Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Kin, Tadahiro*; Araki, Shohei*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.03006_1 - 03006_6, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:83.31(Nuclear Science & Technology)The design of  neutron sources requires comprehensive nuclear data of deuteron-induced reactions. Therefore, we have launched a research project on deuteron nuclear data, which is composed of measurements, theoretical model code development, cross section evaluation, and application to production of radioisotopes for medical use. Our goal is to develop a state-of-art deuteron nuclear data library up to 200 MeV necessary for the design of accelerator neutron sources with deuteron beam. The present status is reported in the presentation.
neutron sources requires comprehensive nuclear data of deuteron-induced reactions. Therefore, we have launched a research project on deuteron nuclear data, which is composed of measurements, theoretical model code development, cross section evaluation, and application to production of radioisotopes for medical use. Our goal is to develop a state-of-art deuteron nuclear data library up to 200 MeV necessary for the design of accelerator neutron sources with deuteron beam. The present status is reported in the presentation.
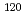 Sn,
Sn, 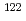 Sn and
Sn and 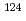 Sn with the array of Ge spectrometer at the J-PARC/MLF/ANNRI
Sn with the array of Ge spectrometer at the J-PARC/MLF/ANNRIKimura, Atsushi; Harada, Hideo; Nakamura, Shoji; Toh, Yosuke; Igashira, Masayuki*; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Mizumoto, Motoharu*; Hori, Junichi*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.11031_1 - 11031_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:58.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nakayama, Shinsuke; Kono, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ye, T.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.12025_1 - 12025_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:91.33(Nuclear Science & Technology)Recently, intensive neutron sources using deuteron accelerator have been proposed for various applications. Accurate and comprehensive deuteron nuclear data library over wide ranges of target mass number and incident energy are indispensable for the design of deuteron accelerator neutron sources. Thus, we have developed an integrated code system dedicated for analysis and prediction of deuteron-induced reactions, which is called DEUteron-induced Reaction Analysis Code System (DEURACS). In the present work, the analysis of  reactions is extended to higher incident energy up to nearly 100 MeV and also DEURACS is applied to
reactions is extended to higher incident energy up to nearly 100 MeV and also DEURACS is applied to 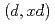 reactions at 80 and 100 MeV. The DEURACS calculations reproduce the experimental double-differential cross sections for the
reactions at 80 and 100 MeV. The DEURACS calculations reproduce the experimental double-differential cross sections for the  and
and 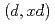 reactions well.
reactions well.
Kunieda, Satoshi
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.12029_1 - 12029_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:91.33(Nuclear Science & Technology)The cross-sections on the light-nuclei are drawing attention for the ion-beam analysis, the astrophysics and the medical applications and so on. However, there still exist inconsistencies between the measured and evaluated data, which could bring a large uncertainty in the practical applications. The R-matrix formalism is rigorous and straightforward to the quantum mechanics, in which the S-matrix is deduced from the measured cross-sections in the resonance energy region. We present the status of the code with new features on the theoretical calculation and the correction for the measurements. Some example evaluations are also presented for the p +  Li reaction. Especially, we focus on the covariance analysis on the resonance parameters and the cross-sections. This is relevant not only to the estimation of the cross-sections uncertainty but also to visualizing natures in the resonant reactions.
Li reaction. Especially, we focus on the covariance analysis on the resonance parameters and the cross-sections. This is relevant not only to the estimation of the cross-sections uncertainty but also to visualizing natures in the resonant reactions.
Capote, R.*; Hilaire, S.*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Kawano, Toshihiko*; Sin, M.*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.12034_1 - 12034_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:93.65(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nakao, Taro; Terada, Kazushi; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Osamu; Harada, Hideo; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Hori, Junichi*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.03021_1 - 03021_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:95.11(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new data acquisition system (DAQ system) in J-PARC Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) ANNRI was developed. Increasing beam power of MLF in recent years allows beam line users to obtain high quantity experimental data yields. Compared to 2008, more than 20 times beam current is achieved in 2015. For the purpose to correspond strong beam power of MLF, a new DAQ system for the array of the Ge detectors in ANNRI is developed. The DAQ system is also going to be used for processing signals from a Li glass detector, which is under development at ANNRI for measurement of total neutron cross sections. Commissioning experiment of a new DAQ system at ANNRI was performed by using 0.1mmt Au sample with 500kW J-PARC proton beam power. An applicability of time-of-flight method for both neutron capture and total cross-sections measurements was checked. ADC and TDC nonlinearity, energy resolution, multi-channel coincidence and dead time performance for the array of the Ge detectors were also evaluated. The dead time value for Ge detectors was successfully decreased to 1/4 from the previous DAQ system with minor deterioration on energy resolution. The author would like to thank the accelerator and technical staff at J-PARC for operation of the accelerator and the neutron production target and for the other experimental supports. Present study includes the result of "Research and Development for accuracy improvement of neutron nuclear data on minor actinides" entrusted to the Japan Atomic Energy Agency by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (MEXT).
Harada, Hideo; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kimura, Atsushi; Terada, Kazushi; Nakao, Taro; Nakamura, Shoji; Mizuyama, Kazuhito; Igashira, Masayuki*; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.11001_1 - 11001_6, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:75.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)Iwamoto, Osamu; Shibata, Keiichi; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kunieda, Satoshi; Minato, Futoshi; Ichihara, Akira; Nakayama, Shinsuke
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.02005_1 - 02005_6, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:58.02(Nuclear Science & Technology) Am and
Am and  Np capture cross sections
Np capture cross sections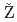 erovnik, G.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; Cano-Ott, D.*; Jandel, M.*; Hori, Junichi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Rossbach, M.*; Letourneau, A.*; Noguere, G.*; Leconte, P.*; et al.
erovnik, G.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; Cano-Ott, D.*; Jandel, M.*; Hori, Junichi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Rossbach, M.*; Letourneau, A.*; Noguere, G.*; Leconte, P.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.11035_1 - 11035_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:83.31(Nuclear Science & Technology) -ray spectroscopy combined with active neutron interrogation for nuclear security and safeguards
-ray spectroscopy combined with active neutron interrogation for nuclear security and safeguardsKoizumi, Mitsuo; Rossi, F.; Rodriguez, D.; Takamine, Jun; Seya, Michio; Bogucarska, T.*; Crochemore, J.-M.*; Varasano, G.*; Abbas, K.*; Pedersen, B.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.09018_1 - 09018_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:83.31(Nuclear Science & Technology)Paradela, C.*; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Tsuchiya, Harufumi
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.09002_1 - 09002_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:97.40(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kitatani, Fumito; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Takamine, Jun; Hori, Junichi*; Sano, Tadafumi*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.09032_1 - 09032_3, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Konno, Chikara; Tada, Kenichi; Kwon, Saerom*; Ota, Masayuki*; Sato, Satoshi*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.02040_1 - 02040_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:91.33(Nuclear Science & Technology)So far we pointed out that KERMA factors and DPA cross-section data of a lot of nuclei in the official ACE file were different among nuclear data libraries for the following reasons; (1) incorrect nuclear data, (2) NJOY bugs, (3) huge helium production cross section data, (4) mf6 mt102 data, (5) no secondary particle data (energy-angular distribution data). Now we compare the KERMA factors and DPA cross section data included in the official ACE files of JENDL-4.0, ENDF/B-VII.1 and JEFF-3.2 in more detail. As a result, we find out new reasons of differences among the KERMA factors and DPA cross section data in the three nuclear data libraries. The reasons are categorized to no secondary charged particle data, no secondary  data, wrong secondary
data, wrong secondary  spectra, wrong production yields and mf12-15 mt3 data for the capture reaction, some of which seem to be unsupported with NJOY. The ACE files of JENDL-4.0, ENDF/B-VII.1 and JEFF-3.2 with these problems should be revised based on this study.
spectra, wrong production yields and mf12-15 mt3 data for the capture reaction, some of which seem to be unsupported with NJOY. The ACE files of JENDL-4.0, ENDF/B-VII.1 and JEFF-3.2 with these problems should be revised based on this study.
Koura, Hiroyuki; Yoshida, Tadashi*; Tachibana, Takahiro*; Chiba, Satoshi*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.12003_1 - 12003_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:83.31(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; L guillon, R.*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Orlandi, R.; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Smallcombe, J.*; Chiba, Satoshi*; Aritomo, Yoshihiro*; Tanaka, Shoya*; et al.
guillon, R.*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Orlandi, R.; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Smallcombe, J.*; Chiba, Satoshi*; Aritomo, Yoshihiro*; Tanaka, Shoya*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.04009_1 - 04009_6, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:83.31(Nuclear Science & Technology)Chen, Y. H.*; Tassan-Got, L.*; Harada, Hideo; Kimura, Atsushi; n_TOF Collaboration*; 130 of others*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.03020_1 - 03020_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:58.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)The experimental area 2 (EAR-2) at CERNs neutron time-of-flight facility (n_TOF), which is operational since 2014, is designed and built as a short-distance complement to the experimental area 1 (EAR-1). The Parallel Plate Avalanche Counter (PPAC) monitor experiment was performed to characterize the beam profile and the shape of the neutron flux at EAR-2. The prompt  -flash which is used for calibrating the time-of-flight at EAR-1 is not seen by PPAC at EAR-2, shedding light on the physical origin of this
-flash which is used for calibrating the time-of-flight at EAR-1 is not seen by PPAC at EAR-2, shedding light on the physical origin of this  -flash.
-flash.
Chadwick, M. B.*; Capote, R.*; Trkov, A.*; Kahler, A. C.*; Herman, M. W.*; Brown, D. A.*; Hale, G. M.*; Pigni, M.*; Dunn, M.*; Leal, L.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.02001_1 - 02001_9, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:96.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)The CIELO collaboration has studied neutron cross sections on nuclides ( O,
O,  Fe,
Fe, 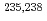 U and
U and  Pu) that significantly impact criticality in nuclear technologies with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality.
Pu) that significantly impact criticality in nuclear technologies with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality.
Araki, Shohei*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Kitajima, Mizuki*; Sadamatsu, Hiroki*; Nakano, Keita*; Kin, Tadahiro*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Satoh, Daiki; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.11027_1 - 11027_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)In recently years, deuteron-induced reaction is considered to produce the neutron source for application fields such as radiation damage fusion materials and boron neutron capture therapy. However, as the experimental data are not sufficient at incident energies above 60 MeV, the theoretical models are not validated. Therefore, we measured the double differential cross sections (DDXs) for Li, Be and C at 100 MeV at the Research Center for Nuclear Physics in Osaka University. The DDXs were measured at 6 angles (0
 25
25 and neutron energy was determined by a time of flight method. Three different-size NE213 liquid organic scintillators located at a distance of 7 m, 24 m and 74 m respectively were adopted as neutron detectors. In the measured DDXs, a broad peak due to deuteron breakup process was observed at approximately half of the deuteron incident energy. The DDXs calculated by PHITS did not reproduce the experimental ones due to lack of theoretical model.
and neutron energy was determined by a time of flight method. Three different-size NE213 liquid organic scintillators located at a distance of 7 m, 24 m and 74 m respectively were adopted as neutron detectors. In the measured DDXs, a broad peak due to deuteron breakup process was observed at approximately half of the deuteron incident energy. The DDXs calculated by PHITS did not reproduce the experimental ones due to lack of theoretical model.
Tada, Kenichi; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Kunieda, Satoshi; Suyama, Kenya; Fukahori, Tokio
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.02028_1 - 02028_5, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:88.62(Nuclear Science & Technology)JAEA has started to develop new nuclear data processing system FRENDY (FRom Evaluated Nuclear Data libralY to any application). In this presentation, the outline of the development of FRENDY is presented. And functions and performances of FRENDY are demonstrated by generation and validation of the continuous energy cross section data libraries for MVP, PHITS and MCNP codes.
Minato, Futoshi; Iwamoto, Osamu; Minomo, Kosho*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kunieda, Satoshi; Furutachi, Naoya
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.12032_1 - 12032_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:58.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)Phenomenological optical potential is known to be able to describe the elastic scattering process. It is applied widely to the nuclear data evaluation of the cross section. Many kinds of the optical potential have been studied so far. However, the parameters in the phenomenological optical potentials are determined so as to reproduce existing experimental data, so that use of it for unmeasured nuclei such as neutron-rich nuclei is not necessarily reliable. Recently, a new optical potential derived from the microscopic effective reaction theory (MERT) was proposed. Since the formulation of MERT is based on the NN effective interaction, any parameterizations in the optical potential aren't needed. Therefore, it is capable of calculating nuclei whose scattering cross section isn't measured. We incorporate the optical potentials of MERT in code CCONE and start nuclear data evaluation of several nuclei. In this work, we discuss difference of cross sections evaluated by MERT's optical potentials and conventional phenomenological ones.