Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Be(p,xn) reaction for new nuclear data library JENDL-5
Be(p,xn) reaction for new nuclear data library JENDL-5国枝 賢; 山本 和喜; 今野 力; 岩元 洋介; 岩本 修; 若林 泰生*; 池田 裕二郎*
Journal of Neutron Research, 24(3-4), p.329 - 335, 2023/01
核データライブラリJENDL-5のために Be(p,xn)反応二重微分断面積の評価を行った。本研究ではまず、理化学研究所で開発された若林関数を内挿法などを工夫してデータベース化し、MCNPやPHITSを用いて薄膜ターゲットに対する検証解析を実施した。それにより、JENDL-4.0/HEや米国のENDF/B-VIII.0と比べて良い予測を与えることを確認した。更に反応断面積の絶対値を若林関数オリジナル値から15%(測定データ間の差異の範囲内で)減少させることにより、更に核データとしての精度が高まることを確認した。以上の知見を投入した新たな核データライブラリJENDL-5を用いることにより、
Be(p,xn)反応二重微分断面積の評価を行った。本研究ではまず、理化学研究所で開発された若林関数を内挿法などを工夫してデータベース化し、MCNPやPHITSを用いて薄膜ターゲットに対する検証解析を実施した。それにより、JENDL-4.0/HEや米国のENDF/B-VIII.0と比べて良い予測を与えることを確認した。更に反応断面積の絶対値を若林関数オリジナル値から15%(測定データ間の差異の範囲内で)減少させることにより、更に核データとしての精度が高まることを確認した。以上の知見を投入した新たな核データライブラリJENDL-5を用いることにより、 Be(p,xn)反応からの中性子スペクトルや収量を世界一の予測精度で計算することが可能である。
Be(p,xn)反応からの中性子スペクトルや収量を世界一の予測精度で計算することが可能である。
 He position-sensitive detector system
He position-sensitive detector system佐藤 節夫*; 梶本 亮一; 稲村 泰弘
Journal of Neutron Research, 24(3-4), p.427 - 434, 2023/01
In many neutron scattering experiments,  He-gas position-sensitive detectors (PSDs) are employed to obtain high-quality data. However, the exact position where a neutron is detected cannot be determined if two or more neutrons are simultaneously captured at different positions. This results in noise and degrades the quality of the data. In particular, such noise is a serious source of spurious scattering in inelastic neutron scattering instruments equipped with a large number of long PSDs recently developed at pulsed neutron sources. Herein, we introduce a pulse-width-discriminating PSD system that monitors the pulse width and height of the collected data. The system utilizes previously developed neutron-readout boards and removes instances of two or more simultaneous captures from the data to significantly improve the performance of PSDs. We also propose a new program to monitor the pulse width from PSD data using a hardware function implemented for other purposes. We confirm that the noise decreases to a level almost equal to that of the background. Although the developed program is applied to an inelastic scattering experiment, it is applicable to other types of experiments in which mispositioned signals should be eliminated as noise.
He-gas position-sensitive detectors (PSDs) are employed to obtain high-quality data. However, the exact position where a neutron is detected cannot be determined if two or more neutrons are simultaneously captured at different positions. This results in noise and degrades the quality of the data. In particular, such noise is a serious source of spurious scattering in inelastic neutron scattering instruments equipped with a large number of long PSDs recently developed at pulsed neutron sources. Herein, we introduce a pulse-width-discriminating PSD system that monitors the pulse width and height of the collected data. The system utilizes previously developed neutron-readout boards and removes instances of two or more simultaneous captures from the data to significantly improve the performance of PSDs. We also propose a new program to monitor the pulse width from PSD data using a hardware function implemented for other purposes. We confirm that the noise decreases to a level almost equal to that of the background. Although the developed program is applied to an inelastic scattering experiment, it is applicable to other types of experiments in which mispositioned signals should be eliminated as noise.
Schillebeeckx, P.*; Alaerts, G.*; Becker, B.*; Paradela, C.*; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Vendelbo, D.*; Wynants, R.*; 原田 秀郎; 北谷 文人; et al.
no journal, ,
中性子共鳴反応を利用して非破壊で試料を分析する手法に、中性子共鳴透過分析法(NRTA)がある。NRTAは中性子を試料に照射し、透過してくる中性子を計測することで試料を分析する。我々はJRC-IRMM(共同研究センター/標準物質・測定研究所)の中性子飛行時間施設GELINAにおいて、核物質の特性を評価するためNRTAの研究開発を行っている。その一環として、過酷事故で発生が予測される粒子状溶融燃料デブリに含まれる核物質の定量にNRTAを適用することを目的とした開発に取り組んできた。その開発の中で、デブリ中の核物質の定量精度が中性子吸収材のボロン( B)の存在量やデブリのさまざまな形や大きさに強く影響を受けることがわかった。こうしたデブリに特徴的な性質に対処するため、解析手法の改良やモデルの開発を行ってきた。本発表では、開発した解析手法やモデルの妥当性を検討するためGELINAで実施したNRTA実験の結果について報告し、中性子吸収材の存在下においても、NRTAでは2%以下の精度で核分裂性物質の量を導出できることを示す。
B)の存在量やデブリのさまざまな形や大きさに強く影響を受けることがわかった。こうしたデブリに特徴的な性質に対処するため、解析手法の改良やモデルの開発を行ってきた。本発表では、開発した解析手法やモデルの妥当性を検討するためGELINAで実施したNRTA実験の結果について報告し、中性子吸収材の存在下においても、NRTAでは2%以下の精度で核分裂性物質の量を導出できることを示す。
徐 平光; 角田 龍之介*; 高村 正人*; 大竹 淑恵*; 鈴木 裕士
no journal, ,
Neutron diffraction is a powerful probe to acquire the bulk averaged information for better bridging the microscopic crystal lattice with the macroscopic properties, in contrast with the X-ray and electron diffractions which are capable for investigating the surface/very limited local regions of polycrystalline materials. In Japan, the RIKEN compact accelerator-driven neutron source facility (RANS) has been developing to improve the instrumental accessibility of neutron diffraction experimental studies, which were mostly carried out on large-scale neutron source facilities. Here, our latest technical progress in RANS neutron diffraction bulk texture measurement will be reported. The comparable study between RANS and another large-scale neutron diffraction facility suggests that the high stereographic resolution realized through the proper fine division of neutron detector panel is valuable to improve the precision and reliability of texture measurement, together with the careful scattering intensity correction of neutron patterns.
徐 平光; 岩本 ちひろ*; 高村 正人*; 大竹 淑恵*; 栗原 諒*; 上野 孝太*; 片岡 美波*; 山本 和喜; Harjo, S.; 菖蒲 敬久
no journal, ,
Neutron diffraction can collect sample-volume averaged diffraction patterns due to the excellent penetrability and the coarse beam spot, valuable for investigating bulk microstructure changes of polycrystalline materials. In recent years, several neutron instruments in Japan have been employed for precise bulk texture evaluation. The engineering materials diffractometer attached with large sample stage and precise radial collimators at J-PARC has realized a reliably combined Rietveld texture evaluation, simultaneously providing crystallographic textures and other profile-analysis-related material parameters such as crystal structures, stress tensors. The RANS compact neutron source has enabled reliable bulk texture evaluation of steel materials through reasonably using a high stereographic angle resolution and a large sample-gauge volume. As a feed-back from the texture measurement technique based on RANS compact neutron source, recently, weak diffraction patterns step-by-step collected in very short time from RESA neutron diffractometer at JRR-3 have been utilized to realize the precise texture evaluation of various polycrystalline materials,  , a standard rock material, and different steel materials.
, a standard rock material, and different steel materials.
岩本 ちひろ*; 高村 正人*; 上野 孝太*; 片岡 美波*; 栗原 諒*; 徐 平光; 大竹 淑恵*
no journal, ,
Neutron diffraction is a powerful non-destructive method for evaluating the microscopic structure and internal stress of metallic materials and related semi-finished parts as a bulk average. To implement on-site stress measurements via the neutron diffraction at laboratories and factories frequently and even daily, we are establishing and upgrading the novel measurement and analysis methodology of time-of-flight neutron diffraction at RIKEN accelerator-driven compact neutron source (RANS). In this study, we have proposed two methods to improve the determination resolution of the diffraction peak position by focusing on delayed neutrons due to background scattering from devices such as reflector surrounding the neutron moderator and the polyethylene collimator. First, an analysis method has been proposed to deconvolute original diffraction peak from the delayed neutron component by defining a new model function to well describe the profile shape of delayed neutron diffraction. Second, a new decoupled collimator system has been developed to reduce the number of delayed neutrons. The diffraction patterns from a powder sample of pure body-centered cubic iron were measured with the decoupled collimator and the diffraction peak of {211} reflection was analyzed by the new analysis method using the neutron diffraction profile model function,  , a single exponential decay function convoluted with a Gaussian function. By this method, the decoupled collimator system has been confirmed to achieve a smaller measurement limit of lattice strain
, a single exponential decay function convoluted with a Gaussian function. By this method, the decoupled collimator system has been confirmed to achieve a smaller measurement limit of lattice strain 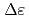 than a small-aperture polyethylene collimator system and a non-collimator system. The currently available
than a small-aperture polyethylene collimator system and a non-collimator system. The currently available 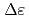 was 6.7
was 6.7 10
10 , which means that the internal stress up to 130 MPa can be well evaluated at RANS for steel materials with a Young's modulus of 200 GPa.
, which means that the internal stress up to 130 MPa can be well evaluated at RANS for steel materials with a Young's modulus of 200 GPa.