Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Si-NMR study of antiferromagnet CeRh
Si-NMR study of antiferromagnet CeRh Si
Si using single crystals
using single crystalsSakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Matsumoto, Yuji; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Haga, Yoshinori
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 63(3), p.352 - 355, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.43(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Si-NMR Study of antiferromagnet CeRh
Si-NMR Study of antiferromagnet CeRh Si
Si with a tetragonal ThCr
with a tetragonal ThCr Si
Si -type structure has been performed using single crystals. The Knight shifts along the
-type structure has been performed using single crystals. The Knight shifts along the  and
and  axes have been measured as a function of temperatures in the paramagnetic state. At ambient pressure, the Knight shifts show the Ising-type anisotropy along the
axes have been measured as a function of temperatures in the paramagnetic state. At ambient pressure, the Knight shifts show the Ising-type anisotropy along the  axis, which is similar to the magnetic susceptibility. The hyperfine coupling constants for
axis, which is similar to the magnetic susceptibility. The hyperfine coupling constants for  Si along the
Si along the  and
and  axes have been determined from Knight shifts versus static susceptibility plots.
axes have been determined from Knight shifts versus static susceptibility plots.
 at pressures above the ferromagnetic critical pressure
at pressures above the ferromagnetic critical pressureTateiwa, Naoyuki; Haga, Yoshinori; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Onuki, Yoshichika; Fisk, Z.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 63(3), p.627 - 631, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)UGe is a ferromagnet with the Curie temperature of 54 K at ambient pressure. The superconductivity appears in the pressure region of 1.0-1.6 GPa where UGe
is a ferromagnet with the Curie temperature of 54 K at ambient pressure. The superconductivity appears in the pressure region of 1.0-1.6 GPa where UGe is in the ferromagnetic state. Ferromagnetic state disappears above
is in the ferromagnetic state. Ferromagnetic state disappears above 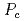 =1.6 GPa. In this study, we have measured the dc-magnetization up to 4.1 GPa using the ceramic anvil high pressure cell. We confirmed the maximum at
=1.6 GPa. In this study, we have measured the dc-magnetization up to 4.1 GPa using the ceramic anvil high pressure cell. We confirmed the maximum at 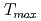 in the temperature dependence of the dc magnetic susceptibility. With increasing pressure,
in the temperature dependence of the dc magnetic susceptibility. With increasing pressure, 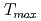 is increased from 24 K at 1.9 GPa to 32 K at 2.6 GPa. The peak structure around
is increased from 24 K at 1.9 GPa to 32 K at 2.6 GPa. The peak structure around 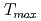 becomes broader with increasing pressure and disappears above 4 GPa. The metamagnetic transition field
becomes broader with increasing pressure and disappears above 4 GPa. The metamagnetic transition field 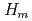 increases rapidly with increasing pressure. We discuss the experimental results with the phenomenological spin-fluctuation theory.
increases rapidly with increasing pressure. We discuss the experimental results with the phenomenological spin-fluctuation theory.
Matsuda, Tatsuma; Tateiwa, Naoyuki; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Haga, Yoshinori; Onuki, Yoshichika; Aoki, Dai*; Flouquet, J.*; Fisk, Z.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 63(3), p.575 - 578, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.01(Physics, Multidisciplinary)
Kobayashi, Riki; Kaneko, Koji; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Chi, S.*; Sanada, Naoyuki*; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Suzuki, Kazuya*
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 63(3), p.337 - 340, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:37.63(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sakai, Toru; Nakano, Hiroki*
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 63(2), p.601 - 604, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.23(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The kagome-lattice antiferromagnet is investigated using the numerical exact diagonalization up to 42-spin clusters. From our investigation of the magnetization process, we found a novel field-induced quantum phase transition, called the "magnetization ramp", at 1/3 of the saturation magnetization. The finite-size scaling analysis of the critical exponents indicated a significant difference of the magnetization ramp from the magnetization plateau observed in the triangular-lattice antiferromagnet.

Haga, Yoshinori; Bauer, E. D.*; Tobash, P. H.*; Mitchell, J. N.*; Ayala-Valenzuela, O.*; McDonald, R. D.*; Mielke, C. H.*; Fisk, Z.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 63(3), p.380 - 382, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.25(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Al
Al (T = transition metal)
(T = transition metal)Matsumoto, Yuji; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Tateiwa, Naoyuki; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Haga, Yoshinori; Fisk, Z.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 63(3), p.363 - 366, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.17(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sugimoto, Kodai*; Toyama, Takami*; Kaneshita, Eiji*; Tsutsui, Kenji
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 63(3), p.632 - 635, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Cr is the representative material of multi-orbital antiferromagnetism. We numerically calculate the band structure and density of states in commensurate antiferromagnetic Cr by multi-orbital Hubbard model with mean-field approximation. The result is adopted to the calculation of optical conductivity. The spectra of the optical conductivity is consistent with experimental data, and this promises the validity of our model.
 electrons with localized and itinerant charancters in
electrons with localized and itinerant charancters in  -US
-US
Metoki, Naoto; Sakai, Hironori; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Haga, Yoshinori; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Ikeda, Shugo*
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 62(12), p.1782 - 1786, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.23(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Magnetic excitation of a narrow gap semiconductor  -US
-US was studied by means of neutron scattering. At low temperatures clear crystalline electric field (CEF) excitations were observed, indicating localized character of 5
was studied by means of neutron scattering. At low temperatures clear crystalline electric field (CEF) excitations were observed, indicating localized character of 5 electrons. The excitation energy
electrons. The excitation energy  7 meV of the pseudo doublet state is consistent with the level scheme based on 5
7 meV of the pseudo doublet state is consistent with the level scheme based on 5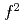 configuration of U
configuration of U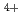 ions, which reproduces the magnetic susceptibility, magnetization, and specific heat. With elevating temperature the conductivity recovers with 5
ions, which reproduces the magnetic susceptibility, magnetization, and specific heat. With elevating temperature the conductivity recovers with 5 carriers excited beyond the gap of 90 K. Simultaneously the CEF excitation becomes weak and broad, and is replaced by a quasi-elastic response of magnetic origin, indicating the crossover of 5
carriers excited beyond the gap of 90 K. Simultaneously the CEF excitation becomes weak and broad, and is replaced by a quasi-elastic response of magnetic origin, indicating the crossover of 5 character from localized to itinerant.
character from localized to itinerant.
Adachi, Hiroto; Maekawa, Sadamichi
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 62(12), p.1753 - 1758, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:60.71(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Maekawa, Sadamichi; Adachi, Hiroto
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 62(12), p.1985 - 1989, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Ieda, Junichi; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Yamane, Yuta
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 62(12), p.1802 - 1806, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.23(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Spinmotive force, which is induced by motion of a nonuniform magnetic nanostructure, reflects real time dynamics of the magnetization texture. Using numerical simulations we study the spinmotive force associated with domain wall motion and find that its dc component scales with an applied magnetic field even in a field range where the wall motion is no longer associated with periodic angular rotation of the wall magnetization. As the field is increased, spikes in the voltage signals start to appear, which are mainly associated with vortex core nucleation and annihilation. At high fields, the slope of the generated dc voltage with the applied field is expected to be only dependent on the spin polarization of conduction electrons and thus can be used to accurately determine the degree of spin polarization in various materials.
 - and
- and  -TbAlB
-TbAlB at low temperature and high magnetic fields
at low temperature and high magnetic fieldsMatsuda, Yasuhiro*; Nakamura, Toshiyuki*; Kuga, Kentaro*; Nakatsuji, Satoru*; Michimura, Shinji*; Inami, Toshiya; Kawamura, Naomi*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 62(12), p.1778 - 1781, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The valence state of Yb ions in  - and
- and  -YbAlB
-YbAlB has been investigated by X-ray absorption and emission spectroscopy at temperatures from 2 to 280 K. It is found that the valence gradually increases with increasing temperature toward 3+ and that the characteristic temperature of the valence fluctuations is about 290 K. We also observe a small increase in the Yb valence (
has been investigated by X-ray absorption and emission spectroscopy at temperatures from 2 to 280 K. It is found that the valence gradually increases with increasing temperature toward 3+ and that the characteristic temperature of the valence fluctuations is about 290 K. We also observe a small increase in the Yb valence ( 0.002) in
0.002) in  -YbAlB
-YbAlB by a magnetic field of 32 T at 40 K.
by a magnetic field of 32 T at 40 K.

Terada, Noriki*; Tsuchiya, Yoshinori*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Metoki, Naoto
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 62(12), p.1905 - 1909, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.25(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have investigated magnetic and nonmagnetic impurity substitution effects on magnetic ordering of a frustrated isosceles triangular lattice antiferromagnet CuMnO by means of the magnetic neutron diffraction measurements on Cu(Mn
by means of the magnetic neutron diffraction measurements on Cu(Mn Ga
Ga )O
)O . While the magnetic wave vector of the magnetic ground state of "magnetically" substituted Cu(Mn
. While the magnetic wave vector of the magnetic ground state of "magnetically" substituted Cu(Mn Cu
Cu )O
)O with x = 0:04 is Q = (-1/2 1/2 0), that in the "nonmagnetically" substituted Cu(Mn
with x = 0:04 is Q = (-1/2 1/2 0), that in the "nonmagnetically" substituted Cu(Mn Ga
Ga )O
)O with y =0.05, 0.15 and 0.20 is Q = (-1/2 1/2 1/2) that is identical to that of pure CuMnO
with y =0.05, 0.15 and 0.20 is Q = (-1/2 1/2 1/2) that is identical to that of pure CuMnO . We discuss an influence of magnetic or nonmagnetic impurity substitution on the magnetic ordering of CuMnO
. We discuss an influence of magnetic or nonmagnetic impurity substitution on the magnetic ordering of CuMnO , by comparing the results of Cu(Mn
, by comparing the results of Cu(Mn Ga
Ga )O
)O with Cu(Mn
with Cu(Mn Cux)O
Cux)O .
.
 C
C
Yamauchi, Hiroki; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Kosaka, Masashi*; Matsuoka, Eiichi*; Onodera, Hideya*
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 62(12), p.2084 - 2087, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.23(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Matsuo, Mamoru; Ieda, Junichi; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 62(10), p.1404 - 1409, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.43(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In the frontier of spintronics, much attention is paid on the control of spin currents. Due to the recent progress of nanoelectromechanics, mechanical manipulation of spins increases its importance. We discuss theoretically the generation of spin currents in both rotationally and linearly accelerating systems. The spin-orbit interaction argumented by inertial effects is derived from the low energy limit of the generally covariant Dirac equation. It is shown that the spin-orbit interaction is responsible for the generation of spin currents by mechanical rotation and vibration. We also investigate SU(2)  U(1) gauge theory in accelerating systems, which allows us to extend the spintronic theory in inertial frame to non-inertial frames.
U(1) gauge theory in accelerating systems, which allows us to extend the spintronic theory in inertial frame to non-inertial frames.
Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Entani, Shiro; Otomo, Manabu; Avramov, P.; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Amemiya, Kenta*; Sakai, Seiji
no journal, ,
Entani, Shiro; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Otomo, Manabu; Avramov, P.; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Sakai, Seiji
no journal, ,
 Pd
Pd with a large magnetocaloric effect
with a large magnetocaloric effectKitazawa, Hideaki*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Terada, Noriki*; Mamiya, Hiroaki*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Doenni, A.*; Kaneko, Koji; Metoki, Naoto; Igawa, Naoki
no journal, ,
We have performed neutron powder diffraction experiments at JRR-3 using polycrystalline Ho Pd
Pd . The magnetic peaks with a propagation vector k = (0.18, 0.18, 0.18) are gradually developing below about 100 K. The peak width is significantly broader than an experimental resolution even temperature is 5 K. These results indicate that Ho
. The magnetic peaks with a propagation vector k = (0.18, 0.18, 0.18) are gradually developing below about 100 K. The peak width is significantly broader than an experimental resolution even temperature is 5 K. These results indicate that Ho Pd
Pd is a short-range ordered antiferromagnet with a long wave length.
is a short-range ordered antiferromagnet with a long wave length.
Agui, Akane; Unno, Tetsuya*; Matsumoto, Sayaka*; Suzuki, Kosuke*; Sakurai, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English