Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Kataoka, Mikio*; Jochi, Yasumasa*; Kitao, Akio*; Shibata, Kaoru; Tokuhisa, Atsushi*; Tsukushi, Itaru*; Go, Nobuhiro
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(2), p.871 - 873, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:53.13(Physics, Condensed Matter)The boson peak of a protein was examined in relation to hydration using staphylococcal nuclease. Although the boson peak is commonly observed in synthetic polymers, glassy materials and amorphous materials, the origin of the boson peak is not fully understood. The motions that contribute to the peak are harmonic vibrations. Upon hydration the peak frequency shifts to a higher frequency and the effective force constant of the vibration increases at low temperatures, suggesting that the protein energy surface is modified. Hydration of the protein leads to a more rugged surface and the vibrational motions are trapped within the local minimum at cryogenic temperatures. The origin of the protein boson peak may be related to this rugged energy surface.
Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*; Kuroki, Ryota
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(2), p.1049 - 1051, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)Our group has two single crystal neutron diffractometers, called BIX-3 and BIX-4, in the JRR-3 reactor-hall at JAERI. Although these diffractometers were designed for bio-macromolecules, these can be used for diffraction measurement of small organic molecules by changing the wavelength of incident neutron beam from 2.9  to 1.5
to 1.5  . Since both BIX-3 and 4 has a large neutron imaging plate as a detector, they can efficiently collect the Bragg reflections of organic crystal which has relatively large unit cell, the longest value of cell dimension is 50
. Since both BIX-3 and 4 has a large neutron imaging plate as a detector, they can efficiently collect the Bragg reflections of organic crystal which has relatively large unit cell, the longest value of cell dimension is 50  and typical value is 20
and typical value is 20  30
30  . In typical measurement, the crystal size is 1
. In typical measurement, the crystal size is 1  3 mm
3 mm , the measurement time is 1
, the measurement time is 1  2 weeks and the minimum
2 weeks and the minimum 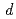 -value is 0.8
-value is 0.8  . In addition, the large imaging plate also makes the efficient measurements of fiber diffraction possible. In this presentation, we introduce the performance of BIX-3 and 4 as diffractometers for small organic molecules.
. In addition, the large imaging plate also makes the efficient measurements of fiber diffraction possible. In this presentation, we introduce the performance of BIX-3 and 4 as diffractometers for small organic molecules.
 Sb
Sb
Kuwahara, Keitaro*; Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Kogi, Masafumi*; Kaneko, Koji; Metoki, Naoto; Raymond, S.*; M asson, M.-A.*; Flouquet, J.*; Sugawara, Hitoshi*; Aoki, Yuji*; et al.
asson, M.-A.*; Flouquet, J.*; Sugawara, Hitoshi*; Aoki, Yuji*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(Part 1), p.82 - 84, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.17(Physics, Condensed Matter)We report inelastic neutron scattering experiments performed to investigate the low energy magnetic excitations on single crystals of the heavy-fermion superconductor PrOs Sb
Sb . The observed excitation clearly softens at a wave vector Q=(1,0,0), which is the same as the modulation vector of the field-induced antiferro-quadrupolar ordering, and its intensity at Q=(1,0,0) is smaller than that around the zone center. This result directly evidences that this excitonic behavior is derived mainly from nonmagnetic quadrupolar interactions. Furthermore, the narrowing of the linewidths of the excitations below the superconducting transition temperature indicates the close connection between the superconductivity and the excitons.
. The observed excitation clearly softens at a wave vector Q=(1,0,0), which is the same as the modulation vector of the field-induced antiferro-quadrupolar ordering, and its intensity at Q=(1,0,0) is smaller than that around the zone center. This result directly evidences that this excitonic behavior is derived mainly from nonmagnetic quadrupolar interactions. Furthermore, the narrowing of the linewidths of the excitations below the superconducting transition temperature indicates the close connection between the superconductivity and the excitons.
Oku, Takayuki; Yamada, Satoru; Sasao, Hajime*; Suzuki, Junichi; Shinohara, Takenao*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ikeda, Kazuaki*; Tsuzaki, Tsuyoshi*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Furusaka, Michihiro*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(2), p.1225 - 1228, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:43.33(Physics, Condensed Matter)We have developed a magnetic neutron lens based on an extended Halbach-type permanent sextupole magnet with magnet pieces of NEOMAX-44H, -35EH and high saturation magnetization material, permendule. The aperture size of the magnet is 35 mm in diameter and the magnet length is 2,400 mm. The magnet generates a sextupole magnetic field 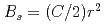 with a gradient coefficient
with a gradient coefficient 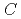 =10,600 T/m
=10,600 T/m inside the aperture, where
inside the aperture, where  is a distance from the magnet center axis. To prevent neutrons from hitting and reflecting at the inner surface of the magnet, the surface is covered with cadmium (Cd) sheets and also Cd pinhole slits with size of 30 mm in diameter are positioned in series inside the magnet aperture, resulting in the effective diameter of 30 mm. The neutron focusing property of the magnet is investigated by using pulsed polarized neutrons. The obtained results are discussed with the precise simulation results. Its application to the focusing-geometry small-angle neutron scattering experiments is also discussed.
is a distance from the magnet center axis. To prevent neutrons from hitting and reflecting at the inner surface of the magnet, the surface is covered with cadmium (Cd) sheets and also Cd pinhole slits with size of 30 mm in diameter are positioned in series inside the magnet aperture, resulting in the effective diameter of 30 mm. The neutron focusing property of the magnet is investigated by using pulsed polarized neutrons. The obtained results are discussed with the precise simulation results. Its application to the focusing-geometry small-angle neutron scattering experiments is also discussed.
Miyamoto, Nobuyoshi; Yamauchi, Kazuhiro*; Hasegawa, Hirokazu*; Hashimoto, Takeji; Koizumi, Satoshi
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(1), p.752 - 755, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:26.29(Physics, Condensed Matter)The living anionic polymerization processes of isoprene and styrene in benzene-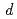
 initiated by
initiated by 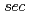 -butyl lithium were studied by in-situ small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) and time-resolved molecular weight (
-butyl lithium were studied by in-situ small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) and time-resolved molecular weight (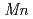 ) measurement by gel permeation chromatography (GPC). In the course of the polymerization of isoprene (
) measurement by gel permeation chromatography (GPC). In the course of the polymerization of isoprene (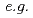
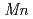 = 5300 g mol
= 5300 g mol ), the small angle scattering increased with the reaction time
), the small angle scattering increased with the reaction time 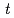 . The molecular weight and its time-change, determined by GPC, is crucial to quantitatively analyze time-resolved SANS measurements; we were able to determine association number
. The molecular weight and its time-change, determined by GPC, is crucial to quantitatively analyze time-resolved SANS measurements; we were able to determine association number 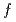 uniquely as a function of
uniquely as a function of 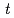 . Upon termination of the living polymerization, SANS profile greatly changed: the scattering intensity in the intermediate
. Upon termination of the living polymerization, SANS profile greatly changed: the scattering intensity in the intermediate 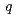 -region (0.2
-region (0.2 
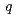
 1.0 nm
1.0 nm ) remarkably decreased, indicating disaggregation of the living ends upon the termination. Also, strong upturn in the low-q region appeared (q
) remarkably decreased, indicating disaggregation of the living ends upon the termination. Also, strong upturn in the low-q region appeared (q  0.1 nm
0.1 nm ) due to the generation of colloidal LiOH or LiO(C
) due to the generation of colloidal LiOH or LiO(C H
H ), which are insoluble in benzene. Detailed data and analyses of isoprene and styrene systems will be given in the presentation.
), which are insoluble in benzene. Detailed data and analyses of isoprene and styrene systems will be given in the presentation.

Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Goto, Kenji*; Osawa, Akira*; Fujisawa, Masashi*; Tanaka, Hidekazu*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(Part 1), p.450 - 452, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.16(Physics, Condensed Matter)KCuCl and TlCuCl
and TlCuCl are singlet ground state systems with excitation gap of 31K and 7.7K, respectively. The origin of the spin gap is the strong antiferromagnetic spin dimer of the chemical Cu
are singlet ground state systems with excitation gap of 31K and 7.7K, respectively. The origin of the spin gap is the strong antiferromagnetic spin dimer of the chemical Cu Cl
Cl unit. These spin dimers are weakly coupled three dimensionally via non-frustrating inter dimer exchanges. The magnetization measurements under applied hydrostatic pressure show the existence of the magnetic order above certain critical pressure Pc=8.8 kbar and 0.42 kbar, respectively. We report on the elastic neutron scattering results of the pressure induced magnetic ordering in these quantum systems. The observed magnetic structures and the possible role of the spin-lattice coupling in the spin reorientation in TlCuCl3 under pressure will be discussed.
unit. These spin dimers are weakly coupled three dimensionally via non-frustrating inter dimer exchanges. The magnetization measurements under applied hydrostatic pressure show the existence of the magnetic order above certain critical pressure Pc=8.8 kbar and 0.42 kbar, respectively. We report on the elastic neutron scattering results of the pressure induced magnetic ordering in these quantum systems. The observed magnetic structures and the possible role of the spin-lattice coupling in the spin reorientation in TlCuCl3 under pressure will be discussed.
Harjo, S.; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Torii, Shuki; Ishigaki, Toru; Yonemura, Masao*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(Part 2), p.1025 - 1028, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:21.89(Physics, Condensed Matter)Ibaraki Prefecture Materials Design Diffractometer of J-PARC is a time-of-flight neutron powder diffractometer with the resolution as good as 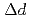 /
/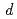 = 0.16 % (almost constant value) for
= 0.16 % (almost constant value) for 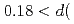
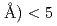 (L1 of 26.5 m). Since this diffractometer has many detectors covering wide 2
(L1 of 26.5 m). Since this diffractometer has many detectors covering wide 2 range, measurements with wide
range, measurements with wide 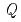 range,
range, 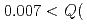
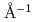
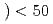 , i.e., PDF analysis and small angle scattering can also be performed. Designing of neutron guide is therefore very important to enhance the performances mentioned above without sacrificing beam intensity. Non-parallel guides including elliptical ones have been compared with a linear-straight guide using the McStas simulation. The elliptical guide having the exit focal points away behind the sample position is available to increase the neutron flux at the sample but give a slight lowering of the instrumental resolution. This elliptical guide gives also Garland peaks at short wavelengths that may give large ambiguities in powder diffraction measurements. Therefore, the linear-straight guide is considered as the best choice for this instrument to keep a good resolution and also a relatively high flux.
, i.e., PDF analysis and small angle scattering can also be performed. Designing of neutron guide is therefore very important to enhance the performances mentioned above without sacrificing beam intensity. Non-parallel guides including elliptical ones have been compared with a linear-straight guide using the McStas simulation. The elliptical guide having the exit focal points away behind the sample position is available to increase the neutron flux at the sample but give a slight lowering of the instrumental resolution. This elliptical guide gives also Garland peaks at short wavelengths that may give large ambiguities in powder diffraction measurements. Therefore, the linear-straight guide is considered as the best choice for this instrument to keep a good resolution and also a relatively high flux.
Takahashi, Nobuaki; Kanaya, Toshiji*; Nishida, Koji*; Takahashi, Yoshiaki*; Arai, Masatoshi
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(1), p.810 - 813, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:30.26(Physics, Condensed Matter)We have studied shear flow effects on physical gelation processes of poly(vinyl alcohol) solutions in a mixture of deuterated dimethyl sulfoxide and heavy water using time-resolved 2D-SANS technique with a rheological setup. Steady shear flow was applied on the sample solution after quenching from 100  C to 25
C to 25  C, and the isothermal measurements were performed. The observed two-dimensional scattering patterns under the shear flow were isotropic while the growth rate of the scattering intensity was affected. It has been revealed in a previous report that the gelation of the solution was caused through crystallization between polymer chains to form the network. Hence, focusing on the scattering intensity from the crystallites, we have evaluated the crystallization rate. It was found that the crystallization rate was accelerated in a low shear rate region (shear rate is smaller than 5 sec
C, and the isothermal measurements were performed. The observed two-dimensional scattering patterns under the shear flow were isotropic while the growth rate of the scattering intensity was affected. It has been revealed in a previous report that the gelation of the solution was caused through crystallization between polymer chains to form the network. Hence, focusing on the scattering intensity from the crystallites, we have evaluated the crystallization rate. It was found that the crystallization rate was accelerated in a low shear rate region (shear rate is smaller than 5 sec ) and decreased with increasing the shear rate in a high rate region (bigger than 5 sec
) and decreased with increasing the shear rate in a high rate region (bigger than 5 sec ) after a maximum at 5 sec
) after a maximum at 5 sec . The results suggest that the local orientation of flexible polymer chains due to the shear flow assist crystal nucleation in the low shear rate region while the once-formed crystallites are destroyed by the shear in the high shear rate region.
. The results suggest that the local orientation of flexible polymer chains due to the shear flow assist crystal nucleation in the low shear rate region while the once-formed crystallites are destroyed by the shear in the high shear rate region.
Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Iwase, Hiroki; Arai, Masatoshi; Kartini, E.*; Russina, M.*; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Taylor, J. W.*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(1), p.552 - 554, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.17(Physics, Condensed Matter)The mechanism of high ionic conductivity in superionic glass constitute an unsolved problem in the field of science.Here we performed inelastic neutron scattering measurements of superionic glass system (AgI) (Ag
(Ag S)
S) (AgPO
(AgPO )
)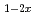 by using MARI spectrometer at ISIS, and found that the
by using MARI spectrometer at ISIS, and found that the  -dependence of inelastic intensity in the energy region from 1 to 3 meV of superionic phase glass shows an excess intensity above
-dependence of inelastic intensity in the energy region from 1 to 3 meV of superionic phase glass shows an excess intensity above  =1.8
=1.8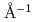 compared with insulator phase one. Similar phenomena were also observed in another superionic glass (AgI)
compared with insulator phase one. Similar phenomena were also observed in another superionic glass (AgI) (AgPO
(AgPO )
) by using NEAT spectrometer at HMI with high resolution measurement. These results clearly suggest peculiar low energy vibrational excitations should be universal features of superionic glass.
by using NEAT spectrometer at HMI with high resolution measurement. These results clearly suggest peculiar low energy vibrational excitations should be universal features of superionic glass.
Fukazawa, Hiroshi; Hoshikawa, Akinori; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Yamaguchi, Yasuo*; Igawa, Naoki; Ishii, Yoshinobu
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(1), p.113 - 115, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.17(Physics, Condensed Matter)We measured neutron diffraction of powdered samples of ice containing impurities (e.g., potassium deuteroxide, sodium deuteroxide) to analyze the formation of ice XI, a deuterium-ordered phase of ice, from ice Ih, a disordered phase. We found that the diffraction profiles changed with time for several days at 62-70 K, which are below the transition temperature 
 = 76 K. From the Rietveld analysis of the diffraction profiles, we determined the change of the structural parameters with the phase transition. The structural analysis provides direct evidence for the existence of deuteron-ordered arrangements in ice containing impurities below
= 76 K. From the Rietveld analysis of the diffraction profiles, we determined the change of the structural parameters with the phase transition. The structural analysis provides direct evidence for the existence of deuteron-ordered arrangements in ice containing impurities below 
 . On the basis of the Rietveld analysis, we obtained the mass fraction (
. On the basis of the Rietveld analysis, we obtained the mass fraction ( ) of ice XI as functions of time and temperature. We report a structural observation for the nucleation and growth of ice XI under various conditions (such as temperature variations and impurity effects), which leads to understand whether or not f reaches unity at an infinite annealing time.
) of ice XI as functions of time and temperature. We report a structural observation for the nucleation and growth of ice XI under various conditions (such as temperature variations and impurity effects), which leads to understand whether or not f reaches unity at an infinite annealing time.
Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Sato, Taku*; Nakajima, Kenji; Arai, Masatoshi
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(2), p.1236 - 1239, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:40.47(Physics, Condensed Matter)Performance of a neutron guide has been studied for the Cold Neutron Double-Chopper Spectrometer (CNDCS) proposed for the spallation neutron source at J-PARC. This spectrometer is dedicated to inelastic neutron scattering studies in vast research fields in an energy range of 

 80 meV. In order to detect weak inelastic signals, increasing neutron flux on sample with suppressing background at detector is very important. Installing a neutron guide is a well-known solution to these problems, because it can deliver much more neutrons to sample, and it can also cut off unwanted fast neutrons when installed in a curved layout. The performance of a neutron guide is much affected by its geometry. We have studied efficiency of the beam transport by a supermirror-coated guide designed for the CNDCS with conventional geometries such as straight, curved and tapered, as well as with advanced geometries such as ballistic, parabolic and elliptical. Energy dependence of gain in intensity, and beam distributions in space and angle obtained by Monte Carlo simulation will be discussed.
80 meV. In order to detect weak inelastic signals, increasing neutron flux on sample with suppressing background at detector is very important. Installing a neutron guide is a well-known solution to these problems, because it can deliver much more neutrons to sample, and it can also cut off unwanted fast neutrons when installed in a curved layout. The performance of a neutron guide is much affected by its geometry. We have studied efficiency of the beam transport by a supermirror-coated guide designed for the CNDCS with conventional geometries such as straight, curved and tapered, as well as with advanced geometries such as ballistic, parabolic and elliptical. Energy dependence of gain in intensity, and beam distributions in space and angle obtained by Monte Carlo simulation will be discussed.
Motokawa, Ryuhei; Koizumi, Satoshi; Hashimoto, Takeji; Nakahira, Takayuki*; Annaka, Masahiko*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(1), p.780 - 782, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.16(Physics, Condensed Matter)A soap-free emulsion polymerization method was employed in an aqueous medium in order to synthesize an amphiphilic block copolymer of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-block-poly(ethylene glycol) (NE), where Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPA) was polymerized from the radically activated chain ends of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG). As the polymerization proceeds, PNIPA block chains form micelle cores stabilized by PEG brush chains emanating therefrom. When this polymerization was employed at temperatures equal to or higher than 34 C, radical polymerization proceeds living-likely. To elucidate origins of the living nature, we carried out time-resolved ultra-small- and small-angle neutron scattering (USANS and SANS). USANS and SANS revealed that (1) from 15 to 60
C, radical polymerization proceeds living-likely. To elucidate origins of the living nature, we carried out time-resolved ultra-small- and small-angle neutron scattering (USANS and SANS). USANS and SANS revealed that (1) from 15 to 60 C, polymerized NE forms micelle in the solution when molecular weight reaches to a critical molecular weight for micelle formation, and (2) as the temperature increases from 34
C, polymerized NE forms micelle in the solution when molecular weight reaches to a critical molecular weight for micelle formation, and (2) as the temperature increases from 34 C, water and monomer content in the micelle core becomes less due to a lower critical solution temperature of PNIPA. These results indicate that low diffusivity of chain end radicals, compartmentalized in the solid-like micelle core, plays an important role to lead a quasi-living polymerization behavior.
C, water and monomer content in the micelle core becomes less due to a lower critical solution temperature of PNIPA. These results indicate that low diffusivity of chain end radicals, compartmentalized in the solid-like micelle core, plays an important role to lead a quasi-living polymerization behavior.
Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Koizumi, Satoshi; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kumada, Takayuki; Aizawa, Kazuya; Hashimoto, Takeji
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(2), p.1190 - 1193, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:55.13(Physics, Condensed Matter)A new tandem analyzing system was introduced on Bonse-Hart ultra-small angle neutron scattering (USANS) spectrometer. In the normal setup of USANS it consumes a considerable time to take a scattering profile of whole q-range (2 10
10 nm
nm
 q
q  7
7 10
10 nm
nm , where q denotes magnitude of scattering vector) due to the step scan system, in which the scattering waves from the sample and having different q are measured step by step. To overcome this difficulty two analyzer channel-cut silicon perfect crystals were settled in tandem and each of them diffracted the scattering wave of different q. In consequence, a simultaneous detection at two different q positions was realized and the measurement time was reduced to half.
, where q denotes magnitude of scattering vector) due to the step scan system, in which the scattering waves from the sample and having different q are measured step by step. To overcome this difficulty two analyzer channel-cut silicon perfect crystals were settled in tandem and each of them diffracted the scattering wave of different q. In consequence, a simultaneous detection at two different q positions was realized and the measurement time was reduced to half.
Tanaka, Hirokazu; Yamauchi, Kazuhiro*; Hasegawa, Hirokazu*; Miyamoto, Nobuyoshi; Koizumi, Satoshi; Hashimoto, Takeji
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(1), p.742 - 744, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:67.22(Physics, Condensed Matter)Polystyrene-block-polyisoprene were synthesized via living anionic polymerization. We have performed in-situ and real-time SANS, GPC, and UV-vis spectroscopy of the polymerization process in order to reveal the structure formation process of the block copolymers, especially the associated structures. From GPC and UV-vs spectroscopy. It is found that isoprene monomers are preferentially polymerized, and after that, styrene monomers are to be polymerized. It is also found from SANS measurements, that living polymers in the reaction solution formed the associated structures during the polymerization process. Moerover, it is also strongly suggested that in the earlier stage of polymerization, living polymers are mainly composed of polyisoprene with association number of 4, and once styrene monomers are polymerized, the association number drastically begins to decrease from 4 to 2.
Kanaya, Toshiji*; Takahashi, Nobuaki; Nishida, Koji*; Seto, Hideki*; Nagao, Michihiro*; Takeda, Takayoshi*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(1), p.676 - 681, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:50.83(Physics, Condensed Matter)We report neutron spin-echo measurements on three types of poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) gels. The first is PVA gel in a mixture of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and water with volume ratio 60/40, the second is PVA gel in an aqueous borax solution and the third is chemically cross-linked PVA gel. The observed normalized intermediate scattering functions I(Q,t)/I(Q,0) were very different among them. The I(Q,t)/I(Q,0) of the first and third gels showed a non-decaying component in addition to a decaying component, but the second one did not have the non-decaying one. This clearly indicates that the fluctuations in the first and third PVA gels consist of static and dynamic fluctuations whereas the second PVA gel does include only the dynamic fluctuations. The dynamic and static fluctuations of the PVA gels were analyzed in terms of a restricted motion in the gel network and the Zimm motion, respectively.
Kamiyama, Takashi*; Seki, Naoki*; Iwasa, Hirokatsu*; Uchida, Tsutomu*; Ebinuma, Takao*; Narita, Hideo*; Igawa, Naoki; Ishii, Yoshinobu; Bennington, S. M.*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(1), p.202 - 204, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:34.09(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Hirokazu; Koizumi, Satoshi; Hashimoto, Takeji; Kurosaki, Kazuhiro*; Omae, Masashi*; Kobayashi, Shiro*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(1), p.814 - 817, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.17(Physics, Condensed Matter)We have investigated a self-assembling process of cellulose artificially synthesized via enzymatic polymerization by means of in-situ and time-resolved small-angle neutron scattering (SANS). The results elucidated the following: (1) cellulose molecules were synthesized at a special reaction site of the enzyme (cellulase) located on or near the smooth surface of the self-assembled enzymes formed in the reaction medium; (2) the synthesized molecules associated themselves via diffusion-limited aggregation (DLA) and crystallized into fibrils and (3) the fibrils formed the aggregates, which had the surface fractal dimension D increasing from 2 to 2.3 with the reaction time, on the smooth surface of the enzyme aggregates.
increasing from 2 to 2.3 with the reaction time, on the smooth surface of the enzyme aggregates.
Maruyama, Ryuji; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Hino, Masahiro*; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(2), p.1256 - 1258, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:71.28(Physics, Condensed Matter)Neutron supermirror has become an important device to transport, bending and focusing a neutron beam. We have developed it using ion beam sputtering (IBS) instrument since it enables us to produce good quality layers with high density and small grain size. We have also investigated ion-polishing technique, which suppresses the interface roughness of multilayers. We have now installed new IBS instrument with effective deposit area of 500 mm in diameter for the realization of supermirror guide and bender with large effective critical angle. In this presentation, the performance of the supermirrors fabricated with it and the future development of neutron optical devices using supermirrors will be discussed.
 Sb
Sb Te
Te and GeBi
and GeBi Te
Te
Shamoto, Shinichi; Yamada, Noboru*; Matsunaga, Toshiyuki*; Proffen, T.*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(1), p.574 - 577, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:26.29(Physics, Condensed Matter)Crystal structures of optical recording materials Ge Sb
Sb Te
Te and GeBi
and GeBi Te
Te have been studied in terms of the fast phase transition mechanism by both of real and reciprocal space Rietveld analyses of pulsed neutron powder diffraction data. These crystalline phases had large local lattice distortions. In addition, the crystallite size of GeBi
have been studied in terms of the fast phase transition mechanism by both of real and reciprocal space Rietveld analyses of pulsed neutron powder diffraction data. These crystalline phases had large local lattice distortions. In addition, the crystallite size of GeBi Te
Te was very small (about 150
was very small (about 150 ). These results suggest that the similarity of entropy between crystalline and amorphous phases plays an important role in terms of the fast phase transition mechanisms.
). These results suggest that the similarity of entropy between crystalline and amorphous phases plays an important role in terms of the fast phase transition mechanisms.
Sakai, Kenji; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Kai, Tetsuya; Oi, Motoki; Kaminaga, Masanori; Kato, Takashi; Furusaka, Michihiro*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(2), p.1324 - 1326, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.17(Physics, Condensed Matter)A general control system of MLF (MLF-GCS) is required to control all the subsystems of MLF including in the muon and neutron target, moderator, target station, experimental hall, and so on. It is an independent system, but it has to work closely with the control systems of accelerator and other facilities in J-PARC. A conceptual design of MLF-GCS has already been conducted and detailed designs are now in progress. This paper reports an overview and the development status of MLF-GCS.