Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O
O studied by polarized neutron techniques
studied by polarized neutron techniquesMatsuda, Masaaki; Osawa, Akira*; Takeda, Masayasu; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Leli vre-Berna, E.*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Chung, J.-H.*; Lee, S.-H.*; Ueda, Hiroaki*; Takagi, Hidenori*
vre-Berna, E.*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Chung, J.-H.*; Lee, S.-H.*; Ueda, Hiroaki*; Takagi, Hidenori*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Machida, Masahiko; Ohashi, Yoji*; Koyama, Tomio*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -electron systems with multipole degrees of freedom
-electron systems with multipole degrees of freedomKubo, Katsunori; Hotta, Takashi
no journal, ,
Recently, an interesting possibility of superconductivityinduced by multipole fluctuations has been discussed insome  -electron materials. In order to clarify such exotic superconductivity from a microscopic viewpoint, we apply fluctuation exchange approximationto an
-electron materials. In order to clarify such exotic superconductivity from a microscopic viewpoint, we apply fluctuation exchange approximationto an  -electron model with active orbital degree of freedomon the basis of a
-electron model with active orbital degree of freedomon the basis of a 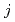 -
-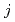 coupling scheme. First, we evaluate orbital dependent fluctuations andeffective paring interactions within the FLEX approximation. Then, we determine the symmetry of the gap function amongpossible superconducting states by solving the Eliashberg equation. In particular, we pay our attention to the effect of crystallineelectric field on the appearance of superconductivity. By further decomposing complex orbital dependent fluctuationsinto multipole components, we also discuss possible relevance ofmultipole fluctuations to exotic superconductivity.
coupling scheme. First, we evaluate orbital dependent fluctuations andeffective paring interactions within the FLEX approximation. Then, we determine the symmetry of the gap function amongpossible superconducting states by solving the Eliashberg equation. In particular, we pay our attention to the effect of crystallineelectric field on the appearance of superconductivity. By further decomposing complex orbital dependent fluctuationsinto multipole components, we also discuss possible relevance ofmultipole fluctuations to exotic superconductivity.
Sakai, Toru; Poilblanc, D.*
no journal, ,
The effect of in-plane oxygen phonons is investigated by numerical exact diagonalizations of the t-J Holstein model. The present study indicates that the breathing vibration mode gives rise to a polaronic effect which yields a broadening of the single hole quasiparticle spectrum and a shift from the chemical potential, as the one observed in angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy.
 source from high contrast fs laser plasmas in regime of Relativistic Engineering
source from high contrast fs laser plasmas in regime of Relativistic EngineeringChen, L.-M.; Koga, J. K.; Kando, Masaki; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Nakajima, Kazuhisa; Bulanov, S. V.; Tajima, Toshiki; Xu, M. H.*; Li, Y.-T.*; Dong, Q. L.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Interaction of intense Ti: Sapphire laser with Cu foil targets has been studied by measuring hard X-ray generation. Hard X-ray spectroscopy and K X-ray conversion efficiency (
X-ray conversion efficiency (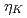 ) from Cu plasma have been studied as a function of laser intensity via pulse duration scan (60 fs
) from Cu plasma have been studied as a function of laser intensity via pulse duration scan (60 fs  600 fs), laser pulse energy scan (60 mJ
600 fs), laser pulse energy scan (60 mJ  600 mJ) and target displacement scan from best focus. For intensity I
600 mJ) and target displacement scan from best focus. For intensity I 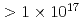 W/cm
W/cm , the Cu
, the Cu 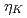 keep on increasing to reach a maximum value of
keep on increasing to reach a maximum value of 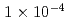 at an intensity
at an intensity 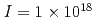 W/cm
W/cm . The focusing is varied widely to give a range of intensities from 10
. The focusing is varied widely to give a range of intensities from 10 W/cm
W/cm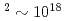 W/cm
W/cm . Comparing to a recent publication, two individual emission peaks are obtained, one is at best focal spot and the other is at larger target offset corresponding to
. Comparing to a recent publication, two individual emission peaks are obtained, one is at best focal spot and the other is at larger target offset corresponding to 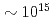 W/cm
W/cm . Each peak is corresponding to different energy absorption mechanism. In addition, when we introduce slightly detuning of compressor gratings at the best focal condition, it shows
. Each peak is corresponding to different energy absorption mechanism. In addition, when we introduce slightly detuning of compressor gratings at the best focal condition, it shows 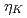 generated by negatively skewed 100 fs pulse width laser irradiation reach
generated by negatively skewed 100 fs pulse width laser irradiation reach 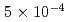 and almost 7 times greater than the case of positively skewed pulse. Vacuum Heating is greatly stimulated in this case and preciously control of pre-plasma is the key factor in tuning control of X-ray emission in relativistic fs regime.
and almost 7 times greater than the case of positively skewed pulse. Vacuum Heating is greatly stimulated in this case and preciously control of pre-plasma is the key factor in tuning control of X-ray emission in relativistic fs regime.
Koga, J. K.; Chen, L.-M.; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Nakajima, Kazuhisa; Bulanov, S. V.; Tajima, Toshiki; Gu, Y. Q.*; Peng, H. S.*; Hua, J. F.*; An, W. M.*; et al.
no journal, ,
First experiments for electron acceleration with the laser-gas plasma interaction have been carried out with 30 fs, 100 TW relativistic Ti:Sapphier laser pulse into a long slit (1.2  10 mm
10 mm ) gas plasma. The 10 mm length plasma channel formed that was longer than 20 times the Rayleigh length. Plasma density was the key factor for this long channel stimulation under 100 TW laser pulse irradiation that was much higher than critical power for relativistic self-focusing. For the first time, channel characteristics such as laser bending, hosing and cavity formation were demonstrated experimentally. In case of long channel guiding, accelerated electron bunch was tightly collimated with low emmitance
) gas plasma. The 10 mm length plasma channel formed that was longer than 20 times the Rayleigh length. Plasma density was the key factor for this long channel stimulation under 100 TW laser pulse irradiation that was much higher than critical power for relativistic self-focusing. For the first time, channel characteristics such as laser bending, hosing and cavity formation were demonstrated experimentally. In case of long channel guiding, accelerated electron bunch was tightly collimated with low emmitance 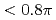 mm mrad and quasi-monoenergetic electron bunch (
mm mrad and quasi-monoenergetic electron bunch ( 70 MeV) was obtained as well. Accelerated electron charge current with electron energy
70 MeV) was obtained as well. Accelerated electron charge current with electron energy  1 MeV was
1 MeV was  10 nC/shot which was highest value in laser accelerator, to our knowledge, and ascribed to the contribution of long plasma channel. These well controlled laser-driven acceleration is an important cornerstone of relativistic engineering.
10 nC/shot which was highest value in laser accelerator, to our knowledge, and ascribed to the contribution of long plasma channel. These well controlled laser-driven acceleration is an important cornerstone of relativistic engineering.
 SR measurements on the superconducting penetration depth in aged PuCoGa
SR measurements on the superconducting penetration depth in aged PuCoGa
Heffner, R. H.; Oishi, Kazuki; Higemoto, Wataru; Ito, Takashi; Morris, G. D.*; Fluss, M. J.*; MacLaughlin, D. E.*; Shu, L.*; Bauer, E. D.*; Sarrao, J. L.*
no journal, ,
The superconductor PuCoGa possesses a relatively high critical temperature (T
possesses a relatively high critical temperature (T = 18.5 K), a moderate mass enhancement (Sommerfeld coefficient
= 18.5 K), a moderate mass enhancement (Sommerfeld coefficient 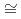 80 mJ/mol-K
80 mJ/mol-K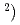 and exhibits behavior consistent with spin-fluctuation-induced d-wave superconductivity. It is also radioactive, with its dominant radioisotope
and exhibits behavior consistent with spin-fluctuation-induced d-wave superconductivity. It is also radioactive, with its dominant radioisotope  Pu having a half-life of 2.4
Pu having a half-life of 2.4  10
10 yrs. We report
yrs. We report 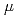 SR measurements of the temperature and field dependence of the magnetic field penetration depth
SR measurements of the temperature and field dependence of the magnetic field penetration depth 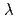 (T,H) in a 400 day-old sample of PuCoGa
(T,H) in a 400 day-old sample of PuCoGa (T
(T = 15 K), and compare these results to data obtained on the same sample approximately one year earlier. In 600 Oe applied field both measurements show a linear low-temperature behavior for
= 15 K), and compare these results to data obtained on the same sample approximately one year earlier. In 600 Oe applied field both measurements show a linear low-temperature behavior for 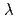 (T) -
(T) - 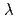 (0) = bT for T/T
(0) = bT for T/T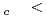 0.5 with the same coefficient b. The magnitude of
0.5 with the same coefficient b. The magnitude of 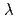 (0) in the aged sample has increased by a factor of about 1.8. The results are discussed in terms of the effects of radiation damage on the postulated d-wave superconducting order parameter.
(0) in the aged sample has increased by a factor of about 1.8. The results are discussed in terms of the effects of radiation damage on the postulated d-wave superconducting order parameter.
 Cu
Cu O
O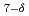 and Nd
and Nd Ce
Ce CuO
CuO
Ishii, Kenji
no journal, ,
We have carried out resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) studies on two high-Tc superconductors at the optimal carrier concentration, YBa Cu
Cu O
O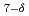 (YBCO) and Nd
(YBCO) and Nd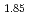 Ce
Ce CuO
CuO (NCCO). Using a twin-free YBCO, we could successfully differentiate the Mott gap excitation in the CuO chain from that in the CuO
(NCCO). Using a twin-free YBCO, we could successfully differentiate the Mott gap excitation in the CuO chain from that in the CuO plane, that is, the excitation in the chain is enhanced at 2 eV near the zone boundary of the chain direction, while the excitation in the plane is broad and almost independent of the momentum transfer. Furthremore we found that the Mott gap of the chain is smaller than that of the plane. In NCCO, we observed intraband excitation in the upper Hubbard band for the first time by tuning the incident energy of X-ray to the condition that the intraband is enhanced. The observed momentum dependence of the intraband excitation is similar to that of the dynamical density response function of the two-dimensional Hubbard model.
plane, that is, the excitation in the chain is enhanced at 2 eV near the zone boundary of the chain direction, while the excitation in the plane is broad and almost independent of the momentum transfer. Furthremore we found that the Mott gap of the chain is smaller than that of the plane. In NCCO, we observed intraband excitation in the upper Hubbard band for the first time by tuning the incident energy of X-ray to the condition that the intraband is enhanced. The observed momentum dependence of the intraband excitation is similar to that of the dynamical density response function of the two-dimensional Hubbard model.
 Sr
Sr CuO
CuO
Wakimoto, Shuichi; Birgeneau, R. J.*; Frost, C. D.*; Kagedan, A.*; Kim, H.*; Swainson, I.*; Tranquada, J. M.*; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*; Zhang, H.*
no journal, ,
Spin excitations of LSCO in the overdoped regime has been studied by neutron scattering. Incommensurate excitations around 6 meV which are clearly observed in the 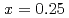 sample decrease with
sample decrease with  as doping increases, and finally, become unobservable at
as doping increases, and finally, become unobservable at 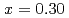 coincidentally with the disappearance of bulk superconductivity. High-energy measurements performed at the MAPS spectrometer show remarkably weakened magnetic excitations of the overdoped samples also in the high energy region. These observations are apparently consistent with a microscopic phase separation of the overdoped samples into the superconducting and Fermi liquid phases based on muSR results. In contrast, magnetization measurements of overdoped LSCO with and without Zn impurities have revealed that the superconductivity vanishes in the overdoped regime as a result of a competition between the superconductivity and paramagnetism which is induced even in the Zn-free overdoped LSCO.
coincidentally with the disappearance of bulk superconductivity. High-energy measurements performed at the MAPS spectrometer show remarkably weakened magnetic excitations of the overdoped samples also in the high energy region. These observations are apparently consistent with a microscopic phase separation of the overdoped samples into the superconducting and Fermi liquid phases based on muSR results. In contrast, magnetization measurements of overdoped LSCO with and without Zn impurities have revealed that the superconductivity vanishes in the overdoped regime as a result of a competition between the superconductivity and paramagnetism which is induced even in the Zn-free overdoped LSCO.
 -electron systems
-electron systemsOnishi, Hiroaki; Hotta, Takashi
no journal, ,
By exploiting a density matrix renormalization group method, we analyze a one-dimensional three-orbital Hubbard model on the basis of a 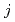 -
-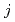 coupling scheme. When we take account of the level splitting between
coupling scheme. When we take account of the level splitting between 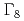 and
and 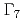 orbitals, due to the competition between itinerant and localized orbitals, we observe a characteristic change of
orbitals, due to the competition between itinerant and localized orbitals, we observe a characteristic change of 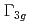 quadrupole correlation into an incommensurate structure in accordance with the change of the orbital structure.
quadrupole correlation into an incommensurate structure in accordance with the change of the orbital structure.