Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakamura, Hironobu; Beddingfield, D. H.*; Nakamichi, Hideo; Kurita, Tsutomu
Proceedings of INMM 51st Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2010/07
The Distributed Source-Term Analysis (DSTA) technique has been used in a variety of safeguards applications to determine location and quantity of material contained within large sample volumes. It can provide user with knowledge of the location of neutron-producing materials and magnitude of the localized activity. Operator can use this information to identify the physical location of holdup during cleanout operations. In this paper, we present the concept of using the DSTA method as a 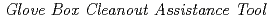 (BCAT) that is used by operator during cleanout to increase recovered material, to decrease unmeasured inventory, and to perform the cleanout activity effectively in order to reduce operator radiation-exposure. We confirmed good consistency between the difference of neutron activity before and after cleanout calculated by BCAT and neutron activity of actual recovered material.
(BCAT) that is used by operator during cleanout to increase recovered material, to decrease unmeasured inventory, and to perform the cleanout activity effectively in order to reduce operator radiation-exposure. We confirmed good consistency between the difference of neutron activity before and after cleanout calculated by BCAT and neutron activity of actual recovered material.
 -rays in material accountancy and safeguards verification for future nuclear fuel cycle facilities
-rays in material accountancy and safeguards verification for future nuclear fuel cycle facilitiesSeya, Michio; Hajima, Ryoichi; Nishimori, Nobuyuki; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Hayakawa, Takehito; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Fujiwara, Mamoru
Proceedings of INMM 51st Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2010/07
This article introduces possibilities of various applications of ERL (Energy Recovery Linac) based laser Compton scattering (LCS) X- and  -ray sources to nondestructive assay (NDA) in material accountancy and safeguards verification for future nuclear fuel cycle (FNFC) facilities. The NDA system using 1-3 MeV LCS
-ray sources to nondestructive assay (NDA) in material accountancy and safeguards verification for future nuclear fuel cycle (FNFC) facilities. The NDA system using 1-3 MeV LCS  -ray source (350 MeV electrons + laser) with having semi-monochromatic energy distribution and enough intensity could be applied to measurement of Pu not only in spent nuclear fuel but also in fresh MOX fuel with FPs (fission products) and MAs (minor actinides) by NRF (nuclear resonance fluorescence) method. This NDA system is as well applicable for measuring Pu in hulls or vitrified waste. The NDA system using 100-150 keV LCS X-ray source (85 MeV electrons + laser) could be applied to measurement of concentrations of U, Pu, MAs in solutions with higher speed than the present Hybrid K-edge/XRF densitometer.
-ray source (350 MeV electrons + laser) with having semi-monochromatic energy distribution and enough intensity could be applied to measurement of Pu not only in spent nuclear fuel but also in fresh MOX fuel with FPs (fission products) and MAs (minor actinides) by NRF (nuclear resonance fluorescence) method. This NDA system is as well applicable for measuring Pu in hulls or vitrified waste. The NDA system using 100-150 keV LCS X-ray source (85 MeV electrons + laser) could be applied to measurement of concentrations of U, Pu, MAs in solutions with higher speed than the present Hybrid K-edge/XRF densitometer.
Hayakawa, Takehito; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hajima, Ryoichi; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Nishimori, Nobuyuki; Seya, Michio; Fujiwara, Mamoru
Proceedings of INMM 51st Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2010/07
We propose a new nondestructive assay method for  U,
U,  Pu, and minor actinides in spent nuclear fuel assembly in a water pool. Nuclear fuel materials are detected using nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) with laser Compton scattering (LCS)
Pu, and minor actinides in spent nuclear fuel assembly in a water pool. Nuclear fuel materials are detected using nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) with laser Compton scattering (LCS)  -rays, which are generated by collision of high energy electrons and laser photons. This method can identify each isotope of interest hidden in heavy shields such as lead plates with a thickness of several centimeters. A simulation calculation shows that we can detect 1% fraction
-rays, which are generated by collision of high energy electrons and laser photons. This method can identify each isotope of interest hidden in heavy shields such as lead plates with a thickness of several centimeters. A simulation calculation shows that we can detect 1% fraction  Pu in all the fuel rods with statistical error lower than 2% using the proposed high flux LCS
Pu in all the fuel rods with statistical error lower than 2% using the proposed high flux LCS  -ray source in the measurement time of 4000s.
-ray source in the measurement time of 4000s.
Nakamura, Hironobu; Beddingfield, D. H.*; Nakamichi, Hideo; Kurita, Tsutomu
Proceedings of INMM 51st Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2010/07
The Distributed Source-Term Analysis (DSTA) technique has been used in a variety of safeguards applications to determine the location and quantity of material contained within large sample volumes. The DSTA method can provide the user with knowledge of the location of neutron-producing materials and the magnitude of the localized activity. A facility operator can use this information to identify the physical location of holdup during cleanout activities. In this paper, we present the concept of using the DSTA method as a 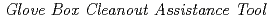 (BCAT) that is used by operator during cleanout activities to increase recovered material and reduce facility MUF. In addition to the above effects, this BCAT concept provides that operator radiation-exposure and unmeasured inventory can be also reduced. We also present the actual powder recovering result performed in PCDF and comparison result between recovered material amount and calculated amount by BCAT.
(BCAT) that is used by operator during cleanout activities to increase recovered material and reduce facility MUF. In addition to the above effects, this BCAT concept provides that operator radiation-exposure and unmeasured inventory can be also reduced. We also present the actual powder recovering result performed in PCDF and comparison result between recovered material amount and calculated amount by BCAT.
Inoue, Naoko; Kaji, Naoya; Suda, Kazunori; Kawakubo, Yoko; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Koyama, Tomozo; Kuno, Yusuke; Senzaki, Masao
Proceedings of INMM 51st Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2010/07
Sumi, Mika; Abe, Katsuo; Kageyama, Tomio; Nakazawa, Hiroaki; Kurosawa, Akira; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Mason, P.*; Neuhoff, J.*; Doubek, N.*; Balsley, S.*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 51st Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2010/07
Large Size Dried (LSD) spikes are currently used in many facilities in Japan (and around the world) for U and Pu accountancy analysis by Isotope Dilution Mass Spectrometry (IDMS). Because of the large quantity of plutonium standard materials are needed to support Japanese facilities for nuclear fuel cycle and expected difficulties in the long term supply and transport of Pu reference materials, JAEA decided to evaluate the possibility of using MOX stored at Plutonium Fuel Development Center (PFDC) as a source of Pu standard material for LSD spike preparation. At PFDC, Pu nitrate solution was prepared from MOX and two types of the LSD spikes were prepared. The samples of each spike were distributed for verification measurements to international and domestic laboratories. Details of the Pu make-up value evaluation, the LSD spike preparation and the evaluation of the verification results will be presented.
Mukai, Yasunobu; Nakamura, Hironobu; Hosoma, Takashi; Yoshimoto, Katsunobu; Tamura, Takayuki*; Iwamoto, Tomonori*
Proceedings of INMM 51st Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2010/07
JNFL and JAEA are collaboratively developing an advanced solution monitoring and measurement system (ASMS) for Rokkasho Reprocessing Plant (RRP). In this study, as a second trial, we designed and fabricated a new demonstration-type detector for ASMS, then installed it to another process tank in PCDF. Using two detectors, tests for process monitoring capability were performed for several operational conditions such as sampling, bubbling, circulation, solution transfer between two tanks, followed by studies in sensitivity of monitoring and studies in stability for the duration of storage. As a result, excellent performances and advantages of ASMS compared with conventional SMMS were confirmed. It is concluded that ASMS can provide very useful information of operation status and Pu amount shared between operator and inspector. It is sure that the combination of current SMMS and the ASMS is very powerful tool to improve transparency in the future safeguards design.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro; Miyabe, Masabumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Niki, Hideaki*; Katsumura, Soichiro; Seya, Michio
no journal, ,
Basic study on remote analysis by combination of LIBS and AIRAS were performed. For the impurity measurement, detection linearity to % order, the detection limit of order 100 ppm and the error of about  3% based on statistical fluctuation were obtained by the use of Lanthanide or Uranium oxide sample. For the isotope analysis, by using the laser system specialized for the resonance spectroscopy, spectrum resolution of 800 MHz was performed and
3% based on statistical fluctuation were obtained by the use of Lanthanide or Uranium oxide sample. For the isotope analysis, by using the laser system specialized for the resonance spectroscopy, spectrum resolution of 800 MHz was performed and  U in natural uranium was clearly detected. These results suggest that the combination of LIBS and AIRAS will be one of the alternative techniques applicable for the safeguards analysis of next generation fuels without neutron detection by
U in natural uranium was clearly detected. These results suggest that the combination of LIBS and AIRAS will be one of the alternative techniques applicable for the safeguards analysis of next generation fuels without neutron detection by  He gas. In the next stage, we are going to apply this remote analysis to the measurement of Pu in MOX fuel. In this program, we develop the compact system inside the grove-box and will plan to accomplish the elemental and isotopic analysis of Pu and U within several ten minutes.
He gas. In the next stage, we are going to apply this remote analysis to the measurement of Pu in MOX fuel. In this program, we develop the compact system inside the grove-box and will plan to accomplish the elemental and isotopic analysis of Pu and U within several ten minutes.