Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Itashiki, Yutaro*; Imabayashi, Yoichi*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Uozumi, Yusuke*; Satoh, Daiki; Kajimoto, Tsuyoshi*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Koba, Yusuke*; Matsufuji, Naruhiro*
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 41(4), p.344 - 349, 2016/12
Carbon ion therapy has achieved satisfactory results because of high curability and minimally invasiveness. However, patients have a risk to get a secondary cancer. In order to estimate the risk, it is essential to understand particle transportation and nuclear reactions in the patient's body. The particle transport Monte Carlo simulation code is a useful tool to understand them. Since the code validation for heavy ion incident reactions is not enough, the experimental data of the elementary reaction processes is needed. We measured neutron production double-differential cross-sections (DDXs) on a carbon bombarded with 430 MeV/nucleon carbon beam which is a possible candidate of future therapy beam. The experiment was performed at PH2 beam line of the HIMAC of National Institute of Radiological Sciences. The 430 MeV/nucleon carbon beam was irradiated on a 5 cm 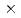 5 cm
5 cm 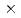 1 cm graphite target rotated 45
1 cm graphite target rotated 45 to the beam axis. The beam intensity was set to 10
to the beam axis. The beam intensity was set to 10 particles / spill. A 0.5 mm thick NE102A plastic scintillator was placed to monitor the beam intensity. Neutrons produced in the target were measured with two sizes of NE213 liquid organic scintillators located at six angles of 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, and 90
particles / spill. A 0.5 mm thick NE102A plastic scintillator was placed to monitor the beam intensity. Neutrons produced in the target were measured with two sizes of NE213 liquid organic scintillators located at six angles of 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, and 90 . The 5.08 cm long one was used to obtain the neutron spectra from 1 MeV to 10 MeV and the 12.7 cm long one was used above 5 MeV. The 2 mm thick NE102A plastic scintillators to discriminate charged particles were set in front of the neutron detectors. The kinetic energies of neutrons were determined by the time-of-flight (TOF) method. Background neutrons were estimated by a measurement with iron shadow bars between the target and each neutron detector. An electronic circuit for data acquisition consisted of NIM and CAMAC modules. The experimental data was compared with calculated results obtained by Monte Carlo simulation codes as PHITS. The PHITS code reproduced the experimental data well.
. The 5.08 cm long one was used to obtain the neutron spectra from 1 MeV to 10 MeV and the 12.7 cm long one was used above 5 MeV. The 2 mm thick NE102A plastic scintillators to discriminate charged particles were set in front of the neutron detectors. The kinetic energies of neutrons were determined by the time-of-flight (TOF) method. Background neutrons were estimated by a measurement with iron shadow bars between the target and each neutron detector. An electronic circuit for data acquisition consisted of NIM and CAMAC modules. The experimental data was compared with calculated results obtained by Monte Carlo simulation codes as PHITS. The PHITS code reproduced the experimental data well.
 Am-Be sources in JAEA-FRS
Am-Be sources in JAEA-FRSNishino, Sho; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Ebata, Yoshiaki*; Yoshizawa, Michio
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 41(3), p.211 - 215, 2016/09
We developed the graphite-moderated neutron calibration fields using  Am-Be sources at the Facility of Radiation Standard in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The neutron spectra of the fields were evaluated by Monte-Carlo calculation and measurements using the Bonner Multi-sphere Spectrometer. Reference values of fluence rates and dose equivalent rates of H
Am-Be sources at the Facility of Radiation Standard in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The neutron spectra of the fields were evaluated by Monte-Carlo calculation and measurements using the Bonner Multi-sphere Spectrometer. Reference values of fluence rates and dose equivalent rates of H (10) and H
(10) and H (10) were determined from neutron spectra by measurements. Currently, our fields are available for calibration or performance test of neutron measuring instruments.
(10) were determined from neutron spectra by measurements. Currently, our fields are available for calibration or performance test of neutron measuring instruments.
Nakamura, Takemi; Sakasai, Kaoru; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Takamiya, Koichi*; Kumada, Hiroaki*
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 41(2), p.105 - 109, 2016/06
no abstracts in English
 -ray dose rates on the upper core structure of the experimental fast reactor Joyo
-ray dose rates on the upper core structure of the experimental fast reactor JoyoIto, Chikara; Yamamoto, Takahiro; Maeda, Shigetaka; Ito, Hideaki; Sekine, Takashi
no journal, ,
In the experimental fast reactor Joyo, the upper core structure (UCS) was replaced. We have evaluated  -ray dose rates on UCS in order to conduct radiation shielding design of the UCS cask and radiation exposure control in the UCS removal work. The
-ray dose rates on UCS in order to conduct radiation shielding design of the UCS cask and radiation exposure control in the UCS removal work. The  -ray dose rates was calculated using the QAD-CGGP2R and corrected by the measured in-vessel axial distributions of
-ray dose rates was calculated using the QAD-CGGP2R and corrected by the measured in-vessel axial distributions of  -ray dose rate. In order to verify the
-ray dose rate. In order to verify the  -ray dose rate evaluation procedure, we measured spatial distribution of
-ray dose rate evaluation procedure, we measured spatial distribution of  -ray on the surface of the cask, which contained UCS using plastic scintillating optical fiber (PSF) during the UCS removal work. The calculated PSF output values were approximately twice as large as measured through the UCS. Correcting the calculated
-ray on the surface of the cask, which contained UCS using plastic scintillating optical fiber (PSF) during the UCS removal work. The calculated PSF output values were approximately twice as large as measured through the UCS. Correcting the calculated  -ray dose rates on the surface of the cask by results of the comparison has shown appropriate
-ray dose rates on the surface of the cask by results of the comparison has shown appropriate  -ray dose rates distribution.
-ray dose rates distribution.
 Li(p,n) quasi-monoenergetic neutron source at RCNP using a proton recoil telescope
Li(p,n) quasi-monoenergetic neutron source at RCNP using a proton recoil telescopeHagiwara, Masayuki*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Satoh, Daiki; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Masuda, Akihiko*; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Tamii, Atsushi*; Hatanaka, Kichiji*; et al.
no journal, ,
A  Li(p,n) quasi-monoenergetic neutron source for the 100-400 MeV range has been established at the Research Center for Nuclear Physics of Osaka University. The neutron energy spectrum and its intensity were determined by a time of flight (TOF) method and a liquid organic scintillator. However, the neutron-carbon interaction and the light output of the reaction products in the scintillator are not well known. Therefore, the neutron energy spectrum has large uncertainty due to the accuracy of the detection efficiency calculated by Monte Carlo method. In this study, we have measured the neutron itensity with a proton recoils telescope (PRT), because the detection efficiency of PRT can be determined accurately using the well-known differential n-p scattering cross section. We compared the intensity of the peak neutrons obtained by PRT with data with TOF method. As a result, the neutron spectra obtained by PRT and by TOF were generally consistent.
Li(p,n) quasi-monoenergetic neutron source for the 100-400 MeV range has been established at the Research Center for Nuclear Physics of Osaka University. The neutron energy spectrum and its intensity were determined by a time of flight (TOF) method and a liquid organic scintillator. However, the neutron-carbon interaction and the light output of the reaction products in the scintillator are not well known. Therefore, the neutron energy spectrum has large uncertainty due to the accuracy of the detection efficiency calculated by Monte Carlo method. In this study, we have measured the neutron itensity with a proton recoils telescope (PRT), because the detection efficiency of PRT can be determined accurately using the well-known differential n-p scattering cross section. We compared the intensity of the peak neutrons obtained by PRT with data with TOF method. As a result, the neutron spectra obtained by PRT and by TOF were generally consistent.