Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takubo, Yusaku*; Takayama, Yusuke; Idiart, A.*; Tanaka, Tatsuya*; Ishida, Keisuke*; Fujisaki, Kiyoshi*
Proceedings of 2022 International High Level Radioactive Waste Management Conference (IHLRWM 2022) (Internet), p.906 - 915, 2022/11
no abstracts in English
Tsai, P.-E.; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 121(1), p.13 - 16, 2019/11
The importance of PKA characteristics to radiation damage assessment for proton accelerators has been demonstrated in the paper by the PHITS simulations. In order to obtain accurate results of displacement cross section calculated by PHITS, it is therefore critical to have the physics models implemented in PHITS be properly validated by experimental data. With the new measurement system, which has been being developed here at JAEA, it is expected to provide experimental PKA data with low measurement thresholds and good mass resolutions. The test result we obtained at CYRIC, Tohoku University, for the 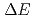 -
- gas ionization chamber as a part of the new measurement system was very promising. We were able to successfully distinguish C, B, Be, Li, and He elements with threshold energies lower than 1 MeV/nucleon in the configuration of 70-MeV proton beam and 920-nm thick C target. More experiments and tests shall continue in the future with heavier targets and higher proton beam energies.
gas ionization chamber as a part of the new measurement system was very promising. We were able to successfully distinguish C, B, Be, Li, and He elements with threshold energies lower than 1 MeV/nucleon in the configuration of 70-MeV proton beam and 920-nm thick C target. More experiments and tests shall continue in the future with heavier targets and higher proton beam energies.
Karahan, A.*; Kawada, Kenichi; Tentner, A.*
Proceedings of 2018 ANS Winter Meeting and Nuclear Technology Expo; Embedded Topical International Topical Meeting on Advances in Thermal Hydraulics (ATH 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 4 Pages, 2018/11
Uchibori, Akihiro; Takata, Takashi; Yanagisawa, Hideki*; Li, J.*; Jang, S.*
Proceedings of 2018 ANS Winter Meeting and Nuclear Technology Expo; Embedded Topical International Topical Meeting on Advances in Thermal Hydraulics (ATH 2018) (USB Flash Drive), p.1289 - 1294, 2018/11
Evaluation of occurrence possibility of tube failure propagation under sodium-water reaction accident is an important issue. In this study, a numerical analysis method to predict occurrence of failure propagation by overheating rupture was constructed to expand application range of an existing computer code. Applicability of the method was constructed through the numerical analysis of the experiment on water vapor discharging in liquid sodium. To improve the evaluation accuracy for the temperature distribution, a Lagrangian particle model for simulating reacting jet was also developed as an alternative method and its basic function was confirmed.
Washiya, Tadahiro; Miyamoto, Yasuaki
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 117(1), p.47 - 50, 2017/10
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS) carried out several international cooperation to gather the knowledge and expertise on decommissioning and accident management. The cooperation fields are radioactive waste management in the decommissioning, characterization of fuel debris, investigation on core degradation process and remote monitoring technology etc.. This paper is explained outline of the CLADS activities and future prospect.
Miyahara, Kaname
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 117(1), p.51 - 52, 2017/10
This presentation highlights JAEA's challenges for contributing to recovering the previous life of residents and the development of resilient communities in Fukushima Prefecture based on considering needs of local people on the environmental restoration categorized by the state of evacuation orders and the lifting of such orders.
Kawada, Kenichi; Suzuki, Toru
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 115(1), p.1597 - 1598, 2016/11
Tanaka, Kosuke; Sasaki, Shinji; Katsuyama, Kozo; Koyama, Shinichi
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 113(1), p.619 - 621, 2015/10
In order to evaluate the microstructural change behavior of Am-MOX fuels at the initial stage of irradiation, detailed investigations using image analysis were performed on X-ray Computed Tomography (X-ray CT) images and on ceramographs from fuels irradiated in both B11 and B14.
Kato, Masato; McClellan, K.*
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 113(1), p.613 - 614, 2015/10
A joint study on advanced oxide fuels is being carried out under the Civil Nuclear Energy Working Group (CNWG) bilateral collaboration between the U.S. Department of Energy and the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The main goal of this study is to support development and validation of a science-based fuel analysis code for minor actinide (MA) bearing MOX fuel. In analysis and evaluation of fuel performance, it is essential to understand the physical properties of the advanced oxide fuels. Therefore, we are investigating physical properties of (U,Pu)O , (U,Ce,)O
, (U,Ce,)O , PuO
, PuO , CeO
, CeO and other related compounds to prepare a physical property database and to construct an integrated mechanistic physical property model. In this paper, we describe the derivation of a model to represent heat capacity and thermal conductivity of (U,Pu)O
and other related compounds to prepare a physical property database and to construct an integrated mechanistic physical property model. In this paper, we describe the derivation of a model to represent heat capacity and thermal conductivity of (U,Pu)O that is based on the experimental database.
that is based on the experimental database.
Ozawa, Takayuki; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Kato, Masato
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 113(1), p.622 - 624, 2015/10
A recycle system for minor actinides (MAs), in which MAs are recycled by reprocessing and irradiating them in a fast reactor, is studied to reduce the degree of hazard and the amount of high-level radioactive wastes. MAs would be used as mixed oxide (MOX) fuels with plutonium and uranium in fast reactors. Since MA content of MA-bearing MOX (MA-MOX) to be used in fast reactors is assumed to reach  5 wt%HM, the effects on not only fuel properties but also fuel behaviors have to be estimated to use MA-MOX as fast reactor fuels. As the MOX fuels to be used will be irradiated at a comparably high linear power and the fuel center temperature would be assumed to be over 2,273 K during irradiation in the fast reactors, fuel restructuring would take place due to void migration towards the fuel center under the radial temperature gradient, and a central void would be formed. Since the fuel center temperature would be decreased by the effect of formation of the central void, the fuel restructuring is one of the most important behaviors for fast reactor fuels. In this study, the effect of MA content on fuel restructuring behavior was estimated from the results of irradiation experiments such as B11 and B14 performed in Joyo to study the irradiation behaviors of MA-MOX and the calculation results using a fuel restructuring model which can take into account MA-MOX dependence on vapor pressure.
5 wt%HM, the effects on not only fuel properties but also fuel behaviors have to be estimated to use MA-MOX as fast reactor fuels. As the MOX fuels to be used will be irradiated at a comparably high linear power and the fuel center temperature would be assumed to be over 2,273 K during irradiation in the fast reactors, fuel restructuring would take place due to void migration towards the fuel center under the radial temperature gradient, and a central void would be formed. Since the fuel center temperature would be decreased by the effect of formation of the central void, the fuel restructuring is one of the most important behaviors for fast reactor fuels. In this study, the effect of MA content on fuel restructuring behavior was estimated from the results of irradiation experiments such as B11 and B14 performed in Joyo to study the irradiation behaviors of MA-MOX and the calculation results using a fuel restructuring model which can take into account MA-MOX dependence on vapor pressure.
 and (U,Pu)O
and (U,Pu)O
Nakamichi, Shinya; Hirooka, Shun; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Kato, Masato; Nelson, A.*; McClellan, K.*
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 113(1), p.617 - 618, 2015/10
Cerium dioxide has been used as a surrogate material for plutonium dioxide. Dorr et al reported the use of hyper-stoichiometric conditions causes the start of shrinkage of (U,Ce)O at low temperature compared with the sintering in reducing atmosphere. However, the precise stoichiometry of the samples investigated was not controlled or otherwise monitored, preventing any quantitative conclusions regarding the similarities or differences between (U,Ce)O
at low temperature compared with the sintering in reducing atmosphere. However, the precise stoichiometry of the samples investigated was not controlled or otherwise monitored, preventing any quantitative conclusions regarding the similarities or differences between (U,Ce)O and (U,Pu)O
and (U,Pu)O . The motivation for the present work is therefore to compare the sintering behavior of MOX and the (U,Ce)O
. The motivation for the present work is therefore to compare the sintering behavior of MOX and the (U,Ce)O MOX surrogates under controlled atmospheres to assess the role of oxygen defects on densification in both systems.
MOX surrogates under controlled atmospheres to assess the role of oxygen defects on densification in both systems.
Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Morev, M. N.*; Kosako, Toshiso*
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 109(2, Part 2), p.1253 - 1255, 2013/11
Depth distributions of radioactive fragments in a thick lead target exposed to 400 MeV/u carbon ions were measured to obtain isotopic production cross-sections of  Pb(
Pb( C,x)X (X=
C,x)X (X=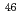 Sc,
Sc,  V,
V,  Mn,
Mn,  Co,
Co,  Co,
Co,  Fe,
Fe,  Se,
Se, 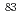 Rb,
Rb,  Sr,
Sr,  Sn,
Sn, 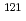 Te,
Te,  Xe,
Xe,  Ba,
Ba,  Ce,
Ce, 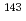 Pm,
Pm,  Pm,
Pm, 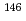 Gd,
Gd, 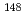 Eu,
Eu,  Gd,
Gd, 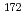 Hf and
Hf and 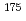 Hf) reactions as excitation functions. The obtained fragment distributions were converted to excitation functions of fragmentation cross-sections by the modified stacked-foil method. This conversion procedure was validated by comparing the obtained data with the available thin target experimental data. The obtained cross-sections were in good agreement with the previously published results. Comparison of the obtained cross-sections and the simulation by PHITS showed that PHITS underestimates fragments lighter than 90 amu by factor of about 10 whereas the fragments heavier than 110 amu were predicted within a factor of 3. Energy and mass dependences of the obtained cross-sections give insight into the reaction mechanism and will be useful for radiation transport code benchmarking. Furthermore, this study clarified that excitation functions of fragmentation reactions induced by heavy ions can be obtained by applying the method adopted in this study.
Hf) reactions as excitation functions. The obtained fragment distributions were converted to excitation functions of fragmentation cross-sections by the modified stacked-foil method. This conversion procedure was validated by comparing the obtained data with the available thin target experimental data. The obtained cross-sections were in good agreement with the previously published results. Comparison of the obtained cross-sections and the simulation by PHITS showed that PHITS underestimates fragments lighter than 90 amu by factor of about 10 whereas the fragments heavier than 110 amu were predicted within a factor of 3. Energy and mass dependences of the obtained cross-sections give insight into the reaction mechanism and will be useful for radiation transport code benchmarking. Furthermore, this study clarified that excitation functions of fragmentation reactions induced by heavy ions can be obtained by applying the method adopted in this study.
 Cs transport in the Ukedo River of Fukushima
Cs transport in the Ukedo River of FukushimaKurikami, Hiroshi; Kitamura, Akihiro; Yamaguchi, Masaaki; Onishi, Yasuo*
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 109(1), p.149 - 152, 2013/11
We applied the TOMAM model to the Ukedo River as a preliminary analysis to roughly understand what was important for cesium migration. The main lessons were as follows: Cesium migrates mainly in high river discharge conditions. Migration in a dissolved form is important in low river discharge conditions, while suspended sediments, especially silt and clay, are main carriers of cesium in high discharge conditions. Bed contamination is mainly reflected by sediment erosion and deposition instead of direct sorption in the riverbed.
 -ray analysis using spallation neutrons at J-PARC
-ray analysis using spallation neutrons at J-PARCToh, Yosuke; Ebihara, Mitsuru*; Harada, Hideo
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 109(1), p.116 - 117, 2013/11
no abstracts in English
Yamashita, Shinichiro; Osaka, Masahiko
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 109(1), p.140 - 142, 2013/11
The decommissioning work of Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F-NPP) is intensively being promoted according to the Mid-and-long Term Roadmap towards the Decommissioning of 1F-NPP units 1-4. Many research and development works are underway in order to ensure the progress of the decommissioning work. One of the R&D programs relates to the removal of fuel assemblies (FAs) from the spent fuel pool (SFP), in which the seawater was injected as an emergency counter-measure for fuel cooling during the accident. For the anticipation of the long term integrity of irradiated FA structural materials that experienced a diluted seawater exposure part of a fundamental research plan was described to support the estimation of the long-term possible influences of corrosive factors on the component materials of FAs. In this study, whether or not acceleration of corrosion occurred was investigated by the immersion test under constant potential for SUS304L and Zircaloy-4.
Kitamura, Akihiro; Machida, Masahiko; Sato, Haruo; Nakayama, Shinichi; Yui, Mikazu
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 109(1), p.156 - 157, 2013/11
Computational modeling and simulating team of Fukushima Environmental Safety Center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been started to develop a number of mathematical models of radioactive contaminants on the land and rivers, lakes, and estuaries in Fukushima, as well as the basic studies of adsorption/absorption mechanism of Cs and soils. These predictions will be utilized for the dose assessment from the environmental contamination and the proposal of countermeasures to dispersion of contaminant. In this presentation we describe the outline of our current activities.
Satoh, Daiki; Kojima, Kensuke; Oizumi, Akito; Matsuda, Norihiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Kugo, Teruhiko; Sakamoto, Yukio*; Endo, Akira; Okajima, Shigeaki
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 109(1), p.1261 - 1263, 2013/11
A computer software, named CDE (Calculation system for Decontamination Effect), has been developed to support planning the decontamination. CDE is programed with VBA (Visual Basic for Applications), and runs on Microsoft Excel with a user friendly graphical interface. It calculates dose rate distributions in a target area before and after the decontamination from a radioactivity distribution and DF (Decontamination Factor), which is a ratio of original radioactivity to remaining one after the decontamination. DRRF (Dose Rate Reduction Factor) is also derived to express the decontamination effect. All the calculation results are visualized on an image of the target area with color map. Owing to its quick calculation speed, CDE is able to investigate the decontamination effect in various cases for a short period. This is very useful to establish a rational decontamination plan before an action.
 Cs distribution on territory of Fukushima
Cs distribution on territory of FukushimaKitamura, Akihiro; Yamaguchi, Masaaki; Oda, Yoshihiro; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Onishi, Yasuo*
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 109(1), p.153 - 155, 2013/11
Long term  Cs transport and its future distribution on the territory of Fukushima were predicted based on the USLE and the GIS. By modeling the soil erosion, transport, and deposition, we simulated the future distributions of air dose rates of
Cs transport and its future distribution on the territory of Fukushima were predicted based on the USLE and the GIS. By modeling the soil erosion, transport, and deposition, we simulated the future distributions of air dose rates of  Cs in mSv/h for 2, 6 and 21 years after the accident. The predictions made by METI were compared with the present results. The predictions of relatively high air dose rate areas were consistently matched between the two models over time. However, our model seemed to predict the decreasing rate of the
Cs in mSv/h for 2, 6 and 21 years after the accident. The predictions made by METI were compared with the present results. The predictions of relatively high air dose rate areas were consistently matched between the two models over time. However, our model seemed to predict the decreasing rate of the  Cs concentration with time to be slightly less than that of METI prediction. Some portions of the results obtained in the present study were used to provide influxes of sediments and
Cs concentration with time to be slightly less than that of METI prediction. Some portions of the results obtained in the present study were used to provide influxes of sediments and  Cs as boundary conditions and lateral inflows for the hydraulic river model.
Cs as boundary conditions and lateral inflows for the hydraulic river model.
Matsumoto, Koji*; Sagara, Hiroshi*; Han, C. Y.*; Onishi, Takashi; Saito, Masaki*; Yamauchi, Ippei*
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 107(1), p.1018 - 1019, 2012/11
Protected plutonium production (P ) with a high proliferation-resistance was proposed by increasing the
) with a high proliferation-resistance was proposed by increasing the  Pu ratio in the total plutonium through minor actinides (MAs) doping into the fresh blanket fuel. Moderator effect on P
Pu ratio in the total plutonium through minor actinides (MAs) doping into the fresh blanket fuel. Moderator effect on P was evaluated. As a result, the transmutation ratio is larger with the heterogeneous moderator than with the homogeneous one, and the isotopic ratio of
was evaluated. As a result, the transmutation ratio is larger with the heterogeneous moderator than with the homogeneous one, and the isotopic ratio of  Pu was increased.
Pu was increased.
Sagara, Hiroshi; Tomikawa, Hirofumi; Watahiki, Masaru; Kuno, Yusuke
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 107(1), p.803 - 804, 2012/11
Fission products(FPs) such as Eu, Ce, Ru have low release ratio in case of core melting event in severe accident to co-exist inside fuel debris in oxide or metallic phase, based on TMI-2 experience and source term experiments. Passive  spectroscopy of Ce-144/Pr-144 was utilized in quantifying special nuclear material in fuel debris of TMI-2 historically, and the same methodology might be applied to high energy
spectroscopy of Ce-144/Pr-144 was utilized in quantifying special nuclear material in fuel debris of TMI-2 historically, and the same methodology might be applied to high energy  emitter, Eu-154 and Ru-106. Passive neutron measurement has been also utilized for quantifying nuclear material practically. Different from conventional spent fuel, however, fuel debris would be lost in information of irradiated profile, release ratio of volatile FPs, and so on. In the present paper, sensitivity analysis of low-volatile FPs and Cm-244 inventory in irradiated nuclear fuel in light water reactor was performed numerically to clarify the uncertainty of low-volatile FP and Cm inventory regarding fuel irradiation parameters and calculation methodology, and to derive applicable index to quantify nuclear material in fuel debris.
emitter, Eu-154 and Ru-106. Passive neutron measurement has been also utilized for quantifying nuclear material practically. Different from conventional spent fuel, however, fuel debris would be lost in information of irradiated profile, release ratio of volatile FPs, and so on. In the present paper, sensitivity analysis of low-volatile FPs and Cm-244 inventory in irradiated nuclear fuel in light water reactor was performed numerically to clarify the uncertainty of low-volatile FP and Cm inventory regarding fuel irradiation parameters and calculation methodology, and to derive applicable index to quantify nuclear material in fuel debris.