure La
plane and the spin component is larger along the b axis, suggesting the remnant of anisotropy in pure La CuO
CuO .
.
Hiraka, Haruhiro*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*
no journal, ,